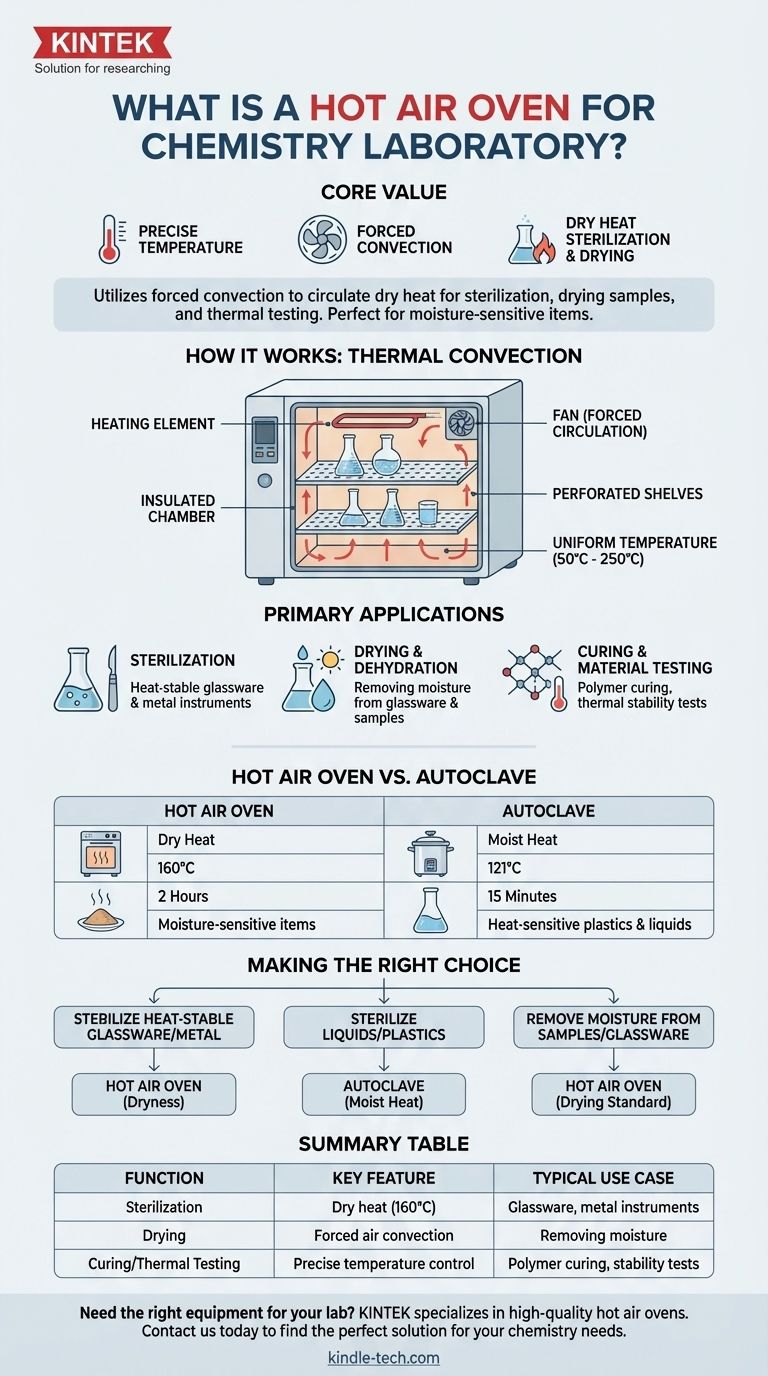
In a chemistry laboratory, a hot air oven is a fundamental instrument that utilizes forced convection to circulate dry heat at precisely controlled temperatures. Its primary purpose is to sterilize materials that can withstand high heat, such as glassware and metal instruments, as well as to dry chemical samples and perform thermal testing.
The core value of a hot air oven lies in its use of dry heat, which allows it to sterilize moisture-sensitive items and completely dry glassware—tasks for which a steam-based autoclave is unsuitable. Its principle is simple, reliable, and critical for many laboratory workflows.

The Core Principle: How a Hot Air Oven Works
A hot air oven operates on the straightforward principle of thermal convection. Understanding its mechanism clarifies its specific role in the lab.
Forced Air Convection
At its heart, the oven contains a heating element and a fan. The element heats the air, and the fan actively circulates this hot air throughout the insulated chamber. This forced circulation ensures a uniform temperature on all surfaces of the objects inside, eliminating hot spots.
The Role of Dry Heat
The critical distinction of this instrument is that it uses dry heat, not steam or moisture. For sterilization, this intense heat works by oxidizing the cellular components of microorganisms, effectively killing them. For drying applications, it efficiently evaporates and removes all traces of water.
Key Components
Most laboratory hot air ovens consist of a few key parts:
- An insulated double-walled chamber to maintain high temperatures efficiently.
- A thermostat for precise temperature control, typically ranging from 50°C to 250°C (122°F to 482°F).
- An internal fan to ensure uniform heat distribution.
- Perforated shelves that allow air to circulate freely around the items.
Primary Applications in the Chemistry Lab
While often associated with sterilization, the hot air oven serves several distinct functions in a chemistry environment.
Sterilization of Glassware and Instruments
This is the oven's most common application. It is ideal for sterilizing items that are heat-stable but could be damaged or corroded by the moisture from an autoclave. This includes flasks, beakers, pipettes, and metal instruments like scalpels and forceps.
Drying and Dehydration
The oven is essential for removing residual moisture from glassware after washing, ensuring no water contaminates a subsequent experiment. It is also used in analytical chemistry to dry samples to a constant weight for gravimetric analysis (determining a substance's mass).
Curing and Material Testing
In materials science and polymer chemistry, hot air ovens are used to cure substances at specific temperatures. They are also employed to test the thermal stability of components and materials by exposing them to high heat over long periods.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hot Air Oven vs. Autoclave
Choosing the correct heating method is a critical decision based on the material you are working with. The primary alternative to a hot air oven is an autoclave.
The Key Difference: Dry Heat vs. Moist Heat
A hot air oven uses dry heat, requiring higher temperatures and longer exposure times to sterilize (e.g., 160°C for 2 hours). An autoclave uses pressurized steam (moist heat), which is more efficient at transferring energy and sterilizes at lower temperatures and in less time (e.g., 121°C for 15 minutes).
When to Choose an Oven
You should use a hot air oven for materials that would be damaged by moisture. This includes anhydrous powders, oils, and sharp metal instruments that could be dulled or rusted by steam. It is the only choice when complete dryness is the desired outcome.
Limitations of Dry Heat
The high temperatures required for dry heat sterilization will destroy or melt many common lab materials. It is unsuitable for most plastics, rubber tubing, liquids, and culture media, as these require the lower temperatures of an autoclave.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, select your equipment based on the specific material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-stable glassware and metal instruments: The hot air oven is your reliable and effective choice, especially when complete dryness is required afterward.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids, culture media, or heat-sensitive plastics: You must use an autoclave, as the hot air oven's high temperatures and dry heat are unsuitable.
- If your primary focus is removing all moisture from a solid sample or piece of glassware: The hot air oven is the standard instrument designed precisely for this task.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of dry heat is the key to using a hot air oven safely and effectively for the correct applications in your laboratory workflow.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Feature | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization | Dry heat (160°C for 2 hours) | Glassware, metal instruments |
| Drying | Forced air convection | Removing moisture from samples & glassware |
| Curing/Thermal Testing | Precise temperature control | Polymer curing, material stability tests |
Need the right equipment for your lab's heating and sterilization tasks?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable hot air ovens designed for precise temperature control and uniform heating. Whether you need to sterilize moisture-sensitive items, dry chemical samples, or perform thermal testing, our solutions are built to enhance your workflow's efficiency and reliability.
Contact us today to find the perfect hot air oven for your chemistry laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in W18Cr4V steel sample preparation? Expert Microstructural Drying Guide



















