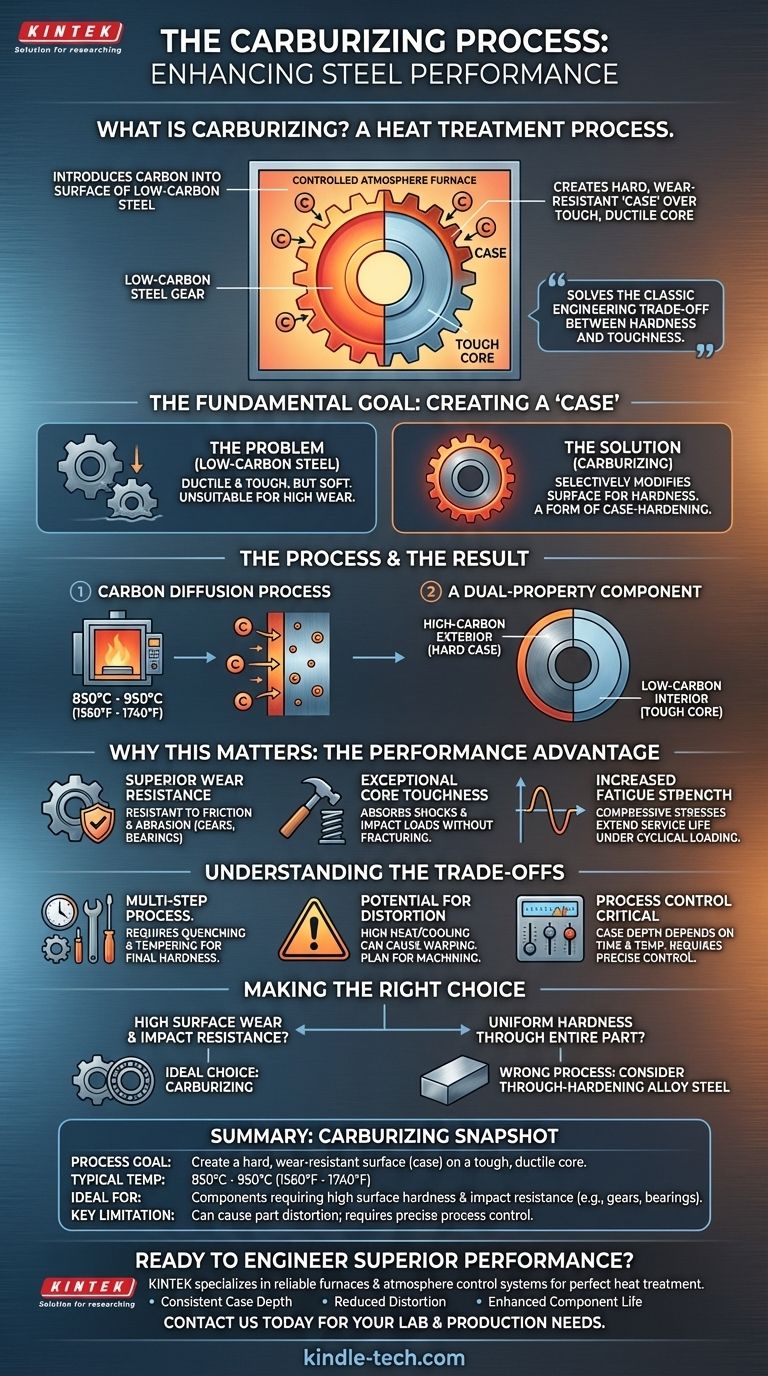
Carburizing is a heat treatment process that introduces carbon into the surface of low-carbon steel. By heating the metal in a carbon-rich environment, it creates an external layer, or "case," that is significantly harder and more wear-resistant than the material's tough, ductile interior core.
Carburizing is not simply about making steel harder; it's about creating a composite material from a single part. It solves the classic engineering trade-off between hardness and toughness by giving you a wear-resistant surface while preserving a shock-absorbent, fracture-resistant core.

The Fundamental Goal: Creating a 'Case'
The primary objective of carburizing is to selectively modify the steel's properties, creating a hard, durable surface layer known as a case over a softer core. This is a form of case-hardening.
The Problem with Low-Carbon Steel
Low-carbon steels are valued for their ductility, toughness, and low cost. However, their inherent softness makes them unsuitable for applications involving high surface wear or friction.
The Carbon Diffusion Process
Carburizing solves this by heating the low-carbon steel part to a high temperature, typically between 850°C and 950°C (1560°F to 1740°F), while it is in contact with a carbon-rich material. At this temperature, carbon atoms from the surrounding environment diffuse into the steel's surface layer.
The Result: A Dual-Property Component
The process does not change the low-carbon core. It only enriches the surface, creating a part with a high-carbon steel exterior and a low-carbon steel interior, combining the most desirable qualities of both.
Why This Matters: The Performance Advantage
This dual-property structure delivers significant performance benefits that are impossible to achieve with a uniform, or "through-hardened," material.
Superior Wear and Abrasion Resistance
The high-carbon case can be quenched to achieve very high hardness levels. This makes carburized components, like gears and bearings, exceptionally resistant to friction and abrasive wear.
Exceptional Core Toughness
While the surface is hard and brittle, the low-carbon core remains tough and ductile. This allows the component to absorb sudden shocks and impact loads without fracturing, a common failure mode for parts that are hard all the way through.
Increased Fatigue Strength
The hardening of the case creates compressive residual stresses on the surface. These stresses help counteract tensile forces that lead to the initiation of fatigue cracks, significantly extending the component's service life under cyclical loading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Carburizing is a powerful process, but it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
A Multi-Step Process
Carburizing only adds carbon; it does not inherently make the part hard. The component must undergo a subsequent quenching (rapid cooling) and tempering cycle to develop the final hardness of the case and refine the properties of the core.
Potential for Distortion
The high temperatures and rapid cooling involved can cause the part to warp or change dimensions. Projects requiring tight tolerances often need to account for final grinding or machining operations after heat treatment.
Process Control is Critical
The depth of the carbon case is a direct function of time and temperature. Achieving a consistent and correct case depth requires precise control over the furnace atmosphere and cycle parameters, making it a more complex process than simple hardening.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use the component's final performance requirements to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is high surface wear combined with impact resistance: Carburizing is an ideal choice for parts like gears, camshafts, and bearings that must endure friction while absorbing shock.
- If your component requires uniform hardness through its entire cross-section: Carburizing is the wrong process; consider using a higher-carbon, through-hardening alloy steel instead.
- If your design prioritizes dimensional stability above all: Be aware that carburizing and quenching can cause distortion, and plan for post-treatment finishing or explore alternative surface treatments like nitriding.
Ultimately, selecting carburizing is a strategic decision to engineer a component with two distinct, high-performance personalities in a single piece of steel.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Create a hard, wear-resistant surface (case) on a tough, ductile core. |
| Typical Temperature | 850°C - 950°C (1560°F - 1740°F) |
| Ideal For | Components requiring high surface hardness & impact resistance (e.g., gears, bearings). |
| Key Limitation | Can cause part distortion; requires precise process control. |
Ready to engineer superior performance into your components?
The carburizing process is a precise science that demands the right equipment for consistent, high-quality results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable furnaces and atmosphere control systems you need to perfect your heat treatment processes.
Let us help you achieve:
- Consistent Case Depth: Precise temperature and atmosphere control for uniform results.
- Reduced Distortion: Equipment designed for optimal thermal management.
- Enhanced Component Life: Produce parts with exceptional wear resistance and fatigue strength.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory and production needs. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















