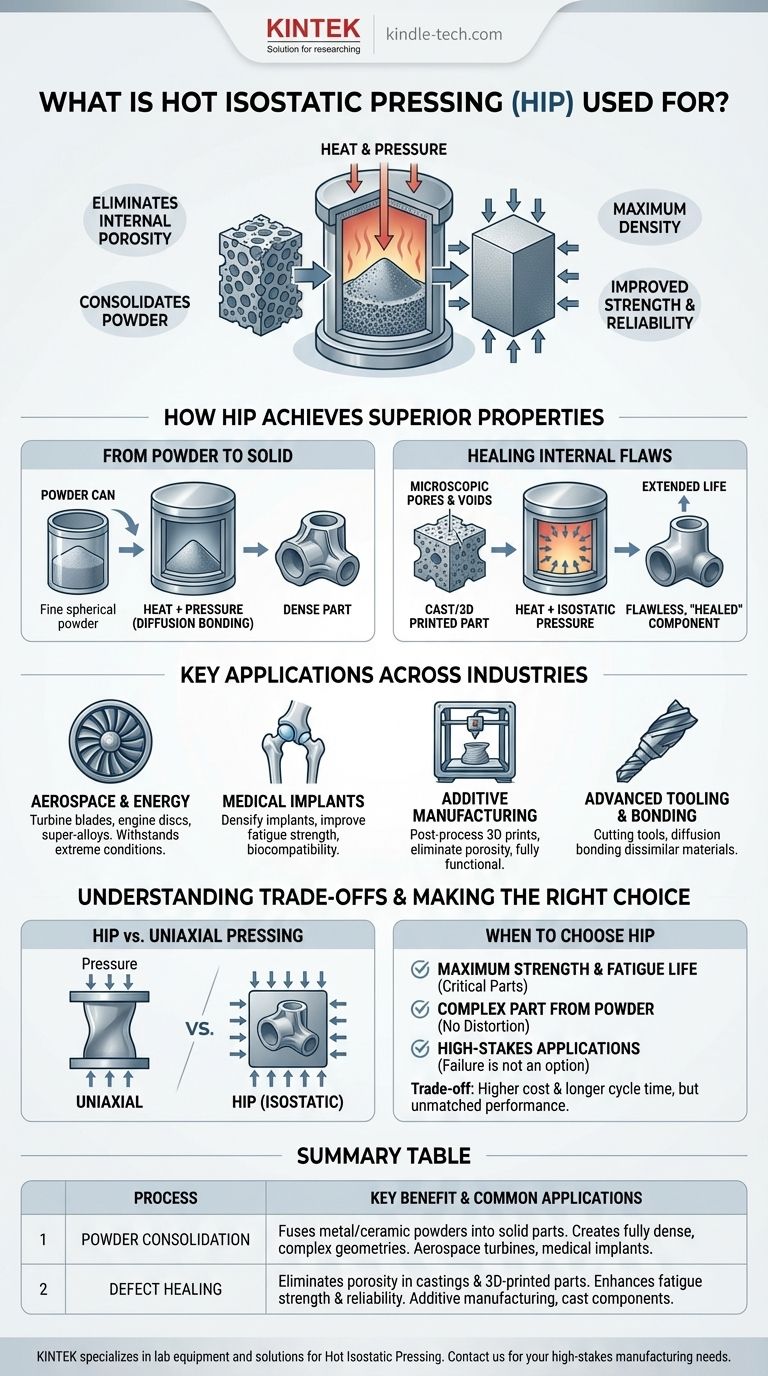
At its core, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a high-performance manufacturing process used for two primary functions: consolidating metal or ceramic powders into a fully solid material, and eliminating internal porosity and defects from castings or 3D-printed parts. Industries like aerospace, medicine, and automotive rely on HIP to create components that demand maximum density, strength, and reliability, such as jet engine turbines and medical implants.
The fundamental problem HIP solves is the elimination of internal voids. By applying high heat and uniform, gas-based pressure, it forces a material into its theoretical maximum density, dramatically improving its mechanical properties and removing the microscopic flaws that cause failure.

How HIP Achieves Superior Material Properties
HIP is not just another heating process; it is a method of structural perfection. Its unique combination of process parameters allows it to transform materials in ways that other methods cannot.
The Fundamental Principle: Heat and Pressure
The process places a part inside a sealed, high-pressure vessel. The chamber is heated to a high temperature, typically around 70% of the material's melting point, which makes the material soft and plastic-like.
Simultaneously, an inert gas like argon is pumped in to create immense, uniform (isostatic) pressure from all directions. This pressure physically collapses any internal voids, pores, or microscopic cracks within the material.
From Powder to a Fully Dense Part
HIP is a cornerstone of modern powder metallurgy. Fine, spherical metal or ceramic powders are sealed in a shaped metal container, or "can."
Under heat and pressure, the individual powder particles bond and fuse together on a molecular level, a process called diffusion bonding. This eliminates the spaces between the particles, resulting in a 100% dense, solid part with properties that are often superior to those of traditional cast or wrought materials.
Healing Internal Flaws in Components
Perhaps the most common use of HIP is for densification. Components made through other processes, like casting or additive manufacturing (3D printing), often contain microscopic internal pores.
These pores are stress concentration points and can lead to fatigue cracks and premature failure. Placing these parts in a HIP unit collapses these voids, "healing" the material from the inside out and significantly extending the component's service life and reliability.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to create flawless, fully dense materials makes HIP indispensable for high-stakes applications where failure is not an option.
Aerospace and Energy
This is the largest market for HIP. It is used to create critical components like turbine blades, engine discs, and structural parts from high-performance super-alloys and titanium. The process eliminates casting defects, ensuring the components can withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress.
Medical Implants
Biocompatibility and long-term reliability are paramount for medical implants like artificial hips and knees. HIP is used to densify cobalt-chrome and titanium implants, improving their fatigue strength and creating a non-porous surface that resists bacterial growth and improves longevity inside the human body.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
HIP is a critical post-processing step for 3D-printed metal parts. The layer-by-layer nature of 3D printing can create internal porosity that compromises strength. HIP is used to densify these printed parts, transforming them from near-net-shape prototypes into fully functional, load-bearing components.
Advanced Tooling and Bonding
HIP is also used to produce high-performance cutting tools and to diffusion bond dissimilar materials together. This allows for the creation of composite parts, such as a wear-resistant coating bonded to a tough substrate, creating a component with properties that a single material could not achieve.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, HIP is a specialized process chosen for specific reasons. Understanding its trade-offs is key to its proper application.
HIP vs. Uniaxial Hot Pressing
Traditional hot pressing applies pressure from only one direction (uniaxially), which can distort a part's shape. Because HIP applies pressure uniformly from all directions (isostatically), it can densify parts with complex geometries without causing distortion.
Cost and Cycle Time
The primary trade-off is expense. HIP systems are costly to acquire and operate, and the process cycle can take several hours. This makes it uneconomical for simple, low-cost parts. Its use is reserved for components where the performance gains justify the significant investment in time and money.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding whether to use HIP comes down to a clear evaluation of your component's performance requirements against the cost of the process.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue life: HIP is an essential step to eliminate internal defects in critical castings or 3D-printed parts.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex part from powder: HIP provides a way to achieve full density from powder without distorting the part's intended geometry.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a non-critical part: Traditional casting or sintering without HIP may be sufficient if some internal porosity is acceptable.
Ultimately, you should view Hot Isostatic Pressing as a tool for achieving material perfection when performance cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Function | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Consolidation | Fuses metal/ceramic powders into solid parts | Creates fully dense, complex geometries | Aerospace turbines, medical implants |
| Defect Healing | Eliminates porosity in castings & 3D-printed parts | Enhances fatigue strength & reliability | Additive manufacturing, cast components |
Need to eliminate internal defects and achieve maximum material density?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing, including solutions for industries leveraging Hot Isostatic Pressing. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or additive manufacturing, our expertise can help you enhance component reliability and performance.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-stakes manufacturing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- What are the components of a hot isostatic pressing system? A Guide to Core HIP Equipment
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard



















