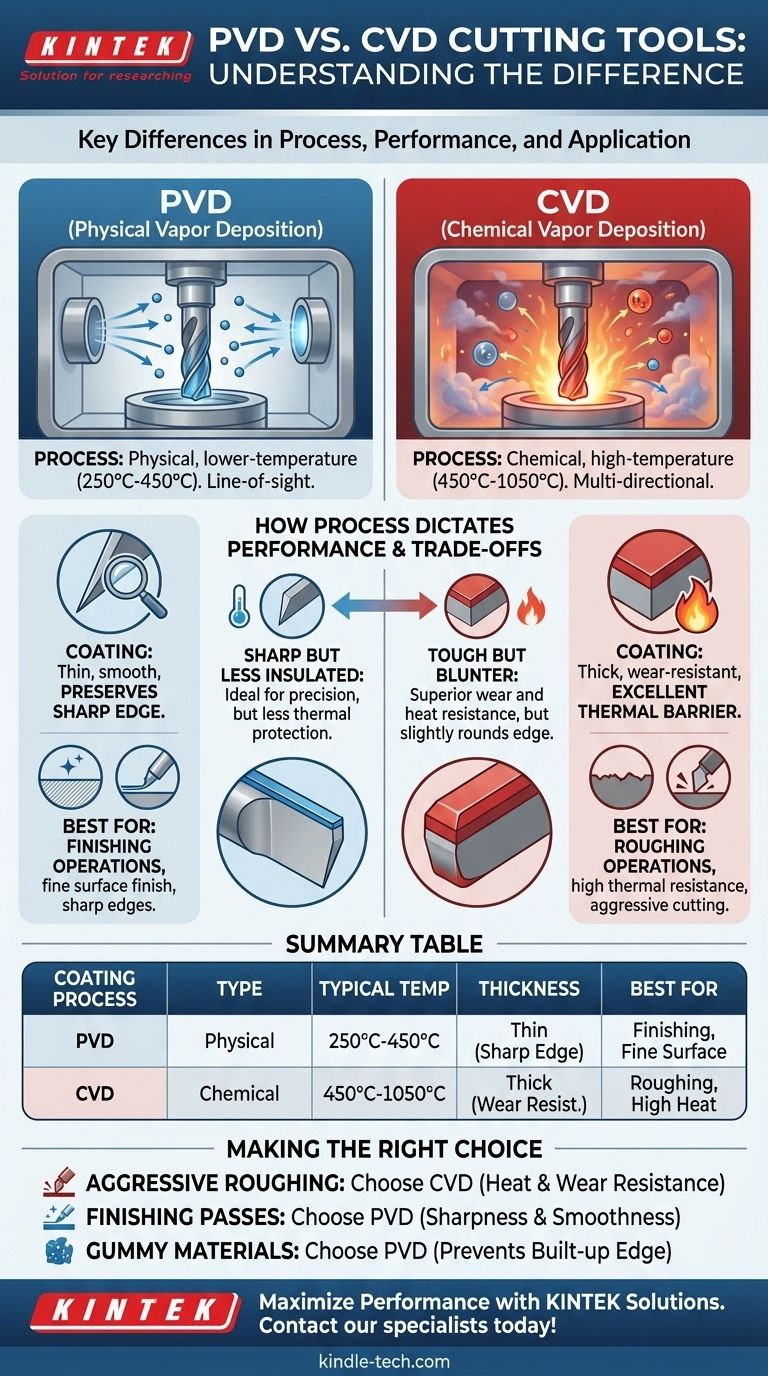
The fundamental difference between PVD and CVD coatings lies in their application process. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a lower-temperature physical process that deposits a thin, smooth coating, preserving a sharp cutting edge. In contrast, CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) is a high-temperature chemical process that creates a thicker, more wear-resistant coating that excels as a thermal barrier.
Your choice of tool coating is not about which process is universally superior, but which one is precisely suited to the task at hand. Use PVD for the precision of finishing passes and CVD for the raw durability required in roughing.

The Fundamental Process Distinction
The names "Physical Vapor Deposition" and "Chemical Vapor Deposition" directly describe their core difference. One relies on physical mechanics, the other on chemical reactions, and this dictates every characteristic of the final coating.
How PVD Works (Physical Deposition)
PVD is a line-of-sight process that typically operates at lower temperatures, between 250°C and 450°C.
In this method, a solid coating material is physically vaporized into atoms in a vacuum. These atoms then travel in a straight line and deposit onto the cutting tool's surface, forming a thin, dense layer. Think of it as an atomic-level spray-painting process.
How CVD Works (Chemical Deposition)
CVD is a multi-directional process that requires significantly higher temperatures, often from 450°C up to 1050°C.
Here, various gases are introduced into a reaction chamber. These gases react with each other and the surface of the tool, forming a solid coating that "grows" on the substrate. This chemical reaction allows the coating to form uniformly over the entire tool, not just the parts in a direct line of sight.
How Process Dictates Performance
The differences in temperature, thickness, and deposition method directly translate to how a coated tool will perform in a specific machining application.
Coating Thickness and Edge Sharpness
PVD creates a thinner coating. This is a significant advantage because it allows the original, sharp, ground edge of the carbide insert to be maintained.
A sharper edge results in lower cutting forces, a cleaner cut, and a better surface finish, making PVD ideal for finishing operations.
Thermal Resistance and Wear
CVD produces a thicker coating. This thickness provides a highly effective thermal barrier, insulating the carbide substrate from the extreme heat generated during heavy cutting.
This superior heat and wear resistance makes CVD the optimal choice for roughing and high-speed machining where tool life is paramount.
Adhesion and Uniformity
The chemical bonding in the CVD process typically results in excellent adhesion to the substrate. Its gaseous nature ensures a very uniform coating, even on complex tool geometries.
While PVD is a line-of-sight process, modern techniques allow for tool rotation to achieve good coverage, and its lower temperature can be a major advantage for certain substrates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither coating method is a perfect solution for every scenario. Understanding their inherent limitations is key to making an effective choice.
PVD: The Sharp but Less Insulated Edge
The primary strength of PVD—its thinness—is also a limitation. The thinner coating provides less thermal insulation compared to CVD, making it less suitable for the high temperatures of aggressive roughing.
CVD: The Tough but Blunter Edge
The thickness of a CVD coating, while excellent for wear resistance, can slightly round the microscopic sharpness of the cutting edge. This makes it less ideal for applications requiring the absolute finest surface finish or for machining gummy materials prone to built-up edge.
Substrate Compatibility
The extreme heat of the CVD process can impact the toughness and metallurgical properties of some carbide grades. The lower temperature of PVD makes it a safer choice for heat-sensitive substrates and is the standard for high-speed steel (HSS) tools that would be damaged by CVD temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct coating, you must first define your operational priority. The goal of the cut dictates the ideal tool.
- If your primary focus is aggressive roughing or high-speed cutting: Choose CVD for its superior thermal barrier and exceptional wear resistance in high-heat conditions.
- If your primary focus is finishing passes and achieving a fine surface finish: Choose PVD to leverage its incredibly sharp edge and smooth coating characteristics.
- If you are machining stainless steel, non-ferrous, or "gummy" materials: Choose a PVD-coated tool, as its sharp edge is critical for preventing built-up edge (BUE).
- If you require a general-purpose tool for mixed-use: Many modern inserts use multi-layer coatings, but understanding the properties of the primary outer layer will help you predict its performance.
Ultimately, aligning the distinct advantages of each coating process with the specific demands of your machining operation is the key to maximizing both performance and tool life.
Summary Table:
| Coating Process | Process Type | Typical Temperature | Coating Thickness | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVD | Physical Vapor Deposition | 250°C - 450°C | Thin (preserves sharp edge) | Finishing operations, sharp edges, fine surface finish |
| CVD | Chemical Vapor Deposition | 450°C - 1050°C | Thick (excellent wear resistance) | Roughing operations, high thermal resistance, aggressive cutting |
Maximize your machining performance with the right tool coating solution from KINTEK!
Choosing between PVD and CVD coatings is critical for achieving optimal results in your laboratory or manufacturing environment. Whether you need the sharp edge precision of PVD for finishing passes or the superior thermal barrier of CVD for roughing operations, KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific cutting tool requirements.
Our experts can help you select the perfect coating technology to enhance tool life, improve surface finish, and boost overall efficiency. Don't leave your machining results to chance – contact our specialists today to discuss how KINTEK's cutting tool solutions can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- What is the frequency of MPCVD? A Guide to Choosing 2.45 GHz vs. 915 MHz for Your Application
- How does microwave plasma work? Unlock Precision Material Synthesis for Advanced Manufacturing
- What are the advantages of microwave plasma? Faster, Purer Processing for Demanding Applications
- What is the microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition process? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Coatings



















