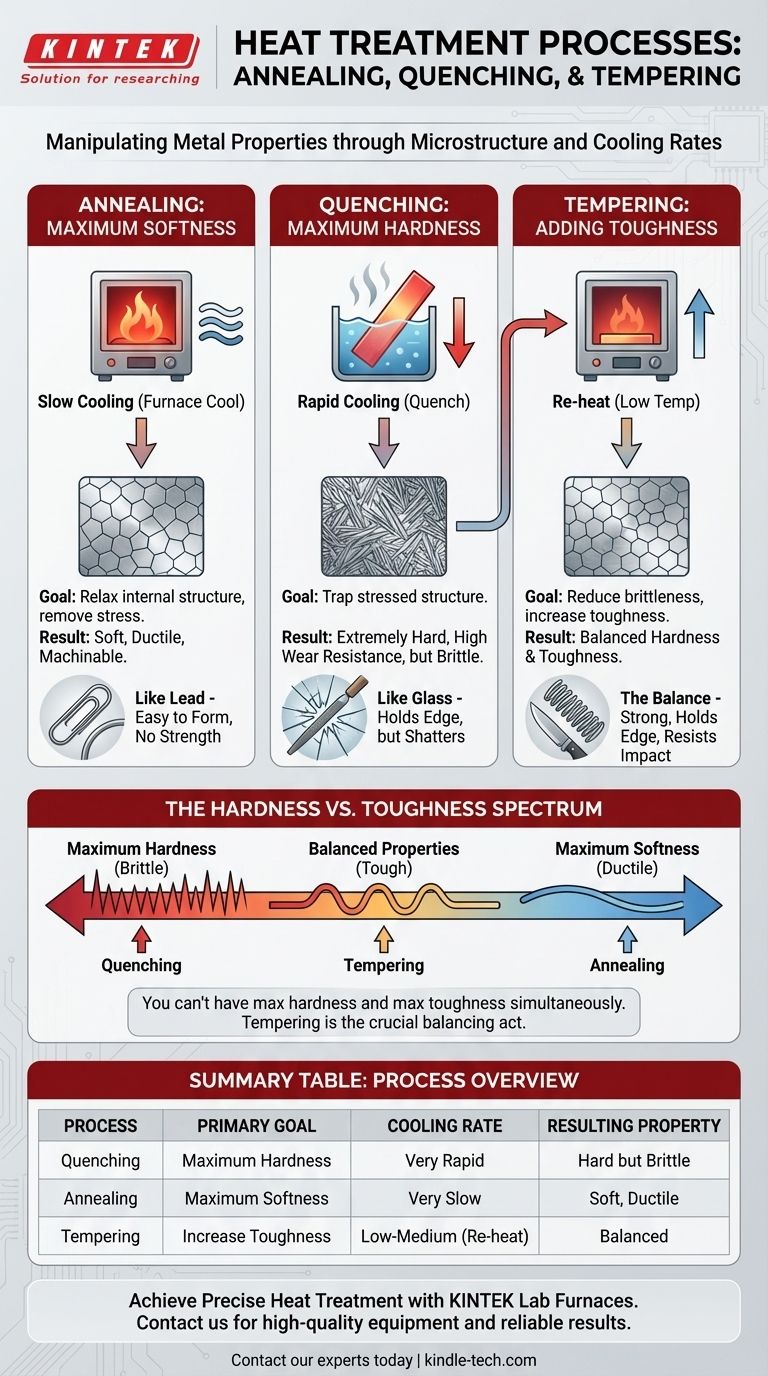
In short, these are three distinct heat treatment processes used to manipulate a metal's physical properties. Quenching rapidly cools metal to make it extremely hard and brittle. Annealing uses a very slow cooling process to make metal as soft and workable as possible. Tempering is a secondary, lower-temperature heating process performed after quenching to reduce brittleness and increase toughness.
The core difference isn't just the process, but the goal. Annealing and quenching represent opposite ends of the hardness spectrum, while tempering is the critical balancing act used to achieve a useful combination of hardness and toughness in a finished part.

The Goal: Controlling a Metal's Microstructure
To understand these processes, you must first understand that you are not just heating and cooling metal—you are fundamentally rearranging its internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure.
What is Microstructure?
Think of a metal's internal structure as being made of different types of building blocks (crystals). The size, shape, and type of these blocks determine the metal's properties.
Processes like quenching and annealing are designed to control which of these blocks form. For steel, this means controlling structures like hard martensite or soft ferrite.
The Role of Temperature and Cooling Rate
The two main levers we can pull are the peak temperature the metal is heated to and, most importantly, the rate at which it cools.
A change in cooling speed can be the difference between a part that is soft enough to bend by hand and one that is hard enough to cut glass.
A Detailed Breakdown of Each Process
While often discussed together, these three processes achieve vastly different outcomes and are used at different stages of manufacturing.
Quenching: For Maximum Hardness
Quenching involves heating a metal (like steel) to a high temperature and then cooling it with extreme rapidity. This is typically done by plunging the hot metal into a liquid like water, oil, or brine.
This rapid cooling traps the metal's crystal structure in a highly stressed, disorganized state called martensite. This structure is incredibly hard but also very brittle.
The primary purpose of quenching is to create a part with high wear resistance and the ability to hold a sharp edge.
Annealing: For Maximum Softness and Machinability
Annealing is the opposite of quenching. The metal is heated to a similar high temperature, but it is then cooled as slowly as possible, often by leaving it inside the insulated furnace to cool overnight.
This slow cooling gives the crystal structure time to form in the most relaxed, orderly, and low-energy state possible. This results in a metal that is very soft, ductile, and free of internal stresses.
The purpose of annealing is to make a metal easy to work with. It's done to make machining, forming, or stamping easier, or to "reset" a piece of metal that has become work-hardened.
Tempering: For Adding Toughness to Hardened Steel
Tempering is a secondary process that is only performed after a part has been quenched. A fully quenched part is often too brittle for practical use and would shatter under impact.
The quenched part is re-heated to a much lower temperature (e.g., 200-600°C or 400-1100°F) and held for a specific time before being cooled.
This process trades a small amount of the extreme hardness gained during quenching for a significant increase in toughness (the ability to resist fracture and impact). The final hardness is precisely controlled by the tempering temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Hardness vs. Toughness Spectrum
You can't have maximum hardness and maximum toughness at the same time. Every heat treatment is a choice along this spectrum.
The Brittleness of Quenched Steel
A part that is only quenched is like glass. It can be incredibly hard and scratch-resistant, but it will shatter if dropped or struck. A file is a good example; it's very hard but will snap if you try to bend it.
The Softness of Annealed Steel
An annealed part is like lead. It is extremely easy to bend and form, but it has no strength, cannot hold an edge, and will not resist wear. A simple paperclip is essentially in an annealed state.
Tempering as the Balancing Act
Tempering is how you make a hardened part useful. It allows you to dial in the exact properties needed for the job. A knife blade is quenched and then tempered to be hard enough to hold an edge but tough enough not to chip. A spring is tempered at a higher temperature to be less hard but much tougher and more flexible.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Goal
The process you choose depends entirely on the intended function of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness for wear or cutting: You will quench the part, followed by a low-temperature temper to relieve the worst of the brittleness.
- If your primary focus is toughness and impact resistance: You will quench the part, followed by a higher-temperature temper to sacrifice more hardness for a significant gain in toughness.
- If your primary focus is machinability or formability: You will fully anneal the raw material before you begin cutting or shaping it.
- If your primary focus is simply to relieve internal stress from welding or heavy machining: You will use a specific sub-category of annealing known as stress relieving, which uses lower temperatures.
Mastering these processes is the key to unlocking the full potential of a metal for any given application.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Heating Temperature | Cooling Rate | Resulting Property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching | Maximum Hardness | High | Very Rapid (e.g., water/oil) | Hard but Brittle |
| Annealing | Maximum Softness/Machinability | High | Very Slow (furnace cool) | Soft, Ductile, Stress-Free |
| Tempering | Increase Toughness (after Quenching) | Low to Medium | Any Rate | Balanced Hardness & Toughness |
Ready to achieve the perfect balance of hardness and toughness in your metal parts? The right lab furnace is critical for precise heat treatment processes like annealing, tempering, and quenching. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment, providing the precise temperature control and uniform heating your laboratory needs for reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal furnace for your heat treatment requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace and its uses? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What energy transfer happens in a furnace? Master Convection, Conduction & Radiation for Your Process
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis
- What are muffle furnaces used for? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace used to measure? Unlock Precise Sample Analysis with High-Temp Heating



















