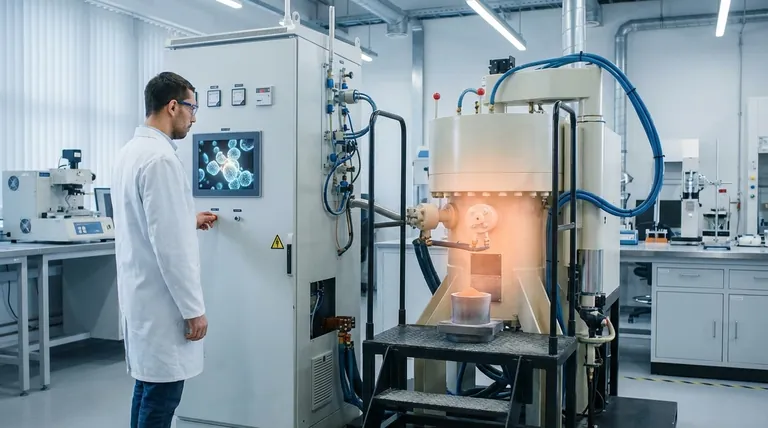
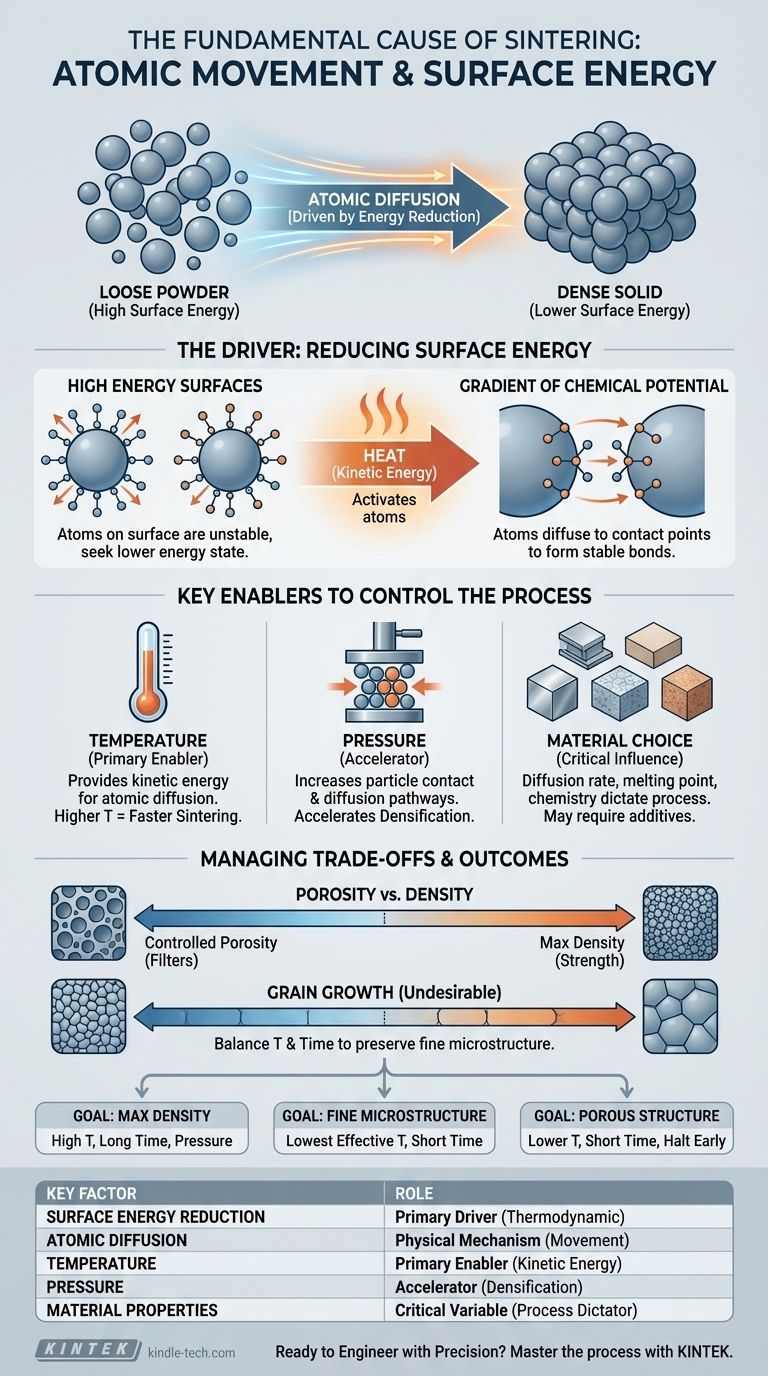
At its core, sintering is a process of atomic movement. It is the method by which a collection of individual particles, like a powder, is transformed into a solid, dense mass using heat, but without melting the material. The fundamental cause is the diffusion of atoms, which are driven to move from areas of high energy to areas of low energy.
The true cause of sintering is a thermodynamic drive to reduce the total surface energy of a system. Individual particles have a vast amount of high-energy surface area, and atoms will spontaneously move and bond together to create a more stable, lower-energy solid structure.

The Fundamental Driver: Reducing Surface Energy
Sintering happens because it is a more stable energetic state for the material. A loose powder is inherently unstable, and the system will naturally seek a lower energy configuration, which is a dense solid.
The High Energy of Surfaces
Every surface of a particle represents a high-energy state. Atoms at the surface have fewer neighbors to bond with compared to atoms in the bulk of the material, making them less stable. A fine powder has an enormous collective surface area, resulting in a large amount of excess surface energy.
The Gradient of Chemical Potential
This excess surface energy creates a gradient of chemical potential. Think of this as a form of pressure at the atomic level. Atoms on the particle surfaces (an area of high chemical potential) are "uncomfortable" and are driven to move to a location with lower chemical potential, such as the contact point between two particles.
Diffusion as the Mechanism for Change
Diffusion is the physical mechanism that allows this change to happen. Heat provides the necessary kinetic energy for atoms to become mobile. Once energized, atoms can move from the particle surfaces and diffuse into the "necks" forming between adjacent particles, creating solid bonds and reducing the overall surface area.
Key Factors That Enable Sintering
While the reduction of surface energy is the "why," several external factors are used to control the "how" and "how fast" of the process. These are the levers we can pull to manage the outcome.
The Role of Temperature
Heat is the primary enabler of sintering. It does not cause sintering on its own, but it provides the thermal energy required for atomic diffusion to occur at a practical rate. Higher temperatures lead to faster diffusion and, consequently, a faster and more complete sintering process.
The Impact of Pressure
Applying external pressure can significantly accelerate densification. Pressure forces particles into closer contact, which increases the number of diffusion pathways and can help overcome barriers to atomic movement. Techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) use pressure in combination with heat to achieve rapid densification.
The Influence of Material Choice
The material itself is a critical factor. The rate of diffusion, melting point, and chemical properties dictate how easily a material will sinter. Some materials require specific atmospheric conditions or the use of additives (sintering aids) to promote effective bonding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Controlling the sintering process is a balancing act. Optimizing for one property often means compromising on another.
Porosity vs. Density
The most fundamental trade-off is between porosity and density. As sintering proceeds, pores between particles are eliminated, and the material's density increases. If your goal is a fully dense, strong part, you aim to eliminate all porosity. However, for applications like filters, a certain level of controlled porosity is the desired outcome.
Grain Growth
A common and often undesirable side effect of sintering is grain growth. As atoms move to densify the material, the individual crystalline grains can merge and grow larger. This can negatively impact mechanical properties, such as making the material more brittle. Managing grain growth often involves using the lowest possible temperature and time.
How to Control the Sintering Outcome
Your approach to sintering must be guided by the desired properties of the final component. By understanding the core cause, you can manipulate the process variables to achieve your goal.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density: Utilize higher temperatures, longer sintering times, or advanced methods like pressure-assisted sintering to drive the process toward the complete elimination of pores.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine microstructure: Employ the lowest effective temperature and shortest time possible to achieve the necessary bonding without allowing significant grain growth.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous structure: Deliberately halt the sintering process early by using lower temperatures or shorter durations, allowing necks to form between particles without achieving full densification.
Ultimately, viewing sintering as a controlled, diffusion-driven process gives you the power to manipulate time, temperature, and pressure to engineer materials with precision.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in the Sintering Process |
|---|---|
| Surface Energy Reduction | The primary driver; atoms move to create a more stable, lower-energy solid structure. |
| Atomic Diffusion | The physical mechanism; heat provides energy for atoms to move and form bonds. |
| Temperature | The primary enabler; increases atomic mobility and accelerates the diffusion rate. |
| Pressure | An accelerator; forces particles into closer contact to enhance densification. |
| Material Properties | A critical variable; dictates diffusion rate and the need for specific conditions or aids. |
Ready to Engineer Your Materials with Precision?
Understanding the cause of sintering is the first step to mastering it. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to control time, temperature, and pressure for perfect results—whether your goal is maximum density, a fine microstructure, or controlled porosity.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the ideal sintering solution for your laboratory's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular RTP Heating Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity and Performance
- What is the pressure for vacuum sintering? Achieve Optimal Material Purity and Density
- What is a sintering furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature Materials Processing
- What temperature does tungsten carbide sinter at? Master the 1350°C-1500°C Liquid-Phase Sintering Process
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance



















