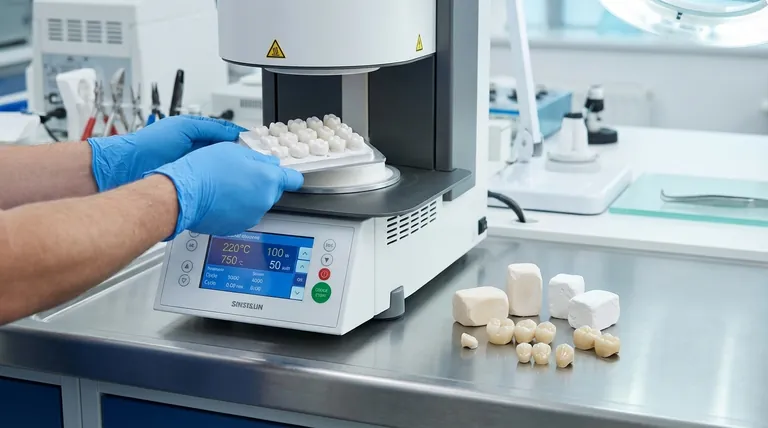
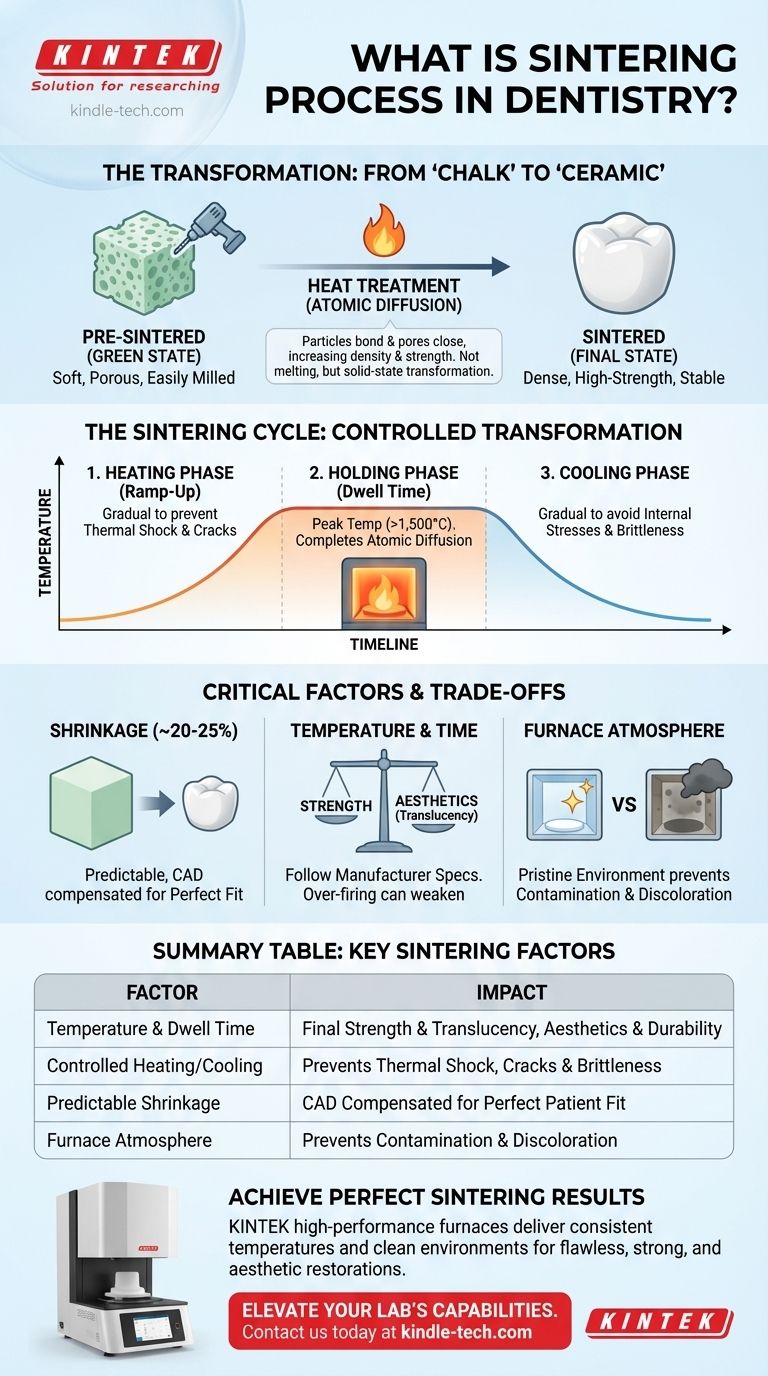
In dental technology, sintering is a critical heat treatment process that transforms a soft, porous dental restoration into its final, high-strength state. This is accomplished by heating the material in a specialized furnace to a temperature below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together and create a dense, solid structure.
Sintering is not a melting process. It is a solid-state transformation that uses controlled heat to eliminate porosity and bond material particles, which is what gives modern dental ceramics like zirconia their exceptional strength and durability.

The Core Principle: From "Chalk" to "Ceramic"
To understand sintering, it's best to think of it as a controlled transformation. A dental restoration, particularly one made of zirconia, begins its life in a completely different state than the one it ends up in.
What is Happening at a Microscopic Level?
Sintering works through a process called atomic diffusion. At high temperatures, the atoms in the material's particles become more mobile. They migrate across the boundaries between particles, effectively closing the microscopic gaps and pores that exist in the initial state.
This process bonds the particles together, significantly increasing the material's density, strength, and stability.
The Role of Pre-Sintered Materials
In a modern dental lab, technicians do not work with raw ceramic powder. Instead, they use industrially produced blocks or discs of material that have already been partially processed.
This "pre-sintered" or "green state" material is dense enough to be handled but soft enough to be easily milled by a CAD/CAM machine. It has a consistency often compared to chalk.
Why Mill Before Sintering?
The primary advantage of this workflow is efficiency and precision. Milling the restoration from a soft, pre-sintered block is significantly faster and causes much less wear on the milling tools (burs).
Machining the material in its final, fully hardened state would be extremely time-consuming and costly.
The Sintering Cycle: A Controlled Transformation
The transformation from a soft to a hard state occurs within a specialized dental furnace. This process, known as the sintering cycle, is meticulously controlled.
The Heating Phase (Ramp-Up)
The furnace temperature is increased gradually over a specific period. A controlled ramp-up is crucial to prevent thermal shock, which could cause cracks or fractures in the delicate restoration before it gains its full strength.
The Holding Phase (Dwell Time)
Once the furnace reaches its peak temperature (which can exceed 1,500°C for some zirconia), it is held there for a prescribed amount of time. This "dwell time" allows the atomic diffusion process to complete, ensuring the restoration reaches its maximum density and desired physical properties.
The Cooling Phase
Just as with heating, the cooling phase must be carefully controlled. Cooling the restoration too quickly can introduce internal stresses, making it brittle and prone to failure later on. A slow, gradual cool-down ensures a stable and stress-free final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Achieving a perfect result with sintering requires understanding the key variables and their consequences. The process is a science, and slight deviations can have a significant impact.
Shrinkage: A Necessary Consequence
The most significant outcome of densification is shrinkage. As the pores between particles are eliminated, the entire restoration shrinks in size.
This shrinkage is not a flaw but a predictable part of the process, typically around 20-25%. CAD design software automatically compensates for this by milling the restoration at a larger scale, ensuring it shrinks to the precise dimensions required for a perfect fit.
Temperature and Time: The Balancing Act
The final temperature and dwell time have a direct impact on the restoration's final properties. For example, sintering zirconia at a higher temperature can increase its translucency, improving aesthetics.
However, over-firing can lead to excessive grain growth within the material, which can paradoxically reduce its flexural strength. Following the material manufacturer's exact specifications is non-negotiable.
Furnace Contamination
The atmosphere inside the furnace must be pristine. Any contaminants can become baked into the ceramic, causing discoloration and compromising the aesthetic outcome of the final restoration. This is why regular furnace cleaning and calibration are essential protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The success of a sintered restoration depends on strict adherence to scientifically validated protocols. Your goal for the final prosthetic dictates where your focus should lie.
- If your primary focus is accuracy and fit: Ensure your CAD software is perfectly calibrated for the specific shrinkage factor of the material block being used.
- If your primary focus is strength and durability: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer's recommended peak temperature and dwell time, as under-sintering will result in a weak and unreliable restoration.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics: Use the precise, manufacturer-validated sintering cycle designed to achieve the desired level of translucency without compromising structural integrity.
Mastering the principles of sintering is fundamental to producing consistently strong, aesthetic, and perfectly fitting dental restorations.
Summary Table:
| Key Sintering Factor | Impact on Final Restoration |
|---|---|
| Temperature & Dwell Time | Determines final strength and translucency. Critical for aesthetics and durability. |
| Controlled Heating/Cooling | Prevents thermal shock and internal stresses, avoiding cracks and brittleness. |
| Predictable Shrinkage (~20-25%) | CAD software compensates for this, ensuring the restoration fits the patient perfectly. |
| Furnace Atmosphere | A pristine environment is essential to prevent contamination and discoloration. |
Achieve Perfect Sintering Results Every Time
Producing strong, aesthetically perfect, and accurately fitting dental restorations like zirconia crowns requires precise control over the sintering process. The right laboratory equipment is fundamental to this success.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance dental sintering furnaces and lab equipment, designed to deliver the consistent temperatures and clean environments necessary for flawless results. Our solutions help dental laboratories enhance efficiency, ensure material integrity, and meet the highest standards of care.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the ideal sintering furnace for your specific materials and workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using a tube furnace with vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Master Ceramic Synthesis
- What are the key differences between incineration and gasification? Explore Waste Management Solutions
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What are the disadvantages of biomass conversion? High Costs, Logistical Hurdles, and Environmental Trade-offs

















