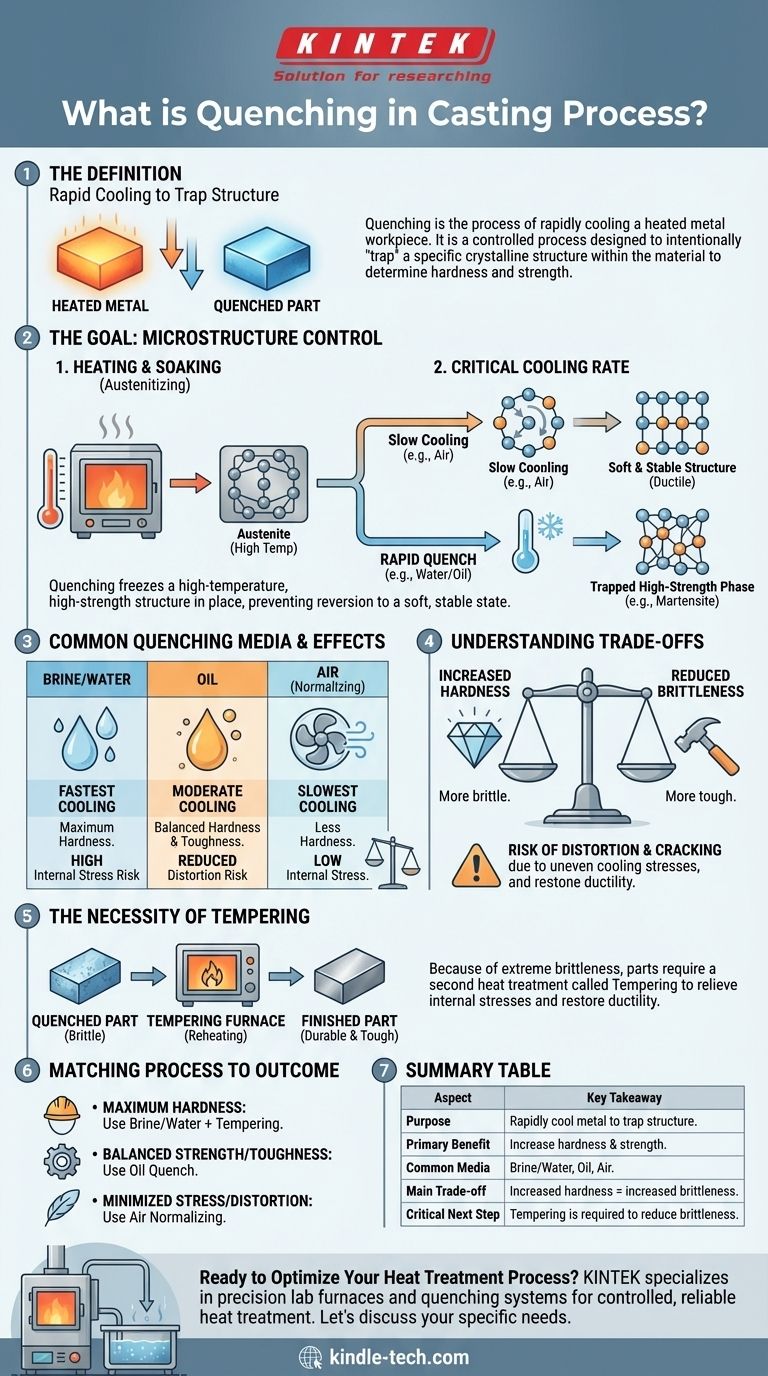
In metal casting and heat treatment, quenching is the process of rapidly cooling a heated metal workpiece. This is not simply about making the metal cold; it is a controlled process designed to intentionally "trap" a specific crystalline structure within the material. This locked-in structure is what determines the final mechanical properties of the part, most notably its hardness and strength.
The core purpose of quenching is to cool a metal so quickly that its internal atomic structure does not have time to revert to its soft, stable, low-temperature state. This controlled intervention freezes a high-temperature, high-strength structure in place, fundamentally altering the material's performance.

The Goal: Controlling the Microstructure
Quenching is a critical step in a broader heat treatment cycle. Its success depends entirely on what happens before and how the cooling itself is executed.
Heating and Soaking: Setting the Stage
Before any cooling can occur, the metal must first be heated to a specific temperature, often below its melting point, and held there. This is known as austenitizing in steels.
This heating and holding phase allows the metal's crystalline structure to transform into a uniform, high-temperature state where elements like carbon are fully dissolved. This creates the necessary starting condition for the quench to be effective.
The Critical Cooling Rate
The speed at which the metal is cooled is the most important variable in quenching.
When a metal cools slowly, its atoms have ample time to rearrange themselves into soft, orderly, and stable crystalline structures. This results in a ductile but weaker material.
Trapping a High-Strength Phase
Quenching introduces thermal shock, cooling the part so rapidly that the atoms cannot complete their normal rearrangement.
Instead, they are trapped in a highly stressed and distorted configuration, such as martensite in steel. This new structure is extremely hard and strong but also very brittle.
Common Quenching Media and Their Effects
The choice of quenching medium directly controls the cooling rate and, therefore, the final properties of the part.
Brine and Water
Brine (salt water) and plain water offer the fastest cooling rates. They are used when maximum hardness is the primary objective. However, this extreme speed creates immense internal stress.
Oil
Oil cools the material more slowly than water. This slower heat extraction reduces the risk of distortion and cracking while still achieving significant hardness, offering a balance between strength and toughness.
Air
Forcing air over the part is a much slower form of quenching, often referred to as normalizing. It results in less hardness compared to liquid quenching but also generates far less internal stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Quenching is a powerful process, but it is defined by a critical set of compromises. Ignoring them leads to failed parts.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
The central trade-off is that as hardness increases, so does brittleness. A fully quenched, untempered steel part may be hard enough to scratch glass, but it might also shatter if dropped.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid and often uneven cooling during a quench creates massive internal stresses within the part. If these stresses exceed the material's strength, the part will warp, change dimensions, or develop cracks.
The Necessity of Tempering
Because of the extreme brittleness induced by quenching, parts are almost never used in a freshly quenched state. A second heat treatment process called tempering is required.
Tempering involves reheating the quenched part to a lower temperature to relieve internal stresses and restore some ductility. This process reduces the hardness slightly but dramatically increases the material's toughness, making it durable and useful.
Matching the Process to the Desired Outcome
The correct quenching strategy is dictated entirely by the final application of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness: You will need a very rapid quench using a medium like brine or water, but you must plan for subsequent tempering to reduce extreme brittleness.
- If your primary focus is balancing strength with toughness: An oil quench is often the optimal choice, as it provides significant hardening with a much lower risk of cracking than water.
- If your primary focus is minimizing internal stress and distortion: A slower cooling process like normalizing in air is preferable, though it will not achieve the high hardness of a liquid quench.
Ultimately, quenching is the critical step that transforms a metal from a simple heated shape into a component with precisely engineered performance characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Rapidly cool metal to trap a high-strength crystalline structure (e.g., martensite). |
| Primary Benefit | Significantly increases hardness and strength of the metal part. |
| Common Media | Brine/Water (fastest), Oil (balanced), Air (slowest). |
| Main Trade-off | Increased hardness comes with increased brittleness and risk of cracking. |
| Critical Next Step | Tempering is required after quenching to reduce brittleness and improve toughness. |
Ready to Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process?
Quenching is a delicate balance between achieving maximum hardness and managing material stress. The right equipment is essential for consistent, high-quality results.
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab furnaces and quenching systems designed for controlled, reliable heat treatment. Whether you're working with steel, alloys, or other metals, our solutions help you achieve the exact mechanical properties your application demands—minimizing distortion and maximizing performance.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect quenching solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy



















