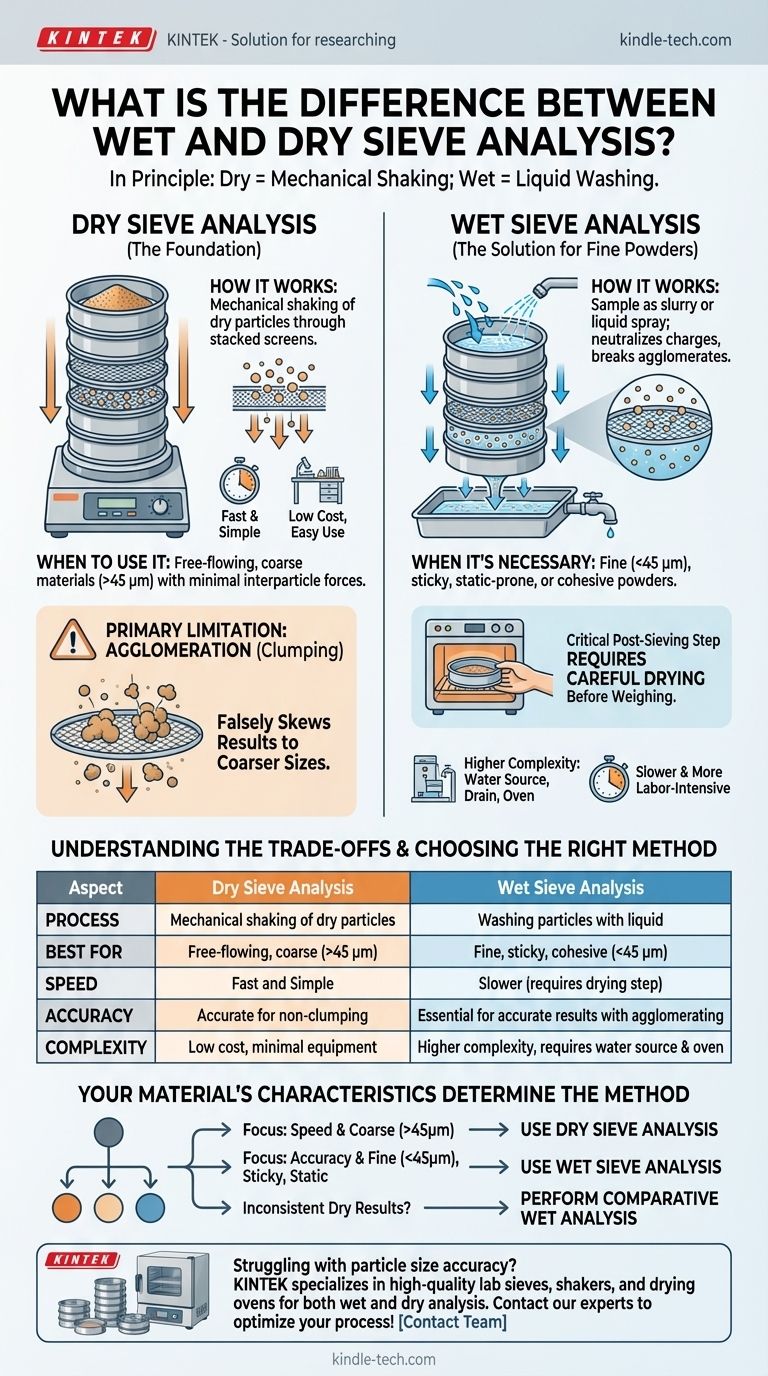
In principle, the primary difference between wet and dry sieve analysis lies in the medium used to separate particles. Dry sieve analysis relies on mechanical shaking to pass dry particles through a stack of screens, while wet sieve analysis uses a liquid—typically water—to wash the particles through the sieves. This fundamental difference in process dictates which method is appropriate for a given material.
The choice between wet and dry sieving is not a matter of preference, but a necessary decision based on your material's properties. Dry sieving is the default for its simplicity, but wet sieving is the essential solution for fine or cohesive powders that would otherwise yield inaccurate results.
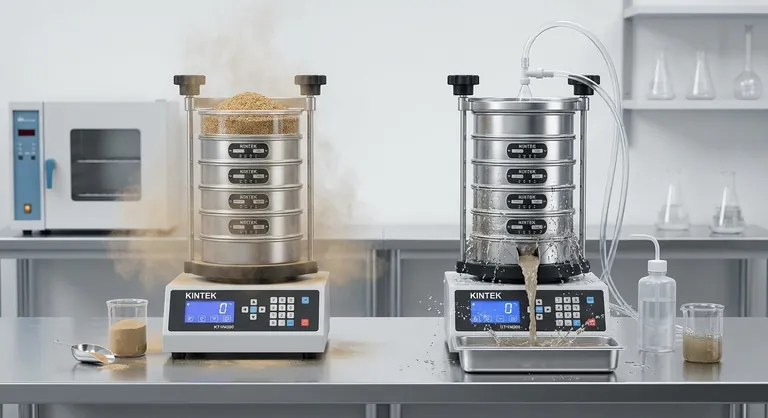

The Foundation: Dry Sieve Analysis
Dry sieving is the most common method for determining particle size distribution due to its low cost and ease of use. It serves as the baseline for particle analysis.
How It Works
A measured sample of dry material is placed on the top sieve of a stacked column. Each sieve in the stack has a finer mesh than the one above it. The entire stack is then agitated by a mechanical shaker, allowing particles to fall through the meshes until they are retained by a sieve with openings smaller than the particle itself.
When to Use It
Dry sieving is the ideal and standard method for materials that are free-flowing and do not clump together. It is most effective for particles larger than approximately 45 micrometers (μm), where interparticle forces are minimal.
The Primary Limitation: Agglomeration
The chief weakness of dry sieving emerges with fine powders. Particles can stick to each other and to the sieve mesh due to static electricity or residual moisture. This clumping, or agglomeration, prevents particles from passing through mesh openings they would otherwise fit through, falsely skewing the results toward a coarser particle size.
The Solution for Fine Powders: Wet Sieve Analysis
Wet sieve analysis is a modification of the standard procedure, specifically designed to overcome the limitations of dry sieving for problematic materials.
How It Works
In wet sieving, the sample is turned into a slurry before being sieved, or a liquid is continuously sprayed over the material during shaking. This liquid serves two purposes: it neutralizes the electrostatic charges and washes away the fine particles, effectively breaking up any agglomerates.
When It's Necessary
Wet sieving is required for materials that are fine (typically <45 μm), prone to static buildup, or tend to stick together. If dry sieving produces inconsistent results or if you suspect particles are clumping, wet sieving is the corrective method.
The Post-Sieving Step
A critical difference in the workflow is that after wet sieving is complete, the material retained on each sieve must be carefully dried in an oven. Only after drying can the fractions be weighed to calculate the final particle size distribution. This adds an extra step and time to the analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct method requires balancing the need for accuracy against the demands of the procedure.
Speed and Simplicity
Dry sieving is significantly faster. It involves fewer steps, requires less specialized equipment, and has a much simpler cleanup process.
Accuracy for Problematic Materials
For fine or cohesive powders, wet sieving is non-negotiable for achieving accurate and reproducible results. It is the only way to ensure that agglomeration does not corrupt the measurement.
Cost and Complexity
Wet sieving introduces complexity. It requires a water source, a drainage system for the collecting pan, and a drying oven. The entire process, including the drying step, is more labor-intensive and time-consuming.
Sample Integrity
The liquid used in wet sieving (the "washing medium") must be chosen carefully. It cannot cause the sample material to dissolve, swell, or otherwise react, as this would invalidate the results. Water is common, but other liquids like alcohol may be necessary.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Material
Your material's characteristics are the sole determinant for which sieving method to employ. Base your decision on the properties of the powder and your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is speed and your material is free-flowing and relatively coarse (>45 µm): Use dry sieve analysis for its efficiency and simplicity.
- If your primary focus is accuracy with fine (<45 µm), sticky, or electrostatically charged powders: Use wet sieve analysis to break apart agglomerates and get a true measurement.
- If you are getting inconsistent dry results or suspect particle clumping: Perform a comparative wet sieve analysis to diagnose and correct the source of the error.
Ultimately, selecting the correct analytical method is the first step toward ensuring the integrity and reliability of your particle size data.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Dry Sieve Analysis | Wet Sieve Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Mechanical shaking of dry particles | Washing particles with liquid (e.g., water) |
| Best For | Free-flowing, coarse materials (>45 µm) | Fine, sticky, or cohesive powders (<45 µm) |
| Speed | Fast and simple | Slower (requires drying step) |
| Accuracy | Accurate for non-clumping materials | Essential for accurate results with agglomerating powders |
| Complexity | Low cost, minimal equipment | Higher complexity, requires water source and oven |
Struggling to get accurate particle size data? The right sieve analysis method is critical for reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves, shakers, and drying ovens to support both wet and dry analysis workflows. Our experts can help you select the perfect equipment for your specific materials—whether you're working with fine powders or coarse aggregates. Contact our team today to optimize your particle sizing process and ensure data integrity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis



















