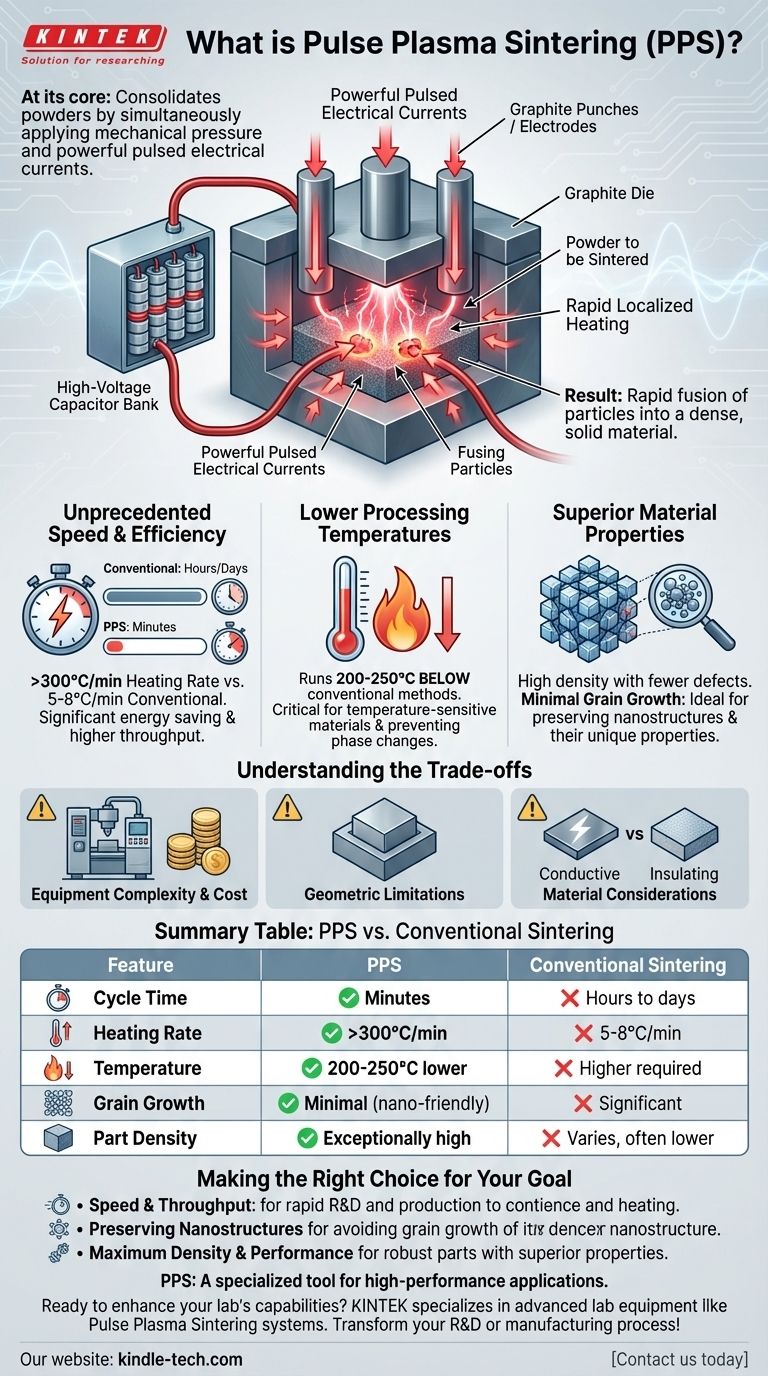
At its core, Pulse Plasma Sintering (PPS) is an advanced manufacturing method that consolidates powders into a dense, solid material. It works by simultaneously applying mechanical pressure and a series of powerful, pulsed electrical currents. These current pulses, generated by discharging a high-voltage capacitor, pass directly through the powder and its tooling, causing extremely rapid and localized heating that fuses the particles together.
The central advantage of PPS and similar techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a dramatic reduction in processing time and temperature. This allows for the creation of high-density materials with superior properties, especially for advanced and nano-sized powders, in a fraction of the time required by conventional furnaces.

How Pulse Plasma Sintering Achieves Its Results
The Core Mechanism
The material to be sintered, in powder form, is placed into a graphite die. It is then contained between two graphite punches, which also act as electrodes.
The entire setup is placed under mechanical pressure. This initial compaction ensures good particle-to-particle contact, which is critical for the next step.
The Role of Pulsed Electrical Current
Instead of heating the material slowly from the outside-in like a traditional furnace, PPS uses a high-voltage capacitor to send massive pulses of electric current directly through the punches and the powder.
This direct electrical heating is incredibly efficient and fast, generating intense heat precisely where it's needed—at the contact points between powder particles. This creates localized plasma, cleans particle surfaces, and promotes rapid bonding.
Key Advantages Over Conventional Sintering
Unprecedented Speed and Efficiency
Conventional sintering can take many hours or even days. PPS can achieve full densification in a matter of minutes.
The heating rates are orders of magnitude higher (over 300°C/min) compared to the slow ramp-up of a standard furnace (5-8°C/min). This translates to significantly lower energy consumption and higher manufacturing throughput.
Lower Processing Temperatures
Because the heating is so efficient and localized, the overall process can be run at a lower temperature, often 200-250°C below what's needed for conventional methods.
This is a critical advantage when working with materials that are sensitive to high temperatures or prone to undesirable phase changes.
Superior Material Properties
The combination of pressure and rapid heating results in exceptionally dense structures with fewer internal defects or voids.
Crucially, the short processing time prevents significant grain growth. This makes PPS an ideal method for consolidating nano-sized powders while preserving their unique nanoscale properties, something that is nearly impossible with slow, high-heat conventional processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Complexity and Cost
PPS systems are far more complex than simple furnaces. They require specialized power supplies, high-voltage capacitor banks, and robust press frames, leading to a higher initial capital investment.
Geometric Limitations
While more flexible than some pressing methods, the use of a rigid die and punch setup places constraints on the shapes and sizes of parts that can be produced. It is not as flexible for complex geometries as a process like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP).
Material Considerations
The process works best with materials that are at least somewhat electrically conductive. While the graphite tooling helps distribute the current, highly insulating ceramic powders can be more challenging to process effectively and may require specialized die setups.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PPS is not a universal replacement for all sintering, but a specialized tool for high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is speed and throughput: The minute-long cycle times of PPS offer an unparalleled advantage for rapid R&D and efficient production.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures: PPS is one of the best available methods, as its low temperature and short duration prevent the grain growth that plagues conventional techniques.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and performance: The simultaneous application of pressure and direct heating creates dense, robust parts with minimal defects, leading to superior mechanical properties.
Ultimately, Pulse Plasma Sintering empowers engineers and scientists to create advanced materials that are stronger, denser, and manufactured far more efficiently than is possible with traditional methods.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pulse Plasma Sintering (PPS) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time | Minutes | Hours to days |
| Heating Rate | >300°C/min | 5-8°C/min |
| Temperature | 200-250°C lower | Higher temperatures required |
| Grain Growth | Minimal (ideal for nanostructures) | Significant |
| Part Density | Exceptionally high | Varies, often lower |
Ready to enhance your lab's material synthesis capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment like Pulse Plasma Sintering systems, designed for researchers and engineers who need rapid, high-density material consolidation while preserving nanoscale properties. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing production throughput, our solutions deliver superior performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how PPS can transform your R&D or manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of remelting heat treatment in a vacuum hot press for UHMWPE? Ensure Oxidative Stability
- Why is vacuum sintering equipment essential for hot pressing sub-micron metal powders? Ensure Purity and Conductivity
- Why is a vacuum hot pressing furnace required for Ni-Mn-Sn-In alloys? Achieve High-Density & Oxidation-Free Sintering
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- How does the temperature control system of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the mechanical properties of tungsten and copper joints? | Optimize Joint Strength
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Superior Densification for 2024Al/Gr/SiC Composites
- What is the function of axial pressure in hot pressing Al-4Cu alloys? Achieve Peak Densification and Strength
- What technical functions does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Optimize CoCrFeNi Alloy Coatings



















