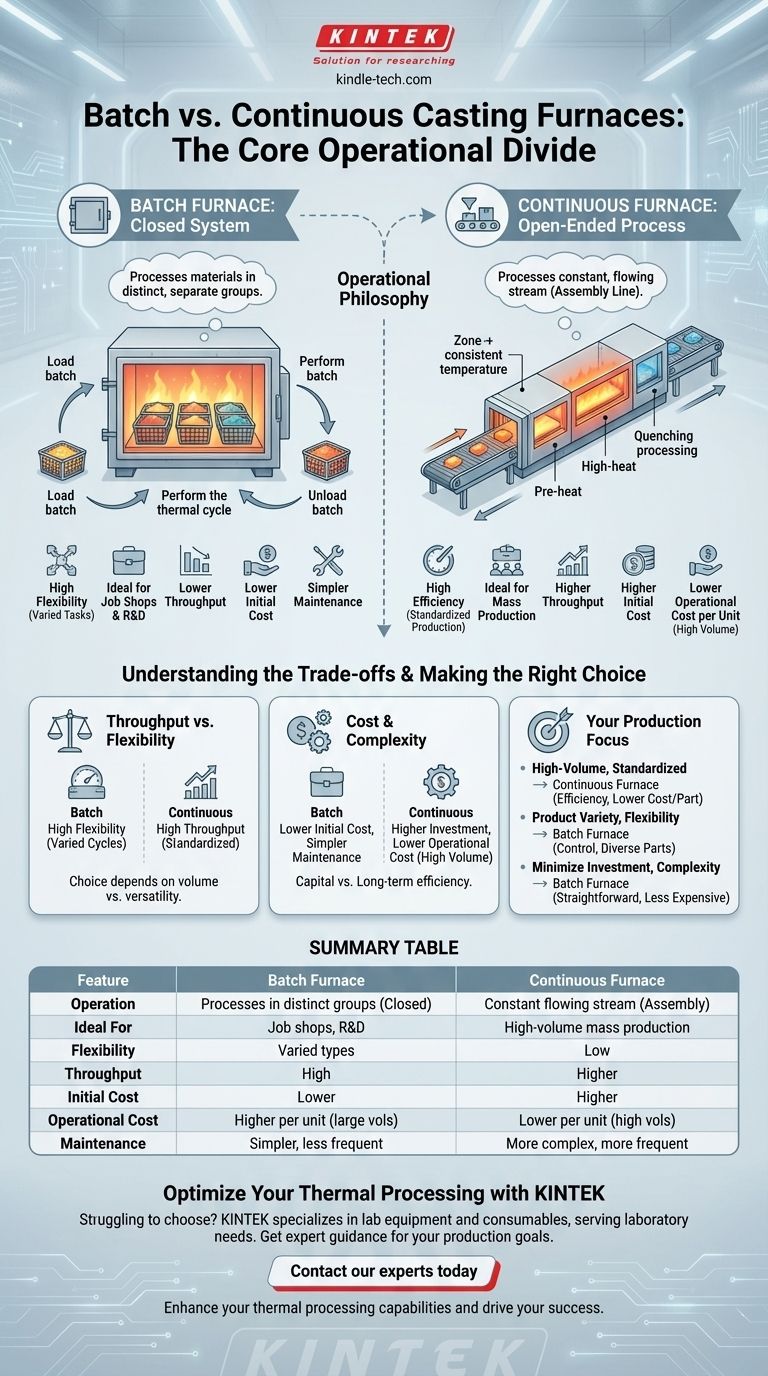
In industrial thermal processing, the core difference is one of operational philosophy. A batch furnace is a closed system that processes materials in distinct, separate groups, while a continuous furnace operates like an assembly line, processing a constant, flowing stream of material from an entry point to an exit. This fundamental distinction dictates their suitability for different production environments.
The choice between a batch and continuous furnace is not about which is superior, but which model aligns with your production goal. Batch furnaces offer flexibility for varied tasks, while continuous furnaces provide efficiency for high-volume, standardized production.

The Core Operational Divide
To understand which furnace is right for a specific application, we must first examine how each one fundamentally operates. Their designs are direct reflections of two different approaches to manufacturing.
The Batch Furnace: A Closed System
A batch furnace functions as a self-contained, closed-process machine. Materials are loaded into the furnace, often using fixtures like baskets or racks.
The entire system is then sealed, and the thermal cycle (heating, soaking, cooling) is performed on the entire group of materials at once. Once the process is complete, the furnace is opened, and the finished batch is unloaded.
This single-chamber approach makes batch furnaces ideal for processes requiring highly controlled environments, such as those needing an inert atmosphere or meeting cleanroom standards.
The Continuous Furnace: An Open-Ended Process
A continuous furnace is a straight-through system designed for uninterrupted production. Materials are loaded at one end and travel through various zones at a constant speed.
These furnaces consist of multiple modules, such as pre-heating, high-heat, and quenching chambers. The central heating chamber typically remains at a constant temperature and, in some designs, under a constant vacuum.
This design eliminates the need to heat and cool the furnace chamber for each load, resulting in high productivity and energy efficiency for consistent, large-scale operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The operational differences lead to significant trade-offs in cost, flexibility, and complexity. Choosing the wrong type can lead to major inefficiencies in your production line.
Throughput vs. Flexibility
The most critical trade-off is between volume and versatility. Continuous furnaces are built for high throughput of a single, standardized product. They are the backbone of mass production for processes like annealing or hardening.
Batch furnaces, conversely, offer superior flexibility. Since each cycle is independent, operators can easily change the temperature, atmosphere, or duration for different products. This makes them ideal for job shops, research and development, or producing a wide variety of parts.
The Cost Equation: Initial vs. Operational
Initial investment and long-term operating costs differ significantly. Batch furnaces are less complex in design, making them less expensive to purchase and install. Their simpler mechanics also lead to easier and less frequent maintenance.
Continuous furnaces represent a much larger capital investment due to their size and complexity. However, by maintaining a constant temperature and processing materials nonstop, they often achieve a lower energy cost per unit produced, making them more economical for high-volume manufacturing.
Complexity and Handling
A continuous furnace is a more complex piece of machinery, requiring more sophisticated control systems and more frequent maintenance to keep the line running smoothly. However, it often reduces the need for manual handling, as parts move through automatically.
A batch furnace is simpler to operate and maintain but requires more work-in-process organization. Materials must be grouped and loaded onto fixtures, and more labor is involved in loading and unloading each distinct batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision must be driven by your specific production strategy and operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace offers unparalleled efficiency and a lower cost per part once operational.
- If your primary focus is product variety and process flexibility: A batch furnace provides the control to run different thermal cycles for diverse parts without major setup changes.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment and maintenance complexity: A batch furnace is the more straightforward and less expensive option to acquire and maintain.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the equipment's inherent operational philosophy to the demands of your specific process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Processes materials in distinct, separate groups (closed system) | Processes a constant, flowing stream of material (assembly line) |
| Ideal For | Job shops, R&D, varied product types | High-volume, standardized mass production |
| Flexibility | High (easy to change cycles for different products) | Low (optimized for a single process) |
| Throughput | Lower | Higher |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Operational Cost | Higher per unit for large volumes | Lower cost per unit for high volumes |
| Maintenance | Simpler, less frequent | More complex, more frequent |
Optimize Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Struggling to choose between a batch or continuous furnace for your laboratory or production line? The right equipment is critical for efficiency, cost control, and product quality.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide expert guidance to help you select the perfect furnace solution that aligns with your production goals, whether you prioritize high-volume throughput or flexible, multi-purpose processing.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation. Let us help you enhance your thermal processing capabilities and drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity



















