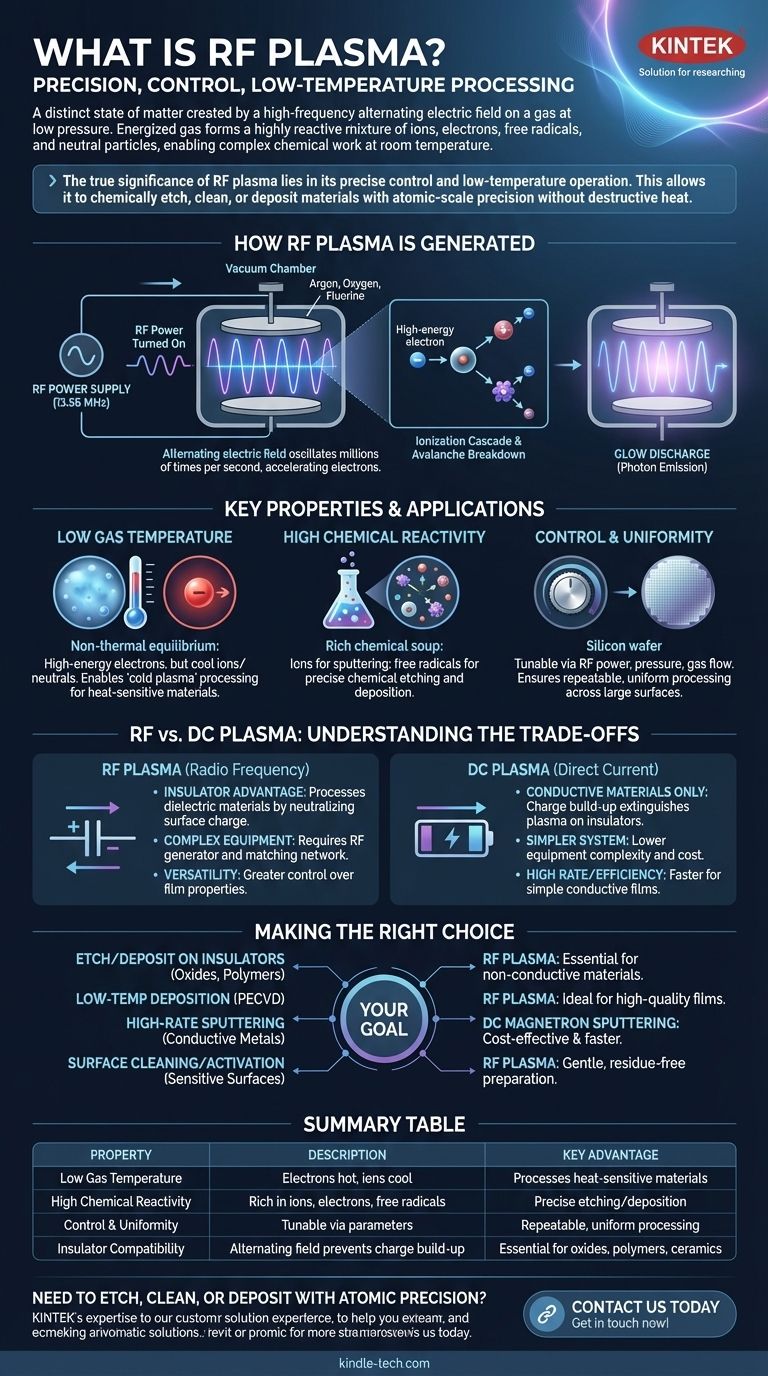
In essence, Radio Frequency (RF) plasma is a distinct state of matter created by applying a high-frequency alternating electric field to a gas at low pressure. The process energizes the gas, stripping electrons from atoms to create a highly reactive mixture of ions, electrons, free radicals, and neutral particles. Unlike a simple heated gas, RF plasma can perform complex chemical work at or near room temperature.
The true significance of RF plasma lies in its precise control and low-temperature operation. This unique combination allows it to chemically etch, clean, or deposit materials with atomic-scale precision, all without the destructive heat that would damage sensitive components like microchips or medical instruments.

How RF Plasma is Generated
The Core Components
The process begins inside a vacuum chamber containing a small amount of a specific gas, such as argon, oxygen, or a fluorine compound. Within this chamber are two electrodes connected to an RF power supply, which typically operates at a federally regulated frequency of 13.56 MHz.
The Role of the Radio Frequency Field
When the RF power is turned on, it creates a rapidly alternating electric field between the electrodes. This field oscillates millions of times per second, grabbing free electrons in the gas and accelerating them back and forth at high speed.
Crucially, the field reverses direction so quickly that the lightweight electrons can gain significant energy, while the much heavier positive ions barely move in response.
The Ionization Cascade
These high-energy electrons collide with neutral gas atoms, knocking more electrons loose. This collision creates a positive ion and another free electron, which is then accelerated by the RF field, leading to more collisions.
This self-sustaining chain reaction, known as an avalanche breakdown, rapidly ionizes a significant portion of the gas, creating the plasma.
The Characteristic "Glow Discharge"
The plasma emits a characteristic glow, which is why it's often called a "glow discharge." This light is produced when energized electrons drop back to lower energy states, releasing their excess energy as photons of a specific color depending on the gas used.
Key Properties and Their Applications
Low Gas Temperature
While the electrons in an RF plasma are extremely energetic (possessing a "temperature" of tens of thousands of degrees), the ions and neutral gas atoms remain cool, often near room temperature.
This non-thermal equilibrium is the single most important property of RF plasma. It enables energetic chemical processes without high heat, a technique known as "cold plasma" processing.
High Chemical Reactivity
An RF plasma is a rich chemical soup. The ions are used for physical bombardment (sputtering), while the electrically neutral but highly reactive free radicals drive many chemical etching and deposition processes.
By choosing the right gas, engineers can create a plasma specifically designed to perform a certain chemical reaction on a material's surface.
Control and Uniformity
The properties of the plasma—its density, chemical composition, and ion energy—can be precisely tuned by adjusting parameters like RF power, gas pressure, and gas flow rates. This allows for highly repeatable and uniform processing across large surfaces, such as a 300mm silicon wafer.
Understanding the Trade-offs: RF vs. DC Plasma
The Insulator Advantage
The primary advantage of RF plasma is its ability to process insulating (dielectric) materials. In a Direct Current (DC) system, positive ions would quickly build up on an insulating surface, creating a positive charge that repels any more incoming ions and extinguishes the plasma.
Because the RF field alternates, it effectively neutralizes this charge build-up on the surface during each cycle, allowing for continuous processing of materials like silicon dioxide, polymers, and ceramics.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
RF plasma systems are inherently more complex and expensive than their DC counterparts. They require a stable RF generator and a sophisticated impedance matching network. This network is crucial for efficiently transferring power from the generator into the plasma, which has a constantly changing electrical impedance.
Process Rates and Efficiency
For depositing simple conductive films, DC plasma systems (specifically DC magnetron sputtering) can often achieve higher deposition rates and are more power-efficient. However, RF plasma offers far greater versatility and control over the properties of the deposited film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use RF plasma is driven entirely by the material you need to process and the outcome you wish to achieve.
- If your primary focus is etching or depositing on non-conductive materials (like oxides, nitrides, or polymers): RF plasma is the essential and often only viable choice.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature deposition with precise chemical control (PECVD): RF plasma provides the low-temperature, high-reactivity environment needed to create high-quality films.
- If your primary focus is high-rate sputtering of a simple conductive metal: A DC magnetron sputtering system may be a more cost-effective and faster solution.
- If your primary focus is gentle, residue-free surface cleaning or activation for bonding: The low-temperature, reactive nature of RF plasma makes it ideal for preparing sensitive surfaces.
Ultimately, RF plasma is a foundational tool for manipulating matter, enabling the fabrication of the advanced technologies that define our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Low Gas Temperature | Electrons are hot, but ions/neutral atoms remain near room temperature. | Processes heat-sensitive materials without damage. |
| High Chemical Reactivity | Rich in ions, electrons, and free radicals. | Drives precise chemical reactions for etching and deposition. |
| Control & Uniformity | Tunable via RF power, pressure, and gas flow. | Ensures repeatable, uniform processing across large surfaces. |
| Insulator Compatibility | Alternating field prevents charge build-up on non-conductive surfaces. | Essential for processing oxides, polymers, and ceramics. |
Need to Etch, Clean, or Deposit on Sensitive Materials with Atomic Precision?
RF plasma technology is the key to achieving high-precision, low-temperature processing for your most delicate components. Whether you're working with microchips, medical instruments, or advanced polymers, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you harness the power of RF plasma.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems



















