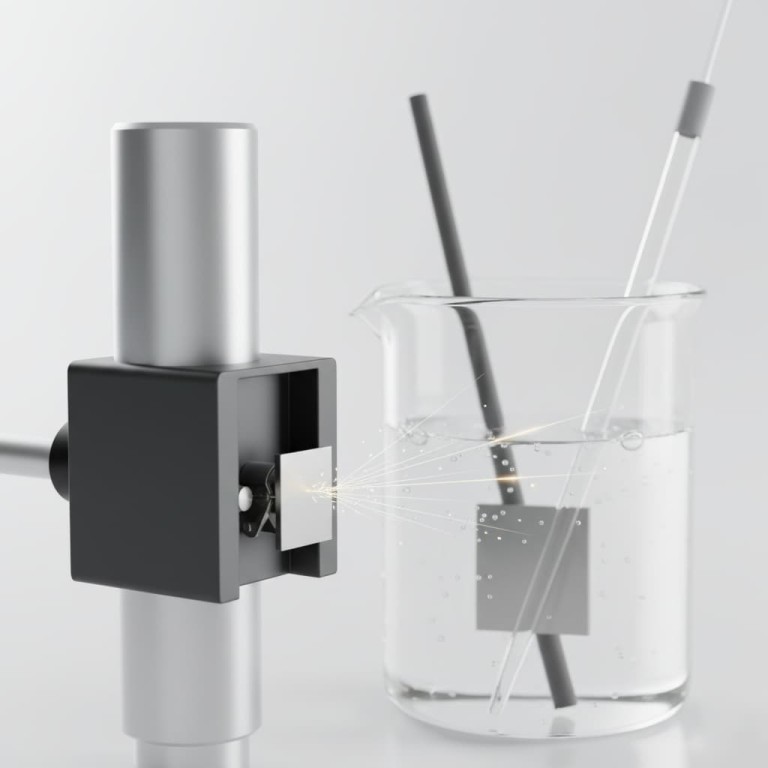
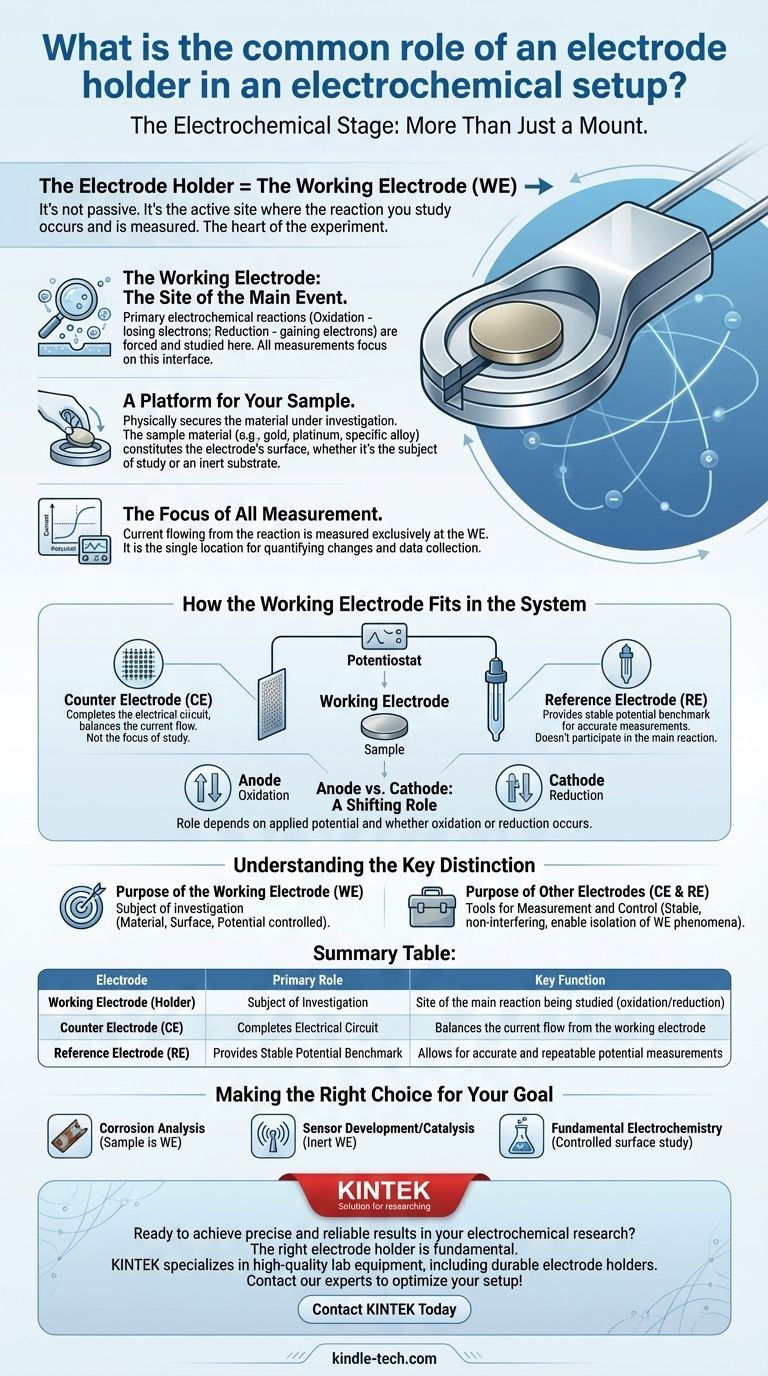
In an electrochemical setup, an electrode holder's primary and most common role is to function as the working electrode (WE). This is not a passive component; it is the active, central stage of the experiment. The holder secures the material sample being tested and serves as the precise location where the electrochemical reactions of interest occur and are measured.
The electrode holder is far more than a simple mount. It is the working electrode—the specific site where the reaction you are studying takes place, making it the most critical component for data collection in your electrochemical cell.

The Working Electrode: The Heart of the Experiment
To understand the role of the holder, you must first understand the function of the working electrode it embodies. In any electrochemical experiment, the goal is to observe a specific reaction, and that observation happens exclusively at the WE.
The Site of the Main Event
The working electrode is the surface where the primary electrochemical reaction—either oxidation (losing electrons) or reduction (gaining electrons)—is forced to happen and is carefully studied.
All the instruments, measurements, and analysis are focused on the current and potential changes occurring at this single interface.
A Platform for Your Sample
The "holder" physically secures the material under investigation. This material, often a metal disk like gold, platinum, or a specific alloy, constitutes the surface of the working electrode.
The choice of material is not arbitrary; it is either the very subject of the study (e.g., studying the corrosion of a steel sample) or an inert substrate for studying another chemical species.
The Focus of All Measurement
The data you collect from your experiment—the current that flows as a result of a reaction—is measured at the working electrode. Its role is analogous to a weight-loss coupon in traditional corrosion testing, where all changes are quantified at a specific location.
How the Working Electrode Fits in the System
The working electrode does not operate in isolation. Its function is only meaningful in the context of a complete electrochemical cell, which typically includes two other key electrodes.
The Role of the Counter Electrode (CE)
The counter electrode (often made of a material like graphite or platinum) exists to complete the electrical circuit. It allows current to flow by balancing the reaction happening at the working electrode.
Critically, the reactions at the counter electrode are not the focus of the study. Its job is simply to ensure the experiment can run without limiting the reaction at the WE.
The Importance of the Reference Electrode (RE)
The reference electrode provides a stable, constant electrochemical potential. All potential measurements of the working electrode are made relative to this stable benchmark.
Without a reference electrode, you could not know the true potential at which your reaction is occurring, making your results unreliable and non-repeatable.
Anode vs. Cathode: A Shifting Role
Depending on the experiment, the working electrode can act as either the anode or the cathode.
If oxidation is occurring at the WE, it is the anode. If reduction is occurring, it is the cathode. This role is not fixed and is determined by the potential you apply to it.
Understanding the Key Distinction
It is crucial to differentiate the roles to avoid invalidating your experimental results. The core distinction is one of purpose.
The Purpose of the Working Electrode
The WE is the subject of investigation. Its material, surface area, and the potential applied to it are all carefully controlled variables.
The Purpose of Other Electrodes
The counter and reference electrodes are tools for measurement and control. They are designed to be as stable and non-interfering as possible, enabling you to isolate and observe the phenomena happening only at the working electrode.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The identity and setup of your working electrode are dictated entirely by your experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is corrosion analysis: Your sample material (e.g., a piece of metal) is the working electrode, allowing you to measure its rate of degradation.
- If your primary focus is sensor development or catalysis: You will likely use an inert working electrode (like gold or platinum) as a stable substrate to study reactions happening on its surface.
- If your primary focus is fundamental electrochemistry: The working electrode is the controlled surface where you will study a specific oxidation or reduction phenomenon under precise conditions.
Ultimately, understanding that the holder functions as the working electrode is the key to designing and interpreting any meaningful electrochemical experiment.
Summary Table:
| Electrode | Primary Role | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Working Electrode (Holder) | Subject of Investigation | Site of the main reaction being studied (oxidation/reduction) |
| Counter Electrode (CE) | Completes Electrical Circuit | Balances the current flow from the working electrode |
| Reference Electrode (RE) | Provides Stable Potential Benchmark | Allows for accurate and repeatable potential measurements |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable results in your electrochemical research? The right electrode holder is fundamental to your success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable electrode holders designed for stability and accurate performance. Let our experts help you select the perfect components for your specific application, from corrosion analysis to sensor development. Contact our team today to optimize your electrochemical setup!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a flat electrochemical cell for corrosion? Achieve Precise Pitting & Crevice Analysis
- What is the volume range of the coating evaluation electrolytic cell? A Guide to Choosing the Right Size
- How does an electrochemical cell system ensure measurement precision during DL-EPR? | Expert Testing Guide
- How does a three-electrode electrolytic cell function? Precision Testing for 8620 Steel in Corrosive Environments
- How is a three-electrode electrochemical electrolytic cell utilized to evaluate Zr-Nb alloy corrosion resistance?















