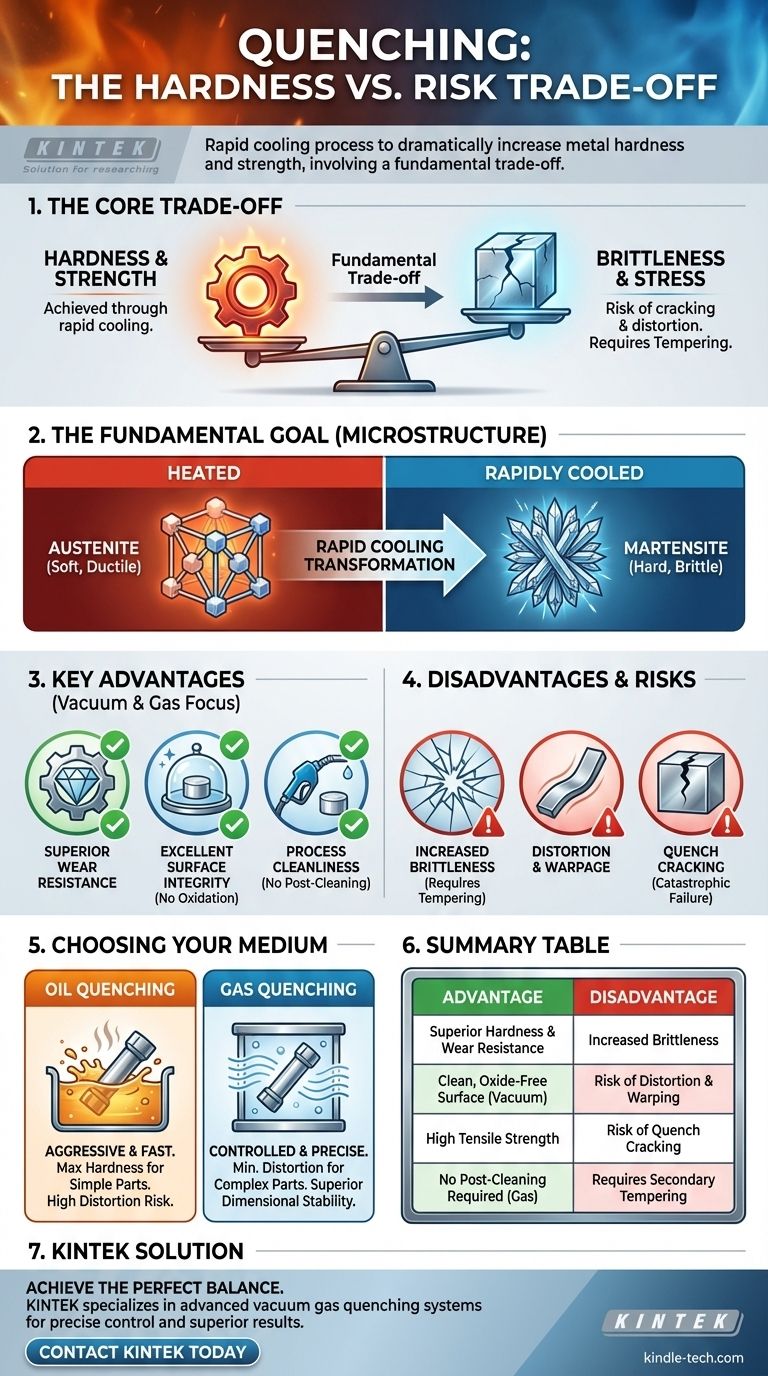
At its core, quenching is a heat treatment process that dramatically increases the hardness and strength of a metal, typically steel. This is achieved by heating the material to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooling it. The primary advantage is achieving superior mechanical properties, while the main disadvantage is the risk of making the material brittle and introducing internal stresses that can cause distortion or cracking.
Quenching is a fundamental trade-off in metallurgy. You sacrifice ductility and introduce significant internal stress to gain exceptional hardness and strength. The success of the process hinges entirely on controlling the rate of cooling to maximize the benefits while mitigating the risks of cracking and deformation.

The Fundamental Goal: Why We Quench
Quenching is not just about cooling metal quickly; it's a precise process designed to lock in a specific, desirable crystalline structure that would not otherwise exist at room temperature.
Achieving Unmatched Hardness
The primary reason to quench a metal alloy is to make it significantly harder and more resistant to wear. This is essential for components like gears, bearings, cutting tools, and structural parts that must withstand high stress and abrasion.
The rapid cooling traps the atomic structure in a highly strained, hardened state. This process is what transforms a relatively soft piece of steel into a material capable of cutting other metals.
Transforming the Microstructure
When steel is heated, its internal crystal structure changes to a form called austenite. If cooled slowly, it reverts to softer structures.
Quenching cools the steel so rapidly that the atoms do not have time to rearrange into their softer forms. Instead, they are trapped in a hard, brittle, and highly stressed structure known as martensite. This martensitic transformation is the metallurgical basis for the hardening effect.
Key Advantages of Modern Quenching
Modern quenching, particularly in a vacuum environment, offers precise control that delivers significant benefits beyond simple hardening.
Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
This is the central advantage. A properly quenched component will have a much higher surface hardness and tensile strength than its non-treated counterpart, leading to a longer service life in demanding applications.
Excellent Surface Integrity
Using a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum furnace, prevents adverse reactions on the metal's surface. This results in no oxidation (scale) and no decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface layer, which would soften it). The finished part is bright, clean, and metallurgically sound from the core to the surface.
Process Cleanliness and Efficiency
Vacuum gas quenching uses inert gases like nitrogen or argon as the cooling medium. This process is exceptionally clean, leaving parts with a smooth surface that requires no subsequent cleaning, unlike parts quenched in oil or other liquids.
Understanding the Disadvantages and Risks
The immense benefits of quenching come with inherent risks that must be carefully managed. The faster the cooling, the greater the hardening effect, but also the greater the risk.
The Inevitable Trade-off: Increased Brittleness
The martensitic structure that makes steel hard also makes it very brittle. A fully hardened, un-tempered piece of steel can be as fragile as glass and may shatter if dropped or subjected to shock.
To counteract this, a secondary heat treatment called tempering is almost always performed after quenching. Tempering involves reheating the part to a lower temperature to relieve stress and restore a small amount of ductility, reducing brittleness to an acceptable level.
The Primary Challenge: Distortion and Warpage
Rapid cooling is never perfectly uniform. The surface of a part cools faster than its core, and thin sections cool faster than thick sections. This differential cooling creates immense internal stresses that can cause the part to distort, warp, or change dimensions.
The Catastrophic Risk: Quench Cracking
If the internal stresses caused by rapid cooling exceed the ultimate tensile strength of the material, the part will crack. This is a catastrophic failure, as the component is rendered useless. Complex geometries, sharp internal corners, and overly aggressive quench rates increase this risk significantly.
Choosing Your Quenching Medium: Oil vs. Gas
The choice of quenching medium (the substance used for cooling) is critical for balancing the hardening effect against the risk of distortion and cracking.
The Case for Oil Quenching: Speed
Oil cools a part much faster than gas. This more aggressive quench is effective for achieving maximum hardness in lower-alloy steels that require a high cooling rate to form martensite. However, this speed also increases the risk of distortion.
The Case for Gas Quenching: Precision
High-pressure gas quenching offers a more controlled, less severe cooling rate. This minimizes distortion and the risk of cracking, making it ideal for complex, high-precision parts or high-alloy steels that harden easily. While slower, it produces cleaner parts and offers superior dimensional stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right quenching strategy requires balancing the desired material properties with the geometric complexity of the part.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on simple, robust parts: An aggressive medium like oil quenching may be the most effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability on complex geometries: A controlled, less severe method like vacuum gas quenching is superior for minimizing distortion and cracking.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish with no post-processing: Vacuum gas quenching provides the cleanest result, eliminating the need for post-quench cleaning operations.
Ultimately, successful heat treatment is an exercise in controlled transformation, ensuring the final component has the ideal balance of strength and toughness for its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Superior Hardness & Wear Resistance | Increased Brittleness |
| Clean, Oxide-Free Surface (in Vacuum) | Risk of Distortion & Warping |
| High Tensile Strength | Risk of Quench Cracking |
| No Post-Cleaning Required (Gas Quenching) | Requires Secondary Tempering Process |
Achieve the perfect balance of hardness and toughness for your metal components.
Quenching is a delicate process where precision is paramount. The right equipment and expertise are critical to maximizing hardness gains while minimizing the risks of cracking and distortion.
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces and heat treatment solutions, including vacuum gas quenching systems. Our equipment provides the precise control needed for complex geometries and high-alloy steels, ensuring superior surface integrity and dimensional stability.
Let our experts help you optimize your heat treatment process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.



















