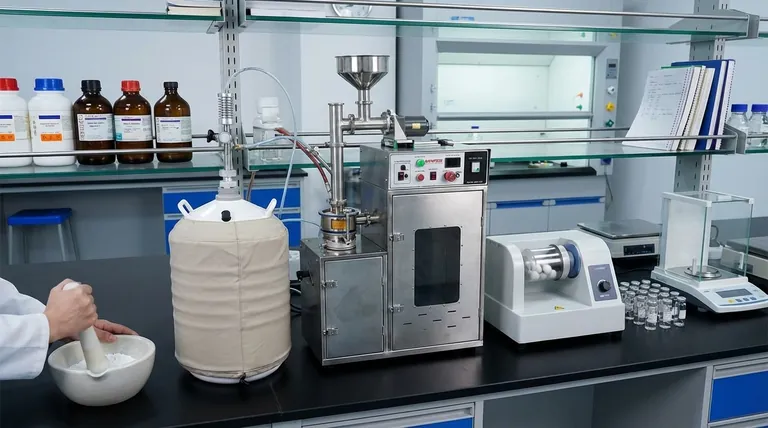
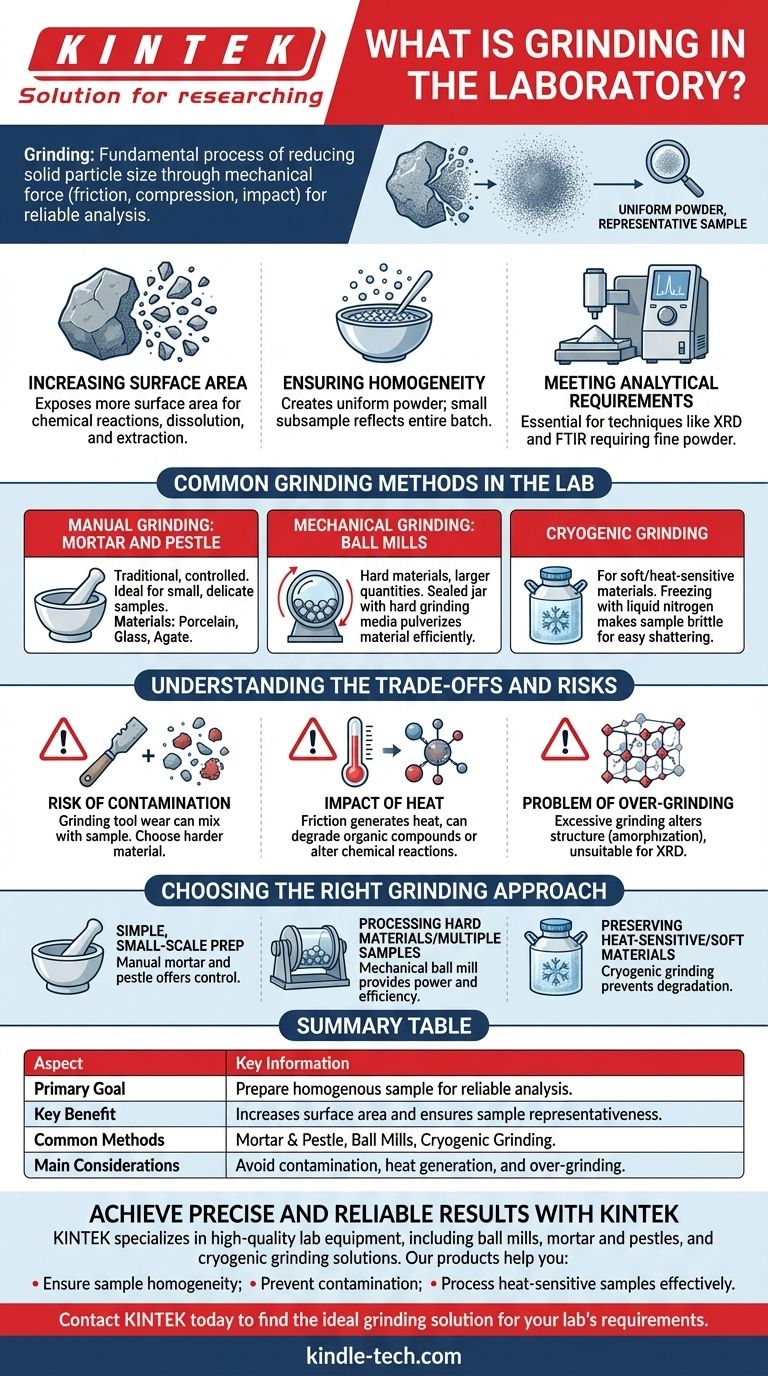
In a laboratory context, grinding is the fundamental process of reducing the size of solid particles. This is achieved by applying mechanical force through friction, compression, or impact, using abrasive materials or dedicated equipment to break down a coarse substance into a fine, uniform powder.
The primary goal of grinding is not just to make something smaller, but to prepare a sample for reliable and repeatable analysis. By creating a uniform powder, you increase the material's surface area and ensure that the small portion being analyzed is truly representative of the entire batch.

The Core Principle: Why Grinding is Essential
Grinding is one of the most common steps in sample preparation. The reasons for performing it are critical to understanding its application in any scientific field.
Increasing Surface Area
Breaking a large particle into many smaller ones dramatically increases the total surface area exposed. This is crucial for processes like chemical reactions, dissolution, and extraction, which occur on the surface of a material.
Ensuring Homogeneity
Most analyses use only a tiny fraction of the original sample. Grinding and mixing create a homogenous powder, where every particle is like its neighbor. This ensures that the small subsample taken for analysis accurately reflects the composition of the whole.
Meeting Analytical Requirements
Many modern analytical instruments require samples to be in a fine powder form. Techniques like X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) depend on a uniform, powdered sample to produce a clear and accurate signal.
Common Grinding Methods in the Lab
The choice of tool depends on the material's properties—such as its hardness and sensitivity to heat—and the desired final particle size.
Manual Grinding: The Mortar and Pestle
This is the most traditional and controlled method. It is ideal for small, delicate samples where you need to carefully monitor the process.
Mortars and pestles are made from different materials, such as porcelain, glass, or agate, chosen based on the hardness of the sample and the need to avoid contamination.
Mechanical Grinding: Ball Mills
For harder materials, larger quantities, or more repetitive tasks, a ball mill is used. A sealed jar containing the sample and hard grinding media (such as ceramic or steel balls) is rotated at high speed.
The repeated impact of the balls pulverizes the material efficiently and consistently, saving significant time and effort.
Cryogenic Grinding
Some materials, like polymers or biological tissues, are soft, elastic, or heat-sensitive at room temperature. They are impossible to grind effectively.
Cryogenic grinding involves freezing the sample with liquid nitrogen, which makes it brittle. In this frozen state, it can be easily shattered into a fine powder without being damaged by heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While essential, grinding is not a benign process. It can introduce errors into your analysis if not performed with care.
The Risk of Contamination
This is the most significant concern. The surface of the grinding tool (the mortar, pestle, or milling balls) can wear away and mix with your sample.
You must always choose a grinding material that is significantly harder than your sample and will not interfere with your downstream analysis. For example, you would not use an alumina mortar if you plan to measure the aluminum content of your sample.
The Impact of Heat
The friction and impact from mechanical grinding generate heat. This can cause sensitive organic compounds to degrade, change the hydration state of minerals, or induce unwanted chemical reactions in your sample.
The Problem of Over-Grinding
Excessive grinding can sometimes alter the fundamental structure of a material. For crystalline materials, grinding for too long can damage the crystal lattice, a process known as amorphization, which renders the sample unsuitable for techniques like XRD.
Choosing the Right Grinding Approach
The best method depends entirely on your material, your budget, and your ultimate analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is simple, small-scale preparation: A manual mortar and pestle offers the most control and is often sufficient for basic tasks.
- If your primary focus is processing hard materials or multiple samples: A mechanical ball mill provides the power and efficiency required for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is preserving heat-sensitive or soft materials: Cryogenic grinding is the only reliable method to prevent degradation and achieve effective size reduction.
Ultimately, proper grinding is the first and most critical step toward obtaining accurate and reproducible scientific data.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prepare a homogenous sample for reliable analysis. |
| Key Benefit | Increases surface area and ensures sample representativeness. |
| Common Methods | Mortar & Pestle, Ball Mills, Cryogenic Grinding. |
| Main Considerations | Avoid contamination, heat generation, and over-grinding. |
Achieve precise and reliable results with the right grinding equipment from KINTEK.
Proper sample preparation is the foundation of accurate analysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including a range of ball mills, mortar and pestles, and cryogenic grinding solutions, designed to meet the specific needs of your laboratory.
Our products help you:
- Ensure sample homogeneity and representativeness.
- Prevent contamination with materials suited to your application.
- Process heat-sensitive samples effectively with cryogenic options.
Let our expertise support your research. Contact KINTEK today to find the ideal grinding solution for your lab's requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill with Screw Feeder
- lab cryogenic grinding use liquid-nitrogen for pulverizing plastic raw materials and heat sensitive materials
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Disc Cup Vibratory Mill for Sample Grinding
People Also Ask
- What features should be considered when choosing an ultra low temperature freezer? Secure Your Samples with Precision
- What is the cryogenic grinding process? Achieve Superior Quality and Efficiency for Sensitive Materials
- What is pulverized material? Unlock Material Potential with Precision Grinding
- Why is cryogenic grinding used? To pulverize tough, heat-sensitive materials effectively.
- What is cold grinding? Achieve Ultra-Fine Particles Without Thermal Damage



















