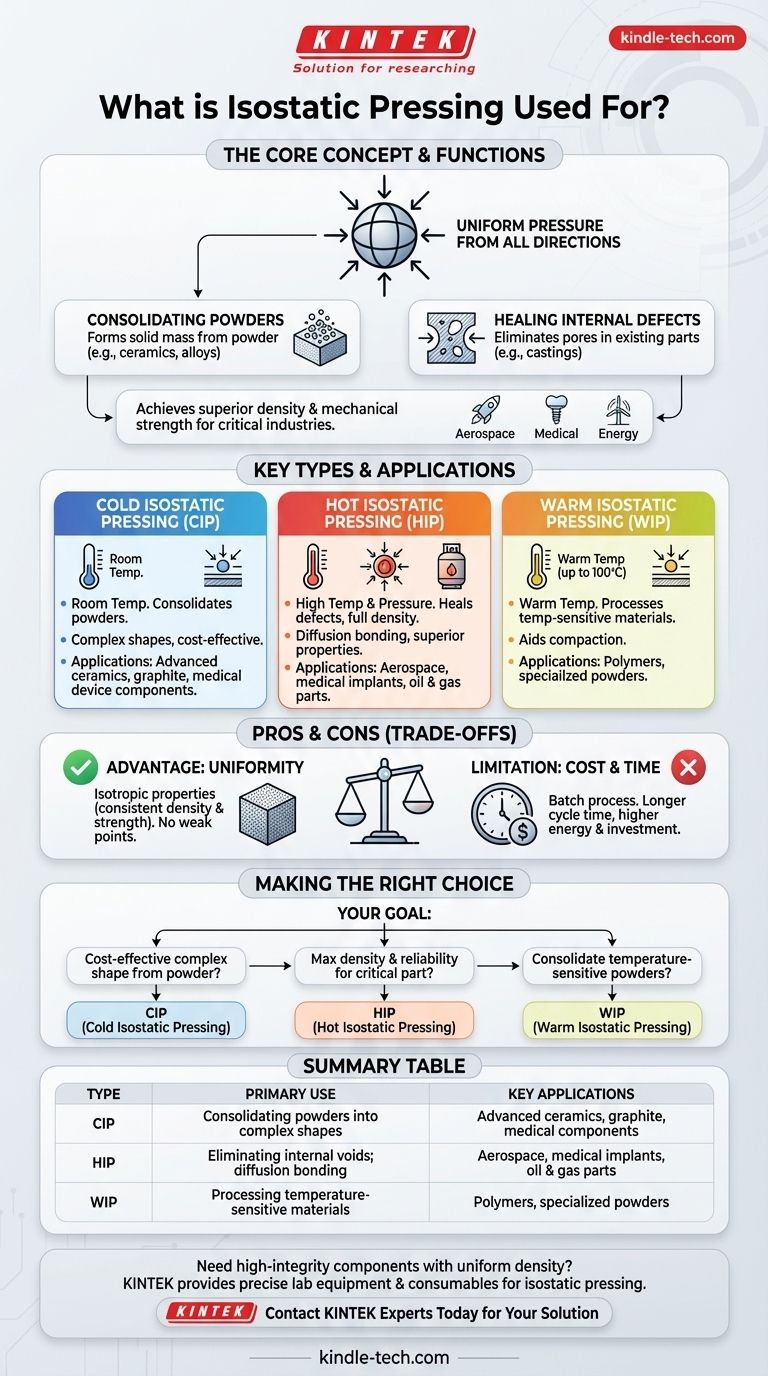
In short, isostatic pressing is used for two primary functions: consolidating powders into a solid mass and healing internal defects in existing parts. This process applies uniform pressure from all directions to materials like metals, ceramics, and composites, resulting in components with superior density and mechanical strength for critical industries such as aerospace, medical, and energy.
The core purpose of isostatic pressing is not simply to shape a part, but to achieve a level of internal density and uniformity that is impossible with traditional, one-directional pressing. It solves the fundamental problem of internal voids and weaknesses in high-performance materials.

The Core Problem Isostatic Pressing Solves
Isostatic pressing is chosen when the internal integrity of a material is non-negotiable. The "isostatic" method, which applies equal pressure from all sides, is the key to its effectiveness.
Consolidating Powders into Solid Forms
Many advanced materials, especially ceramics and specific metal alloys, begin as a fine powder. Isostatic pressing compacts this powder into a dense, uniform shape, often called a "green part."
This initial compaction creates a solid object with enough strength to be handled before it undergoes a final heating process (sintering) to achieve its full strength.
Healing Internal Defects in Existing Parts
Manufacturing processes like casting can leave microscopic voids or pores within a metal component. These defects, known as microshrinkage, can lead to premature failure under stress.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) uses high pressure and high temperature to essentially squeeze these internal voids closed, healing the part from the inside out and dramatically improving its durability.
Key Types and Their Primary Applications
The specific goals of the manufacturing process—whether creating an initial shape or perfecting a final part—determine which type of isostatic pressing is used.
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)
CIP is used at room temperature primarily to consolidate powders into a desired shape. It is an excellent and cost-effective method for forming complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with other pressing techniques.
Common applications include forming advanced ceramics (silicon carbide, silicon nitride), graphite, insulators, and components for medical devices before their final densification.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
HIP combines intense pressure with high temperatures, often in an inert gas environment like argon. This process can create fully dense materials from powder in a single step or, more commonly, eliminate the porosity in previously manufactured parts.
Because it produces superior material properties, HIP is critical for high-performance components in aerospace, oil and gas, and medical implants. It is also used for diffusion bonding, where it clads or joins different materials together at a molecular level.
Warm Isostatic Pressing (WIP)
A less common but important variation, WIP is used for materials that require processing at temperatures above ambient but below those used in HIP (typically up to 100°C). This is often applied to polymers and other materials where a small amount of heat aids in the compaction process.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While powerful, isostatic pressing is a specialized process with clear advantages and limitations that dictate its use.
The Advantage: Unmatched Uniformity
The primary benefit is isotropic (uniform in all directions) properties. Because pressure is applied evenly from every angle, the resulting part has consistent density and strength, without the internal stress lines or weak points common in parts made by uniaxial (one-direction) pressing.
The Limitation: Cycle Time and Cost
Isostatic pressing, particularly HIP, is a batch process. Loading the vessel, pressurizing it, holding it at temperature, and cooling it down takes significantly more time and energy than many other mass-production methods.
This higher cost and slower cycle time mean it is reserved for applications where the enhanced material properties justify the investment. It is not a replacement for conventional, high-volume manufacturing unless performance is the absolute priority.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct isostatic pressing method is entirely dependent on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectively forming a complex shape from powder before final sintering: Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is the ideal starting point.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and eliminating internal flaws in a critical metal or ceramic part: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the definitive technology for ensuring performance and reliability.
- If your primary focus is consolidating temperature-sensitive powders like polymers: Warm Isostatic Pressing (WIP) provides a tailored solution.
Ultimately, isostatic pressing is the essential manufacturing process for any application where material integrity and uniform density cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Type | Primary Use | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Consolidating powders into complex shapes | Advanced ceramics, graphite, medical device components |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Eliminating internal voids in parts; diffusion bonding | Aerospace components, medical implants, oil & gas parts |
| Warm Isostatic Pressing (WIP) | Processing temperature-sensitive materials | Polymers, specialized powders |
Need to manufacture high-integrity components with uniform density? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables required for isostatic pressing processes. Whether you're developing materials for aerospace, medical implants, or energy applications, our solutions help you achieve superior material performance and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your critical manufacturing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
People Also Ask
- What is a cold isostatic press? Achieve Uniform Powder Compaction for Complex Parts
- What is cold isostatic pressing examples? Achieve Uniform Density in Powder Compaction
- What are the applications of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- How much does an isostatic press cost? A Guide to Lab vs. Industrial Pricing
- What is cold isostatic pressing mold material? Essential Elastomers for Uniform Density



















