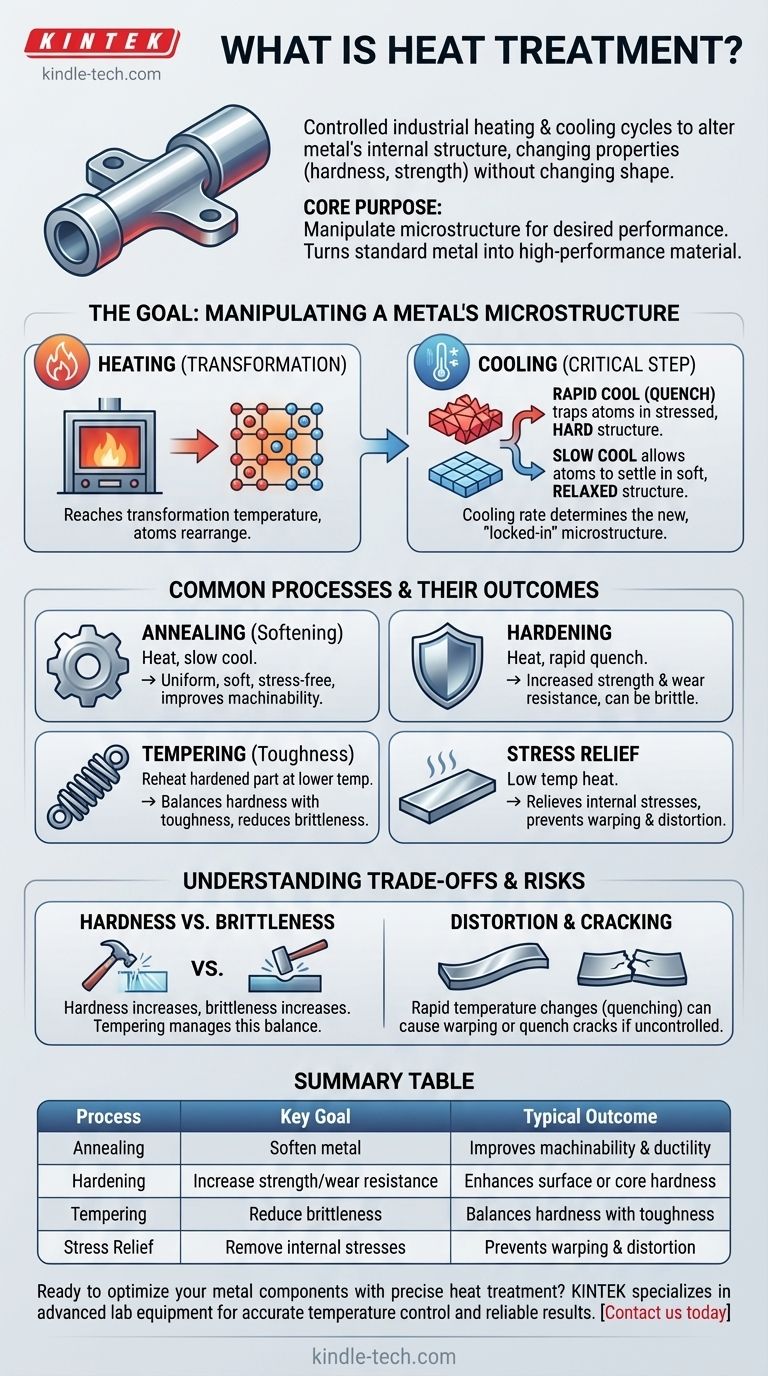
In essence, heat treatment is a group of controlled industrial processes that use carefully managed heating and cooling cycles to alter a metal's internal structure. This is not done to change the part's shape, but to fundamentally change its physical and mechanical properties, such as its hardness, strength, or ductility, to meet a specific engineering requirement.
The core purpose of heat treating is to manipulate a metal's internal crystal structure—its microstructure—to achieve desired performance characteristics that are not present in its original state. It is the art of turning a standard metal into a high-performance material.
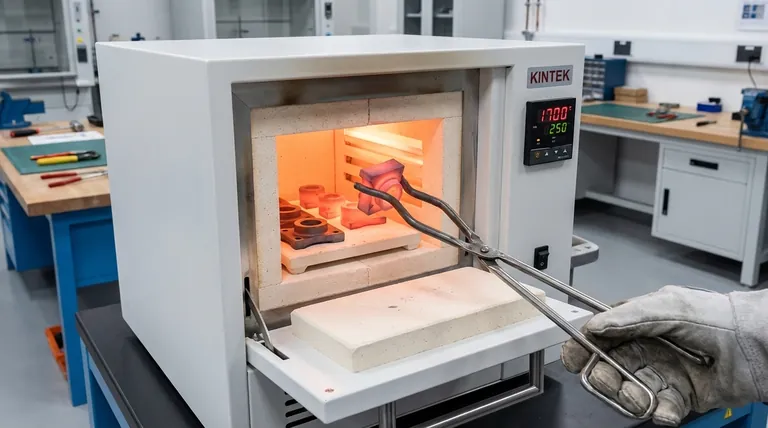

The Goal: Manipulating a Metal's Microstructure
To understand heat treatment, you must first understand that metals are not uniform, solid masses at a microscopic level. They are composed of tiny, individual crystals or grains. The size, shape, and arrangement of these grains—the metal's microstructure—dictate its properties.
The Role of Heating
When a metal is heated to a specific temperature, its atoms gain enough energy to move and rearrange themselves. This allows the internal crystal structure to dissolve and reform into a different, more uniform state.
The critical factor is reaching a transformation temperature, where the microstructure fundamentally changes. Holding the metal at this temperature ensures the entire part undergoes this internal transformation.
The Critical Role of Cooling
The speed at which the metal is cooled from its transformation temperature is the most critical step. The cooling rate determines which new microstructure is "locked in" as the metal returns to room temperature.
A rapid cool, or quench (often in water, oil, or air), traps the atoms in a highly stressed, hard structure. A slow cool allows the atoms to settle into a softer, more relaxed structure.
Common Heat Treatment Processes and Their Outcomes
Different combinations of heating temperatures, holding times, and cooling rates result in distinct processes designed to achieve specific outcomes.
Softening (Annealing)
Annealing involves heating a metal and then cooling it very slowly. This process creates a uniform, soft, and stress-free microstructure.
It is primarily used to make a metal easier to machine, form, or bend without cracking.
Hardening
Hardening processes aim to increase a metal's strength and resistance to wear and abrasion. This is typically achieved by heating the metal to its transformation temperature and then cooling it very rapidly (quenching).
Common methods include through hardening, which hardens the entire part, and case hardening (like carburizing or nitriding), which creates an extremely hard surface layer while leaving the core tougher and more ductile.
Stress Relief
Manufacturing processes like welding, machining, or cold forming can introduce internal stresses into a part. These stresses can cause the part to warp or distort over time or during subsequent operations.
A stress relief heat treatment uses a relatively low temperature to allow these internal stresses to relax without significantly changing the metal's hardness.
Improving Toughness and Resilience (Tempering)
A part that has been hardened is often extremely brittle and can shatter under impact. Tempering is a secondary process performed after hardening.
The part is reheated to a lower temperature, which relieves some of the internal stress from quenching and increases its toughness. This creates a balance, sacrificing a small amount of hardness for a significant gain in ductility and impact resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it involves critical trade-offs that every engineer must consider. It is not a process without risk.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Dilemma
The most fundamental trade-off is that as hardness increases, brittleness also tends to increase. An extremely hard metal can resist scratches and wear but may be prone to fracturing like glass if dropped or subjected to sudden impact.
Processes like tempering are specifically designed to manage this trade-off, finding the optimal balance for the part's application.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid temperature changes involved in heat treatment, especially quenching, cause the material to expand and contract. If not properly controlled, this can lead to part distortion, warping, or even the formation of quench cracks, rendering the part unusable.
Part geometry, material selection, and precise process control are all critical for mitigating this risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process is entirely dependent on the desired end-use of the metallic component.
- If your primary focus is easy machinability or forming: The correct process is annealing to achieve the softest possible state.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and strength: You need a hardening process, followed by tempering to reduce brittleness.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability after machining: A stress relief cycle is necessary to prevent future distortion.
- If your primary focus is durability and impact resistance (e.g., a spring or tool): A carefully controlled hardening and tempering combination is required to balance hardness with toughness.
Ultimately, heat treatment elevates metal from a simple raw material to a precisely engineered component with tailored properties.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Goal | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften metal | Improves machinability and ductility |
| Hardening | Increase strength/wear resistance | Enhances surface or core hardness |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness | Balances hardness with toughness |
| Stress Relief | Remove internal stresses | Prevents warping and distortion |
Ready to optimize your metal components with precise heat treatment? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored for metallurgical processes. Whether you're hardening, annealing, or tempering, our solutions ensure accurate temperature control and reliable results. Let our experts help you achieve the perfect balance of strength, durability, and performance for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a Vacuum Drying Oven in aluminum-coated graphite composite pretreatment? Ensure Material Integrity
- What role does a high-temperature annealing furnace play in LPBF NAB? Optimize Microstructure for Industrial Performance
- What happens when metal is annealed? A Guide to Softer, More Workable Metals
- Why is a high-precision heat treatment furnace essential for ceramic green bodies? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What is the application of quenching effect? Achieve Superior Hardness and Strength in Materials
- Why Use a Vacuum Furnace with a Titanium Trap for Pre-Annealing? Protect Substrates & Prevent LSCF Coating Cracks
- What is a nitriding furnace? Achieve Superior Surface Hardening with Minimal Distortion
- What instrument is used to measure vacuum? Selecting the Right Gauge for Your Pressure Range



















