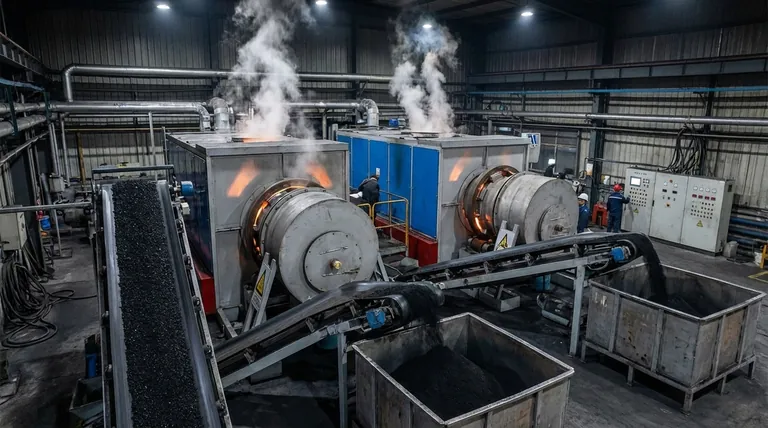
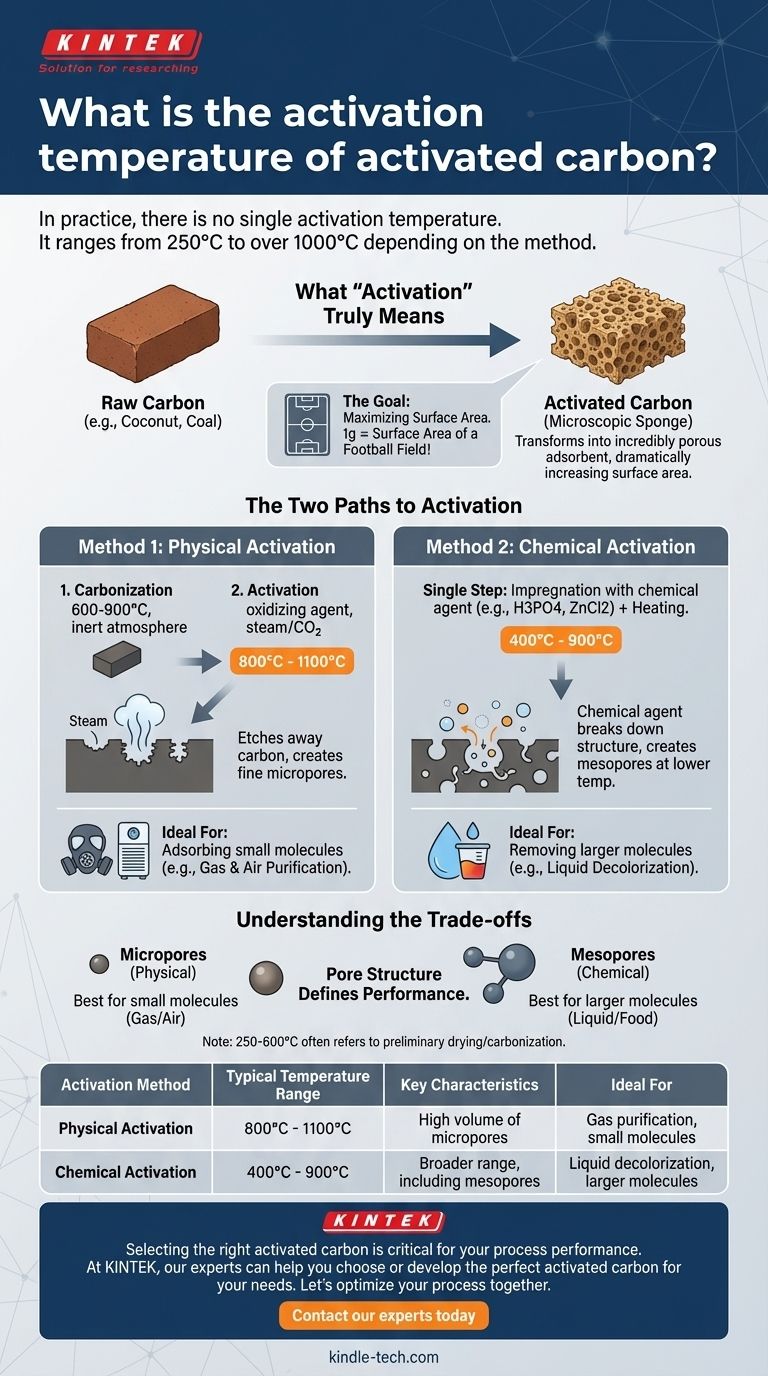
In practice, there is no single activation temperature for activated carbon. The process is more complex, with temperatures ranging from 250°C to over 1000°C depending entirely on the specific activation method being used and the desired outcome. The two primary methods, chemical and physical activation, operate in distinctly different temperature windows.
The specific temperature is not the goal, but a critical variable in a controlled process. The true aim of activation is to create a vast internal network of microscopic pores, and the chosen temperature is simply the tool required by the specific method—chemical or physical—to achieve that structure.

What "Activation" Truly Means
From Carbon to a Microscopic Sponge
Activation is the process that transforms a simple carbonaceous material, like coconut shells or coal, into an incredibly porous adsorbent. This process dramatically increases the material's internal surface area.
Think of it as turning a solid brick into a high-surface-area sponge. The "activation" step is what carves out the millions of tiny tunnels and cavities (micropores) within the brick, giving it the ability to trap and hold molecules.
The Goal: Maximizing Surface Area
The effectiveness of activated carbon is directly tied to its surface area. A single gram of activated carbon can have a surface area equivalent to a football field. This massive area is created by the network of pores developed during the high-temperature activation process.
The Two Paths to Activation
The specific temperature required depends entirely on which of the two primary activation methods is employed. These methods create different pore structures and are chosen based on the intended application of the final product.
Method 1: Physical Activation
Physical activation is a two-step process. First, the raw material is carbonized at high heat (around 600–900°C) in an inert atmosphere.
The crucial second step is activation, where the carbonized material is exposed to an oxidizing agent—typically steam or carbon dioxide—at even higher temperatures, usually ranging from 800°C to 1100°C. This harsh process etches away the carbon structure, developing a fine network of micropores.
Method 2: Chemical Activation
Chemical activation is typically a single-step process. The raw material is first impregnated with a chemical dehydrating and oxidizing agent, such as phosphoric acid or zinc chloride.
This mixture is then heated to a temperature between 400°C and 900°C. The chemical agent works to break down the material's internal structure from within, creating the desired pore network at a significantly lower temperature than physical activation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between physical and chemical activation is a decision based on cost, desired pore structure, and the final application.
Pore Structure Defines Performance
Physical activation tends to produce a structure dominated by very small pores (micropores). This makes it ideal for adsorbing small molecules, such as those found in gas and air purification systems.
Chemical activation can be tailored to create a broader range of pore sizes, including larger mesopores. This is highly effective for removing larger molecules, such as color bodies from liquids in the food and beverage industry.
The Meaning of the 250-600°C Range
The temperature range of 250–600°C mentioned in some contexts often refers to preliminary drying or early-stage carbonization steps. While part of the overall process, the key pore development for most high-grade activated carbons occurs at the higher temperatures described for physical and chemical activation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal activation temperature is determined by the end-use application, which dictates the ideal pore structure of the activated carbon.
- If your primary focus is adsorbing small gas molecules (e.g., in air filters or gas masks): Carbon produced via high-temperature physical activation is often superior due to its high volume of micropores.
- If your primary focus is removing larger molecules from liquids (e.g., decolorizing sugar or water treatment): Carbon from lower-temperature chemical activation may be more effective due to its well-developed mesopore structure.
Ultimately, understanding the link between activation method, temperature, and the resulting pore structure is the key to selecting the most effective material for your needs.
Summary Table:
| Activation Method | Typical Temperature Range | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Activation | 800°C - 1100°C | Creates a high volume of micropores | Gas purification, adsorbing small molecules |
| Chemical Activation | 400°C - 900°C | Creates a broader range of pore sizes, including mesopores | Liquid decolorization, removing larger molecules |
Selecting the right activated carbon is critical for your process performance. The optimal material depends on your specific application, whether it's gas purification or liquid treatment.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material analysis and testing. Our experts can help you choose or develop the perfect activated carbon for your needs, ensuring maximum adsorption efficiency.
Let's optimize your process together. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process



















