The best method for heat treating aluminum depends entirely on your goal. For strengthening specific heat-treatable alloys, the primary method is precipitation hardening. For softening aluminum to make it more formable, the correct process is annealing.
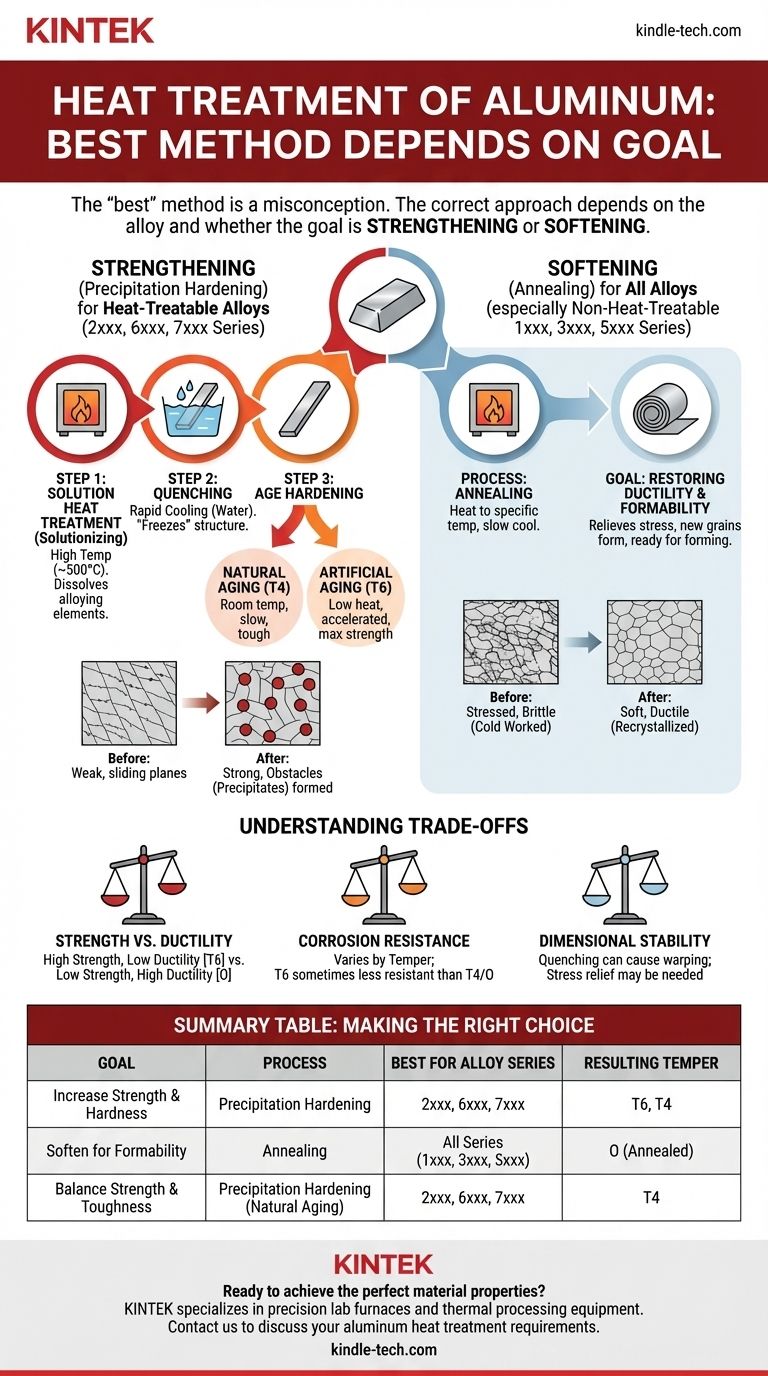
The concept of a single "best" heat treatment for aluminum is a misconception. The correct approach depends entirely on two factors: the specific alloy you are using and whether your goal is to increase its strength or to soften it for forming.
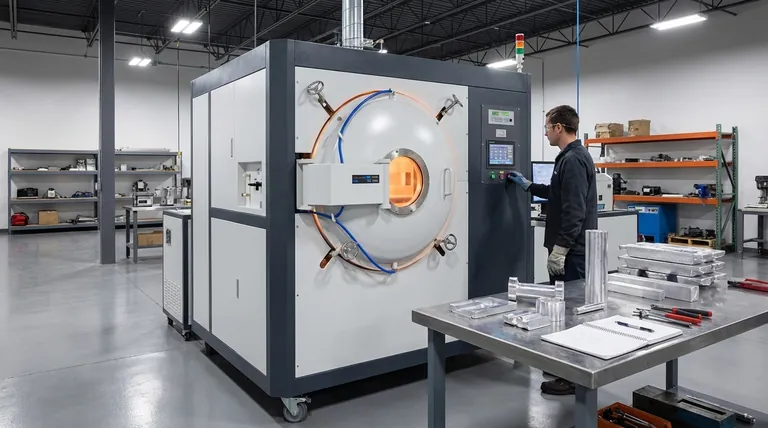

The Fundamental Divide: Heat-Treatable vs. Non-Heat-Treatable Alloys
Before choosing a process, you must first identify your material. Unlike steel, not all aluminum alloys respond to strengthening heat treatments.
Heat-Treatable Alloys
These alloys contain elements like copper, magnesium, silicon, and zinc that allow their strength to be dramatically increased. They are designated by the 2xxx, 6xxx, and 7xxx series.
Non-Heat-Treatable Alloys
These alloys achieve their strength through cold working (strain hardening). Heat treatment is only used to soften them (anneal). They are designated by the 1xxx, 3xxx, and 5xxx series.
The Core Process for Strengthening: Precipitation Hardening
Precipitation hardening is a three-step process designed to create microscopic, strength-giving particles within the metal's grain structure. It is the standard method for strengthening 2xxx, 6xxx, and 7xxx series alloys.
The Goal: Creating Microscopic Obstacles
Imagine the internal structure of the metal as a series of planes. Weakness occurs when these planes slide past each other easily. Precipitation hardening distributes tiny, hard particles throughout the structure that act as obstacles, preventing this slippage and making the material much stronger.
Step 1: Solution Heat Treatment (Solutionizing)
The aluminum is heated to a high temperature (around 500°C / 930°F) and held there. This dissolves the alloying elements into a solid solution, much like dissolving sugar in hot water. The goal is to create a uniform, homogenous structure.
Step 2: Quenching
Immediately after solutionizing, the material is rapidly cooled, typically in water. This "freezes" the dissolved alloying elements in place, creating a supersaturated solution, much like snap-freezing sugar water before the sugar crystals can form.
Step 3: Age Hardening (Precipitation)
This is the final step where the strength is developed. The trapped alloying elements begin to clump together to form those crucial, fine particles (precipitates).
- Natural Aging (T4 Temper): This occurs when the material is left at room temperature for several days. The precipitates form slowly, resulting in a moderately strong but very tough material.
- Artificial Aging (T6 Temper): This process is accelerated by heating the material to a low temperature (e.g., 120-190°C / 250-375°F) for several hours. This creates a higher density of precipitates, resulting in maximum hardness and strength.
The Core Process for Softening: Annealing
Annealing is used on all aluminum alloys, but for very different reasons. For non-heat-treatable alloys, it is the only thermal process used.
The Goal: Restoring Ductility and Formability
When aluminum is bent, rolled, or stamped (cold worked), its internal structure becomes stressed and brittle. Annealing relieves this stress and makes the metal soft and ductile again, ready for further forming.
How It Works: Recrystallization
The process involves heating the aluminum to a specific temperature and allowing it to cool slowly. This allows new, stress-free grains to form within the metal, effectively resetting its properties to a soft, workable state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment is an engineering decision that involves balancing competing properties.
Strength vs. Ductility
This is the primary trade-off. A fully hardened T6 temper aluminum is very strong but will crack if bent. An annealed ('O' temper) material is weak but can be easily formed into complex shapes.
Corrosion Resistance
The heat treatment state can affect how an alloy resists corrosion. In some environments, a T6 temper can be more susceptible to stress corrosion cracking than a T4 temper or an annealed state.
Dimensional Stability
The rapid cooling during quenching can introduce internal stresses into a part, potentially causing it to warp. Complex or high-precision parts may require subsequent stress-relieving steps.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines the process. Identify your desired outcome first, then select the appropriate method.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: Precipitation hardening to a T6 temper is the industry standard for heat-treatable alloys.
- If your primary focus is formability and ductility: Annealing ('O' temper) is the correct process to soften the material, making it easier to bend, stamp, or draw.
- If your primary focus is balancing strength with fracture toughness: Consider a T4 temper (natural aging), which often provides better toughness than a fully aged T6 temper.
Understanding these core processes empowers you to select a heat treatment that precisely engineers the material properties your project demands.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Process | Best For Alloy Series | Resulting Temper |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increase Strength & Hardness | Precipitation Hardening (Solution Treat + Quench + Aging) | 2xxx, 6xxx, 7xxx | T6 (Artificial Aged), T4 (Natural Aged) |
| Soften for Formability | Annealing | All Series (1xxx, 3xxx, 5xxx, etc.) | O (Annealed) |
| Balance Strength & Toughness | Precipitation Hardening (Natural Aging) | 2xxx, 6xxx, 7xxx | T4 (Naturally Aged) |
Ready to achieve the perfect material properties for your aluminum components?
The correct heat treatment is critical to your project's success. KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment, helping you execute perfect precipitation hardening or annealing cycles for your specific aluminum alloy.
We provide the reliable, consistent heat you need to develop maximum strength, improve formability, or optimize toughness. Let our expertise in laboratory heating solutions support your R&D and quality control.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your aluminum heat treatment requirements and find the ideal furnace for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















