In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) on plastic is a vacuum-based coating process that applies a very thin, durable film of material onto a plastic surface. This technique transforms the plastic part, giving it properties it doesn't naturally possess—such as a metallic appearance, scratch resistance, or electrical conductivity—without changing its lightweight nature or underlying shape.
The core purpose of PVD on plastic is to upgrade the performance and appearance of a low-cost, versatile material. It allows engineers and designers to combine the benefits of plastic (lightweight, easy to mold) with the desirable surface properties of metals, ceramics, or other advanced materials.

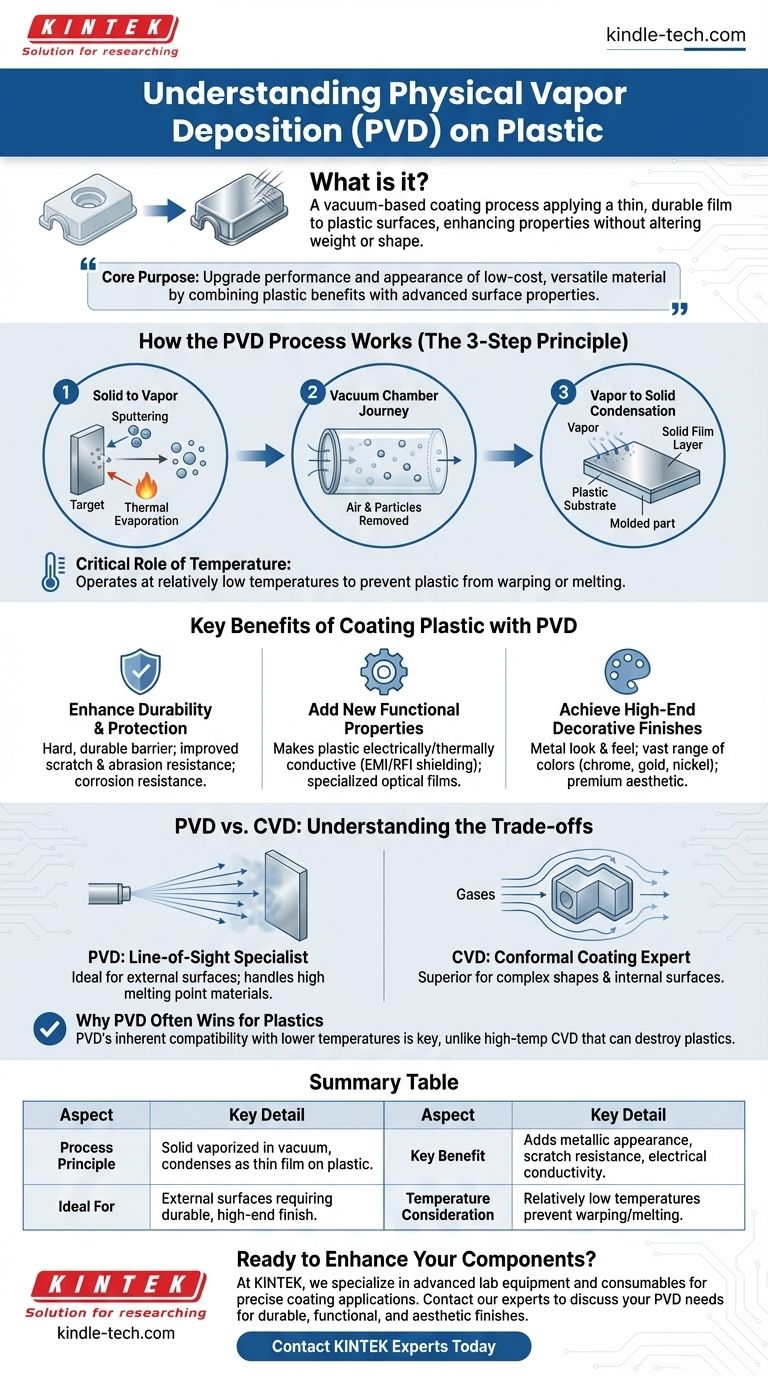
How the PVD Process Works on Plastic
Physical Vapor Deposition is not a single method but a family of processes that share a common principle. Understanding this principle is key to seeing its value.
The Three-Step Principle: Solid to Vapor to Solid
First, a solid source material, often called a "target," is converted into a vapor. This is typically done through methods like sputtering (bombarding the target with ions) or thermal evaporation (heating it until it vaporizes).
Second, this vapor travels through a vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it removes air and other particles, ensuring the vaporized material doesn't react with anything before reaching its destination.
Finally, the vapor condenses onto the plastic substrate, forming a thin, dense, and well-bonded solid film. The result is a plastic part that is now coated with a new material layer.
The Critical Role of Temperature
A key consideration for plastics is their low melting point. PVD processes are advantageous because many can be performed at relatively low temperatures, preventing the plastic substrate from warping, melting, or deforming during the coating process.
Key Benefits of Coating Plastic with PVD
Applying a PVD coating fundamentally changes what a plastic component can do. The benefits are typically functional, decorative, or both.
Enhancing Durability and Protection
PVD coatings create a hard, durable barrier on the plastic surface. This provides significant improvements in scratch and abrasion resistance, making plastic parts suitable for high-wear environments where they would normally fail quickly. It can also add a layer of corrosion resistance.
Adding New Functional Properties
This is where PVD unlocks new engineering possibilities. A PVD film can make a non-conductive plastic electrically or thermally conductive, which is essential for electronics housings that require EMI/RFI shielding. It is also used to apply specialized optical films for lenses or displays.
Achieving High-End Decorative Finishes
PVD is widely used to give plastic parts the look and feel of metal. It can produce a vast range of colors and finishes—from chrome to brushed nickel to gold—providing a premium aesthetic on a cost-effective plastic base.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. an Alternative (CVD)
To fully grasp PVD, it's helpful to compare it to its chemical counterpart, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While the goal is similar, the method and ideal use cases differ significantly.
PVD: The Line-of-Sight Specialist
PVD is a line-of-sight process. This means the vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. It is excellent for coating external surfaces and can handle materials with very high melting points.
CVD: The Conformal Coating Expert
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses chemical reactions between precursor gases to deposit a film. Because gases can flow around an object, CVD is not limited by line-of-sight. This makes it superior for coating complex shapes and internal surfaces evenly.
Why PVD Often Wins for Plastics
The deciding factor is often temperature. While both have low-temperature variants, traditional CVD processes run at very high temperatures that would destroy most plastics. PVD's inherent compatibility with lower-temperature operation makes it a more common and accessible choice for polymer substrates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The decision to use PVD coating on a plastic part depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is adding a durable, metallic finish to an external plastic surface: PVD is almost always the most direct and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating a conductive shield inside a complex electronics housing: A non-line-of-sight method like CVD (or an alternative like electroless plating) might be necessary to ensure complete coverage.
- If your primary focus is improving the scratch resistance of a consumer product: PVD provides a hard, protective layer that dramatically enhances longevity while improving aesthetics.
Ultimately, PVD technology dramatically expands the functional and aesthetic capabilities of plastic components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Principle | Solid material is vaporized in a vacuum and condenses as a thin film on the plastic substrate. |
| Key Benefit | Adds properties like metallic appearance, scratch resistance, and electrical conductivity. |
| Ideal For | Coating external surfaces of plastic parts requiring a durable, high-end finish. |
| Temperature Consideration | Operates at relatively low temperatures to prevent plastic warping or melting. |
Ready to enhance your plastic components with high-performance PVD coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise coating applications. Whether you're developing consumer electronics, automotive parts, or medical devices, our solutions help you achieve durable, functional, and aesthetically superior finishes on plastic substrates.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD technologies can bring your innovative designs to life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















