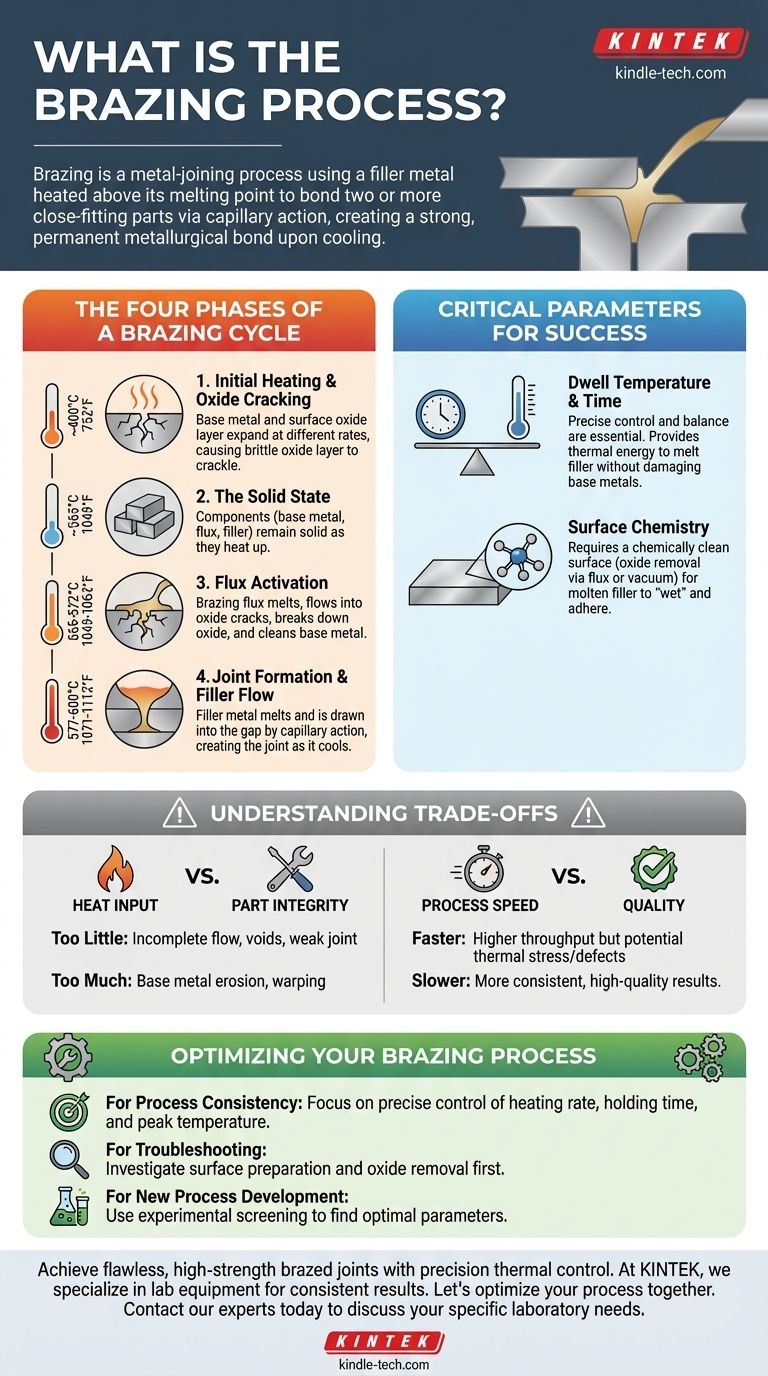
Brazing is a metal-joining process where a filler metal is heated above its melting point and distributed between two or more close-fitting parts by capillary action. The filler metal, which has a lower melting point than the base metals, melts and flows into the gap, creating a strong, permanent metallurgical bond upon cooling.
The success of any brazing operation hinges on the precise control and balance of its two most essential parameters: dwell temperature and time. Achieving the correct combination for your specific materials is the fundamental principle for creating a sound joint.
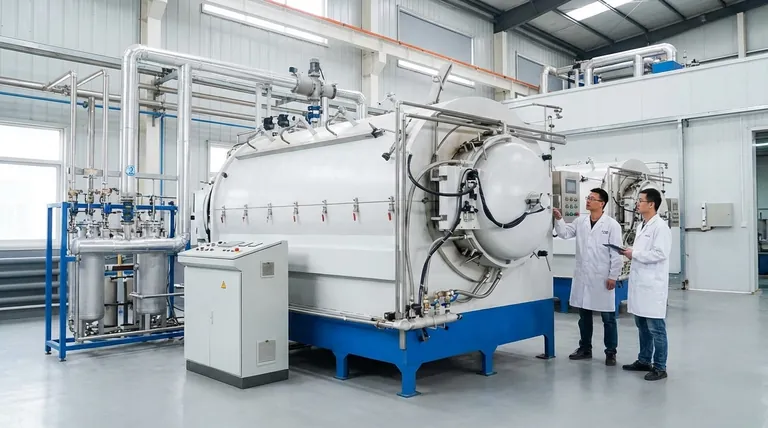

The Four Phases of a Brazing Cycle
For many common materials like aluminum, the brazing process follows a distinct, four-phase thermal cycle. Understanding each phase is key to controlling the outcome.
Phase 1: Initial Heating and Oxide Cracking
As the assembly is heated, it starts to expand. Around 400°C (752°F), the base metal and its surface oxide layer expand at different rates, causing the brittle oxide layer to crackle.
Phase 2: The Solid State
Below approximately 565°C (1049°F), all components of the assembly—the base metal, the flux, and the filler metal—remain in their solid forms. The parts are simply getting hotter.
Phase 3: Flux Activation
Between 565-572°C (1049-1062°F), the brazing flux melts. This liquid flux is chemically active and flows into the cracks in the oxide layer, breaking it down and cleaning the underlying base metal to prepare it for bonding.
Phase 4: Filler Metal Flow and Joint Formation
Once the temperature reaches 577-600°C (1071-1112°F), the filler metal melts. Because the surface has been cleaned by the flux, the molten filler metal is drawn into the gap between the parts by capillary action, creating the brazed joint as it solidifies during cooling.
The Critical Parameters for Success
While the thermal cycle provides the framework, several variables must be managed to ensure a high-quality joint.
The Core Relationship: Time and Temperature
These two parameters are inextricably linked. A process might call for a dwell time of more than 5 minutes at 577°C or a shorter cycle of 1 to 8 minutes at a higher temperature like 585°C. The goal is to provide enough thermal energy to melt the filler metal completely without damaging the base metals.
The Importance of Surface Chemistry
A successful braze is impossible without a chemically clean surface. The process relies on removing the surface oxide film, often with a chemical flux or by using a vacuum atmosphere, so the molten filler metal can "wet" and adhere to the base metals.
Material and Design Considerations
The specific type of metal alloy, the shape and size of the parts, and the required quality of the final joint all influence the ideal process parameters. A large, thick part will require a different heating rate and holding time than a small, thin one.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a brazing process involves balancing competing factors to minimize defects and maximize strength.
Heat Input vs. Part Integrity
The primary trade-off is between applying enough heat for a sufficient time versus causing damage to the base metals.
Too little heat or time results in an incomplete flow of the filler metal, leading to voids and a weak joint.
Too much heat or time can cause the base metal to erode or warp. However, in some cases, longer dwell times at the highest allowed temperatures can improve filler flow and ultimately reduce the amount of scrap.
Process Speed vs. Quality
Faster heating rates and shorter cycle times increase throughput but can also introduce thermal stress or incomplete joint formation if not carefully controlled. Slower, more controlled cycles often yield more consistent, high-quality results.
Optimizing Your Brazing Process
Because so many factors are at play, the ideal parameters for one application will not be a perfect fit for another. The best approach is to establish a baseline and refine it through careful testing.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: Concentrate on precisely controlling the heating rate, holding time, and peak temperature within a very narrow window.
- If you are troubleshooting failed joints: Always investigate surface preparation first; improper cleaning and oxide removal are the most common causes of failure.
- If you are developing a new process: Use experimental screening to determine the optimal combination of parameters for your specific alloys, part geometry, and furnace capabilities.
Ultimately, mastering the brazing process is about understanding and controlling these fundamental principles to create strong, reliable, and repeatable joints.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Phase | Key Temperature Range | Primary Action |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Initial Heating | ~400°C (752°F) | Base metal expands, causing oxide layer to crack. |
| Phase 2: Solid State | Below ~565°C (1049°F) | Components heat up but remain solid. |
| Phase 3: Flux Activation | 565-572°C (1049-1062°F) | Flux melts, cleans the base metal surface. |
| Phase 4: Joint Formation | 577-600°C (1071-1112°F) | Filler metal melts, flows via capillary action to form the bond. |
Achieve flawless, high-strength brazed joints with precision thermal control.
The success of your brazing operation depends on the precise balance of dwell temperature and time. At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables that laboratories rely on for consistent, high-quality results. Whether you are developing a new process or troubleshooting joint failures, our expertise can help you optimize your parameters for maximum strength and minimal scrap.
Let's optimize your brazing process together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a high-temperature reaction furnace in the thermal decomposition of nickel precursors?
- What is the benefits of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Quality and Process Control
- What are the benefits of tempering? Achieve the Perfect Balance of Hardness and Toughness
- What are the two types of quenching? Master Gas vs. Liquid for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does a heat treatment furnace work? Master Precise Thermal Cycles for Superior Material Properties
- What role does a vacuum resistance furnace play in the diffusion chromizing of steel? Achieve 2.8mm Deep Bonding
- What is aluminum vacuum brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, Flux-Free Aluminum Joining
- How does a vacuum drying oven contribute to the preparation of LNMO battery electrodes? Achieve Optimal Stability



















