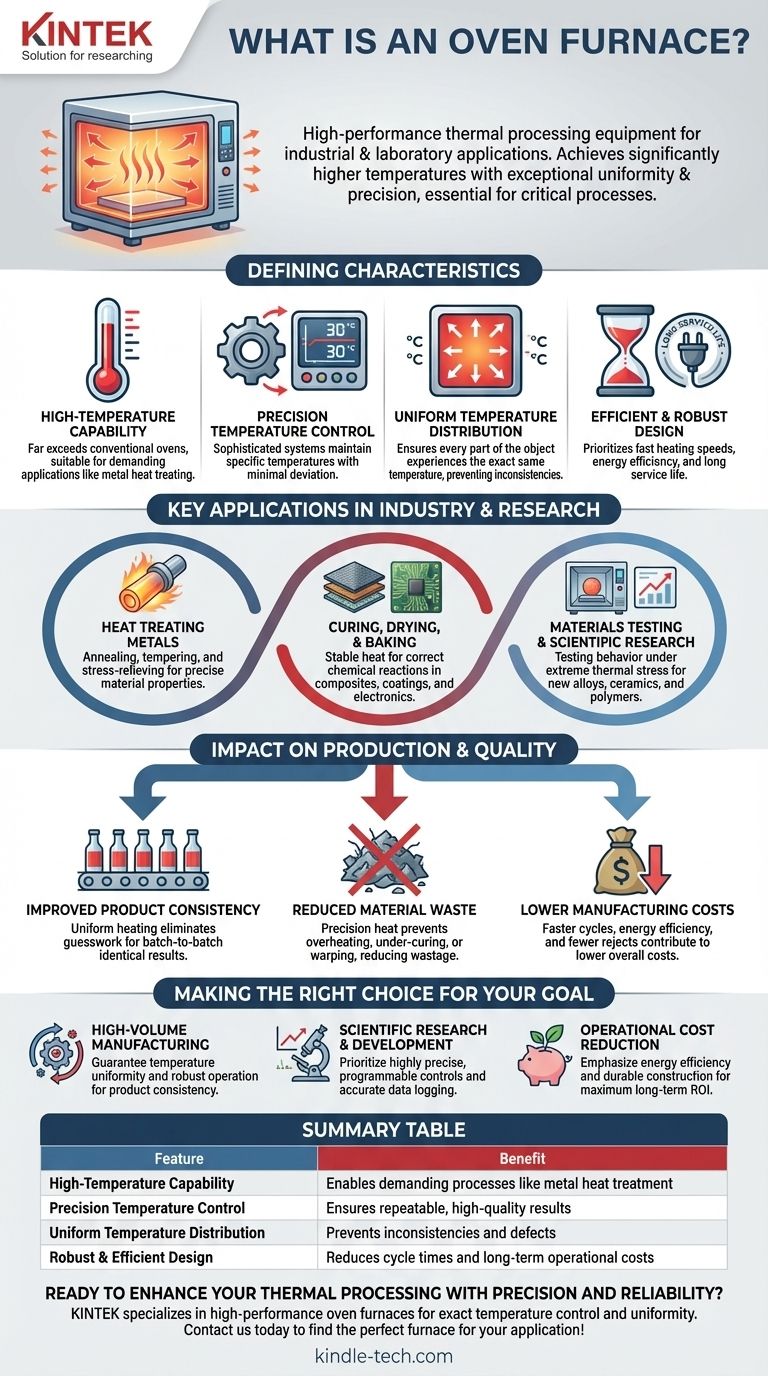
In essence, an oven furnace is a piece of high-performance thermal processing equipment designed for industrial or laboratory applications. Unlike a conventional oven, it is engineered to achieve significantly higher temperatures with exceptional uniformity and precision, making it essential for processes where consistent heat is critical to the outcome.
The core distinction of an oven furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to maintain a highly stable and uniform temperature throughout its entire chamber. This precision is the key to achieving repeatable, high-quality results in manufacturing and scientific research.

What Defines an Oven Furnace?
While a standard oven heats a space, an oven furnace creates a controlled thermal environment. Several key characteristics differentiate it from more common heating equipment.
High-Temperature Capability
An oven furnace is built to operate reliably at temperatures that far exceed those of a domestic or light commercial oven. This is necessary for applications like heat-treating metals or testing advanced materials.
Precision Temperature Control
These units feature sophisticated control systems that maintain a specific temperature setpoint with very little deviation. This stable control is crucial for processes that are sensitive to even minor thermal fluctuations.
Uniform Temperature Distribution
Arguably the most important feature, temperature uniformity ensures that every part of the object being heated experiences the exact same temperature. This prevents inconsistencies, such as weak spots in a metal component or unevenly cured composites.
Efficient and Robust Design
Designed for demanding environments, these furnaces prioritize fast heating speeds to reduce cycle times. They are also built for energy efficiency and a long service life, making them a reliable long-term investment.
Key Applications in Industry and Research
The unique capabilities of oven furnaces make them indispensable across a range of technical fields. Their purpose is to transform materials in a predictable and repeatable way.
Heat Treating Metals
Processes like annealing, tempering, and stress-relieving require exact temperature cycles to alter the physical and mechanical properties of metals. The precision of an oven furnace ensures the final product meets strict engineering specifications.
Curing, Drying, and Baking
From curing composite materials and industrial coatings to baking specialized electronics, an oven furnace provides the stable, uniform heat needed for chemical reactions to complete correctly, ensuring maximum strength and durability.
Materials Testing and Scientific Research
As an ideal piece of scientific research equipment, these furnaces are used to test how materials behave under extreme thermal stress. This data is vital for developing new alloys, ceramics, and polymers.
The Impact on Production and Quality
Investing in the right thermal equipment directly impacts an organization's bottom line and the quality of its output. The benefits are tied directly to the furnace's core engineering principles.
Improved Product Consistency
Uniform and stable heating eliminates guesswork. It produces identical results from batch to batch, which is a cornerstone of any modern quality control system.
Reduced Material Waste
By applying heat with precision, an oven furnace prevents costly errors like overheating, under-curing, or warping. This significantly reduces the wastage of material that would otherwise have to be scrapped.
Lower Manufacturing Costs
Faster heating cycles, energy efficiency, and a reduction in rejected parts all contribute to a lower cost of manufacturing. This makes production more efficient and competitive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal equipment depends entirely on the requirements of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: You need a furnace that guarantees temperature uniformity and robust, reliable operation to ensure product consistency and minimize downtime.
- If your primary focus is scientific research or development: Prioritize a unit with highly precise, programmable controls and the ability to accurately log data from the thermal cycle.
- If your primary focus is operational cost reduction: Emphasize models known for their energy efficiency and durable construction to maximize return on investment over a long service life.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to select the right tool to achieve precise and repeatable thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Capability | Enables demanding processes like metal heat treatment |
| Precision Temperature Control | Ensures repeatable, high-quality results |
| Uniform Temperature Distribution | Prevents inconsistencies and defects |
| Robust & Efficient Design | Reduces cycle times and long-term operational costs |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with precision and reliability? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing oven furnaces that deliver the exact temperature control and uniformity your laboratory or production line needs. Whether for heat treating, curing, or advanced materials testing, our solutions are designed to improve your product consistency and reduce costs. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation



















