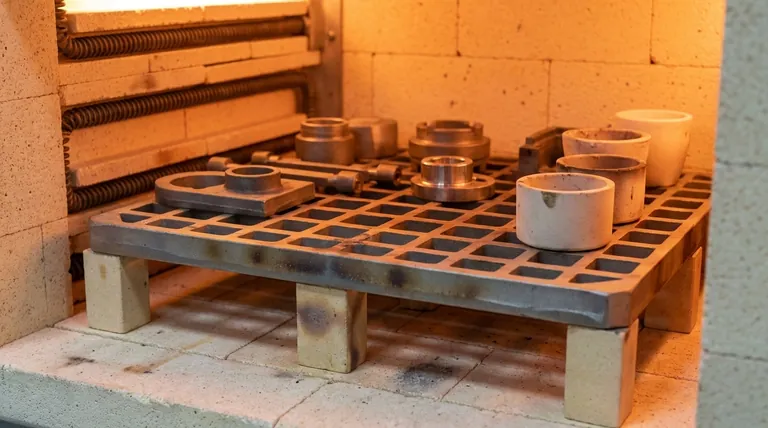
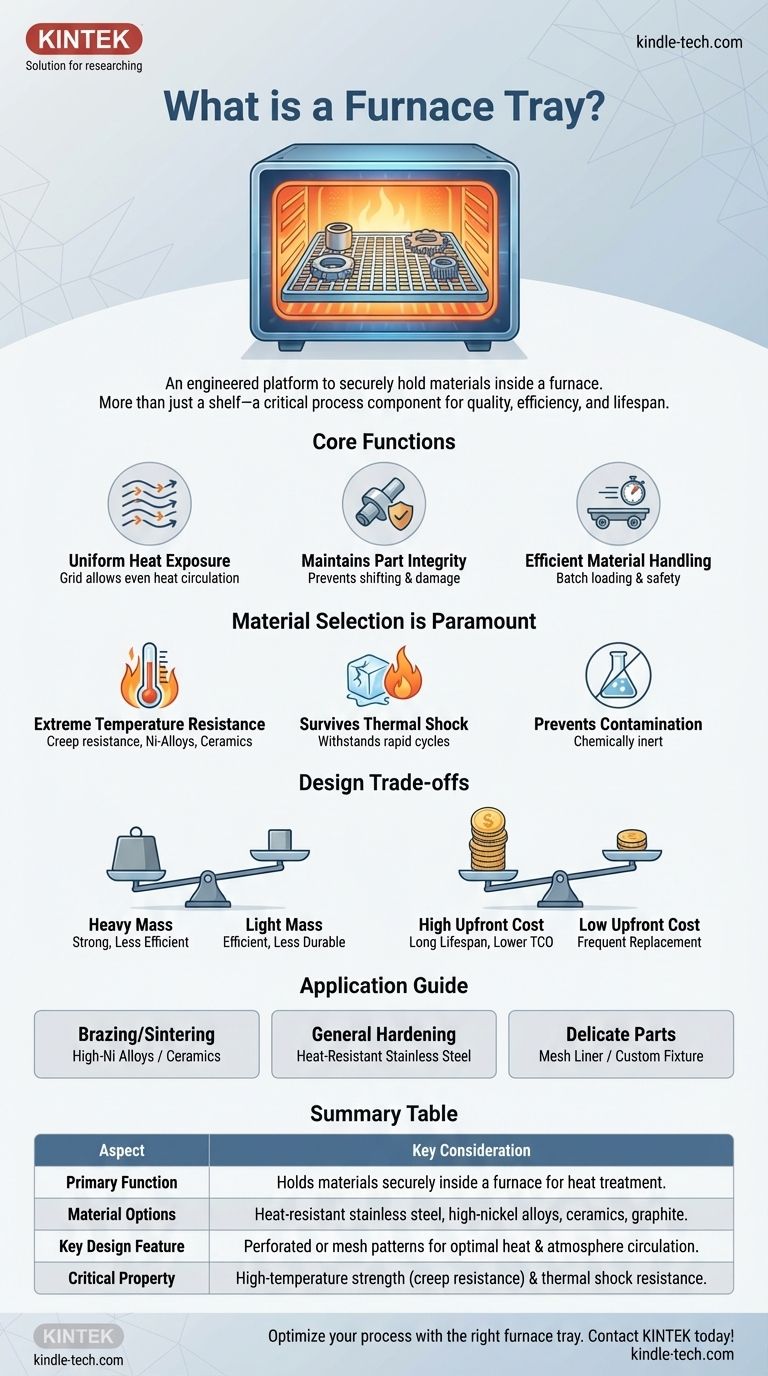
In essence, a furnace tray is a removable, engineered platform designed to securely hold materials or parts inside a furnace during a heat treatment process. It acts as the critical interface between the workpiece and the extreme environment of the furnace, ensuring the process is both successful and repeatable.
The furnace tray should not be viewed as a simple shelf, but as a critical piece of process equipment. Its material composition and structural design directly dictate the quality of the final product, the energy efficiency of the cycle, and the operational lifespan of the equipment itself.

The Core Function of a Furnace Tray
A furnace tray, also known as a fixture or grid, serves several distinct purposes that are fundamental to achieving a controlled and uniform heat treatment process.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Exposure
The primary goal of any heat treatment is uniformity. A well-designed tray facilitates this by allowing heat—whether through radiation, convection, or conduction—to reach all surfaces of the workpiece as evenly as possible.
Designs often feature a grid, mesh, or perforated pattern. This minimizes the tray's contact with the parts and allows the furnace atmosphere and heat to circulate freely.
Maintaining Part Integrity and Placement
The tray provides stable support for workpieces, preventing them from shifting, warping, or coming into direct contact with the furnace's heating elements or refractory lining.
This precise placement is crucial for processes where part geometry must be maintained or where parts should not touch one another.
Facilitating Efficient Material Handling
Furnace trays are designed to be loaded with parts outside the furnace and then moved into the hot zone as a complete batch.
This greatly improves operational efficiency and safety, reducing the time the furnace door is open and minimizing operator exposure to extreme heat.
Why Material Selection is Paramount
The choice of material for a furnace tray is the single most important factor in its design. The material must perform under some of the most demanding conditions found in manufacturing.
Resisting Extreme Temperatures
The tray's material must maintain its structural integrity—a property known as creep resistance—at the furnace's operating temperature. It cannot sag, bend, or deform under the weight of the load.
High-nickel alloys and specialized heat-resistant stainless steels are common choices for their superior high-temperature strength. For non-metallic applications, ceramics or graphite are often used.
Surviving Thermal Shock
Furnaces are not always hot. Trays experience immense stress as they are heated rapidly to extreme temperatures and then cooled again. This is known as thermal shock.
The material must be able to withstand these repeated expansion and contraction cycles without cracking or failing, ensuring a long operational life.
Preventing Product Contamination
The tray must be chemically inert within the furnace's atmosphere. It cannot react with, corrode, or shed particles that could contaminate the surface of the workpiece.
This is especially critical in high-purity applications like medical device manufacturing, aerospace, or electronics.
Understanding Key Design Trade-offs
Designing the optimal furnace tray involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Mass vs. Strength
A thick, heavy tray is inherently stronger and more resistant to warping. However, this added thermal mass requires more energy and time to heat up and cool down, reducing overall process efficiency.
A lighter tray is more energy-efficient but may have a shorter lifespan or a lower load capacity. The goal is to find the lightest design that can reliably handle the required load.
Cost vs. Lifespan
High-performance materials like nickel-based superalloys are very expensive upfront. However, their exceptional durability and long life in harsh conditions often result in a lower total cost of ownership.
Less expensive materials may require more frequent replacement, leading to higher long-term costs and increased production downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific heat treatment application will determine the ideal tray design and material.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature brazing or sintering: Prioritize trays made from high-nickel alloys or specialized ceramics that offer maximum strength and chemical inertness at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose hardening and tempering: A robust, well-designed tray made from heat-resistant stainless steel often provides the best balance of performance, durability, and cost.
- If your primary focus is processing small or delicate parts: Select a tray with a mesh liner or a custom-designed fixture that provides complete support while still allowing for adequate atmospheric flow.
Ultimately, the right furnace tray is an engineered tool that enhances process control, ensures product quality, and maximizes operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Holds materials securely inside a furnace for heat treatment. |
| Material Options | Heat-resistant stainless steel, high-nickel alloys, ceramics, graphite. |
| Key Design Feature | Perforated or mesh patterns for optimal heat and atmosphere circulation. |
| Critical Property | High-temperature strength (creep resistance) and thermal shock resistance. |
Optimize your heat treatment process with the right furnace tray.
The correct furnace tray is not just a shelf; it's a critical component for achieving uniform results, protecting your valuable parts, and maximizing furnace efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including custom furnace trays engineered for your specific application—whether it's brazing, sintering, or hardening.
Let our experts help you select the ideal tray to enhance your process control and product quality. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is temperature controlled in a furnace? Mastering Precise Thermal Management
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















