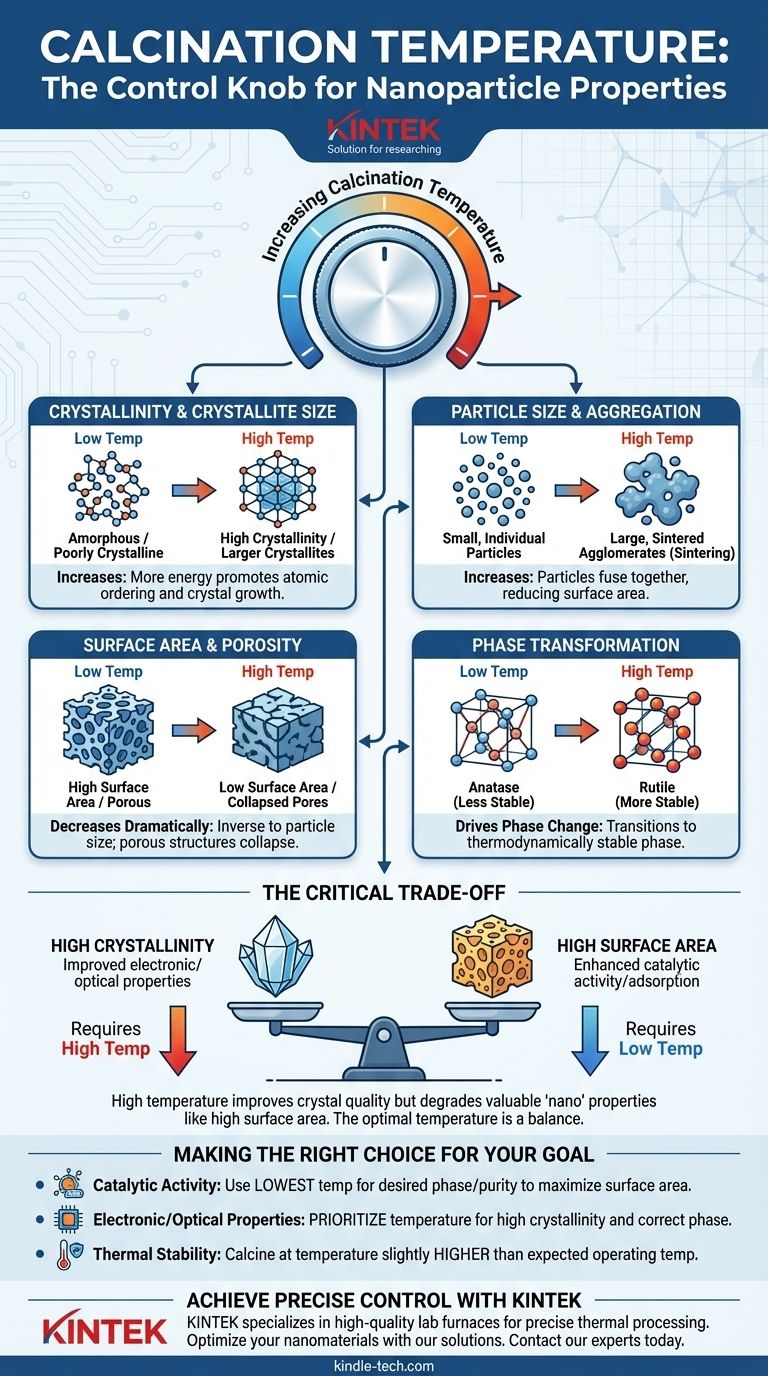
In short, calcination temperature is the primary control knob for tuning the final properties of nanoparticles. Increasing the calcination temperature generally increases the particle size and crystallinity while simultaneously decreasing the surface area. This process is used to remove residual chemicals, induce phase transitions, and achieve the desired material structure for a specific application.
The core challenge of calcination is managing a critical trade-off: The same high temperatures that improve crystal quality and purity also tend to degrade the most valuable "nano" properties, such as high surface area. The optimal temperature is therefore not the highest possible, but the one that strikes the perfect balance for your end goal.

The Purpose of Calcination
Calcination is a controlled heating process performed in a specific atmosphere (like air or an inert gas) below the material's melting point. It is not simply a drying step; it is a deliberate thermal treatment designed to induce fundamental changes in the material.
Driving Material Transformation
The primary goal is to convert a precursor material, such as a metal salt or hydroxide, into a more stable, usable form, typically a metal oxide.
Removing Impurities
The process burns off volatile organic residues, solvents, or other unwanted chemical precursors left over from the synthesis stage, resulting in a purer final product.
Controlling Crystallinity
Calcination provides the thermal energy necessary for atoms to arrange themselves into an ordered, crystalline lattice, transforming amorphous or poorly crystalline materials into well-defined structures.
How Temperature Directly Influences Nanoparticle Properties
Varying the calcination temperature directly and predictably alters the physical and chemical characteristics of the final nanoparticles.
Crystallinity and Crystallite Size
Higher temperatures provide more energy for atomic diffusion. This allows atoms to move into more stable, ordered positions, increasing the overall crystallinity of the material.
This energy also promotes the growth of individual crystal domains, or crystallites. Smaller, less stable crystals dissolve and redeposit onto larger, more stable ones, leading to a larger average crystallite size.
Particle Size and Aggregation
As temperature rises, nanoparticles gain enough energy to fuse together in a process called sintering. This causes individual particles to grow and form larger, hard agglomerates.
Even a modest increase in temperature, such as from 400°C to 600°C, can often double the average particle size.
Surface Area and Porosity
Surface area is inversely proportional to particle size. As nanoparticles grow and sinter together, the total available surface area per gram of material decreases dramatically.
High temperatures can also cause the collapse of porous structures within the material, further reducing the surface area and accessibility for reactions.
Phase Transformation
Many materials can exist in multiple crystal structures, or phases. For example, titanium dioxide (TiO₂) can exist as anatase, rutile, or brookite.
Calcination temperature is the key parameter used to drive the transformation from a less stable phase (e.g., anatase) to a more thermodynamically stable phase (e.g., rutile). Each phase has distinct electronic and catalytic properties.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a calcination temperature is rarely about maximizing one property. It is an exercise in balancing competing factors.
Crystallinity vs. Surface Area
This is the most common trade-off. High crystallinity is often essential for applications like photocatalysis or electronics, but the high temperatures needed to achieve it will inevitably reduce the surface area.
For applications like adsorption or heterogeneous catalysis, a high surface area is paramount, often forcing a compromise on crystal perfection.
Purity vs. Desired Nanostructure
The temperature required to completely burn off all synthesis residues might be high enough to cause unwanted particle growth or phase changes.
You may need to accept minor impurities to preserve the optimal nanostructure, or find a temperature that offers an acceptable compromise between purity and particle size.
Sintering and Loss of Function
If the temperature is too high, extensive sintering can occur. This can lead to the complete loss of nanostructure, turning your carefully synthesized nanoparticles into a bulk ceramic with vastly different and often undesirable properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" calcination temperature is entirely dependent on the intended application of the nanoparticles. To determine the optimal conditions, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high catalytic activity: Use the lowest temperature possible that achieves the desired crystal phase and purity to maximize surface area.
- If your primary focus is specific electronic or optical properties: Prioritize the temperature required to achieve high crystallinity and the correct phase, even at the expense of surface area.
- If your primary focus is thermal stability: Calcine at a temperature slightly higher than the material's expected operating temperature to ensure its structure does not change during use.
Ultimately, mastering calcination temperature gives you precise control over the final performance of your nanomaterials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Effect of Increasing Calcination Temperature |
|---|---|
| Crystallinity & Crystallite Size | Increases |
| Particle Size & Aggregation | Increases (sintering) |
| Surface Area & Porosity | Decreases |
| Phase Purity/Transformation | Drives phase change to stable state |
Achieve Precise Control Over Your Nanomaterials
Mastering the calcination process is critical to developing nanoparticles with the exact properties your research or product requires. The right equipment is essential for precise temperature control and reproducible results.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables designed for advanced thermal processing like calcination. Our solutions help you strike the perfect balance between crystallinity, surface area, and phase purity, ensuring your nanomaterials perform as intended.
Let us help you optimize your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal thermal treatment solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- At what temperature is it safe to open a muffle furnace? A Guide to Preventing Injury and Equipment Damage
- What is a muffle furnace used in determination of? Precise Ash Content and Material Composition
- What is a muffle furnace used for? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace in the environment? Achieve Clean, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What are the parts of a muffle furnace? Uncover the Core Components for Precision Heating



















