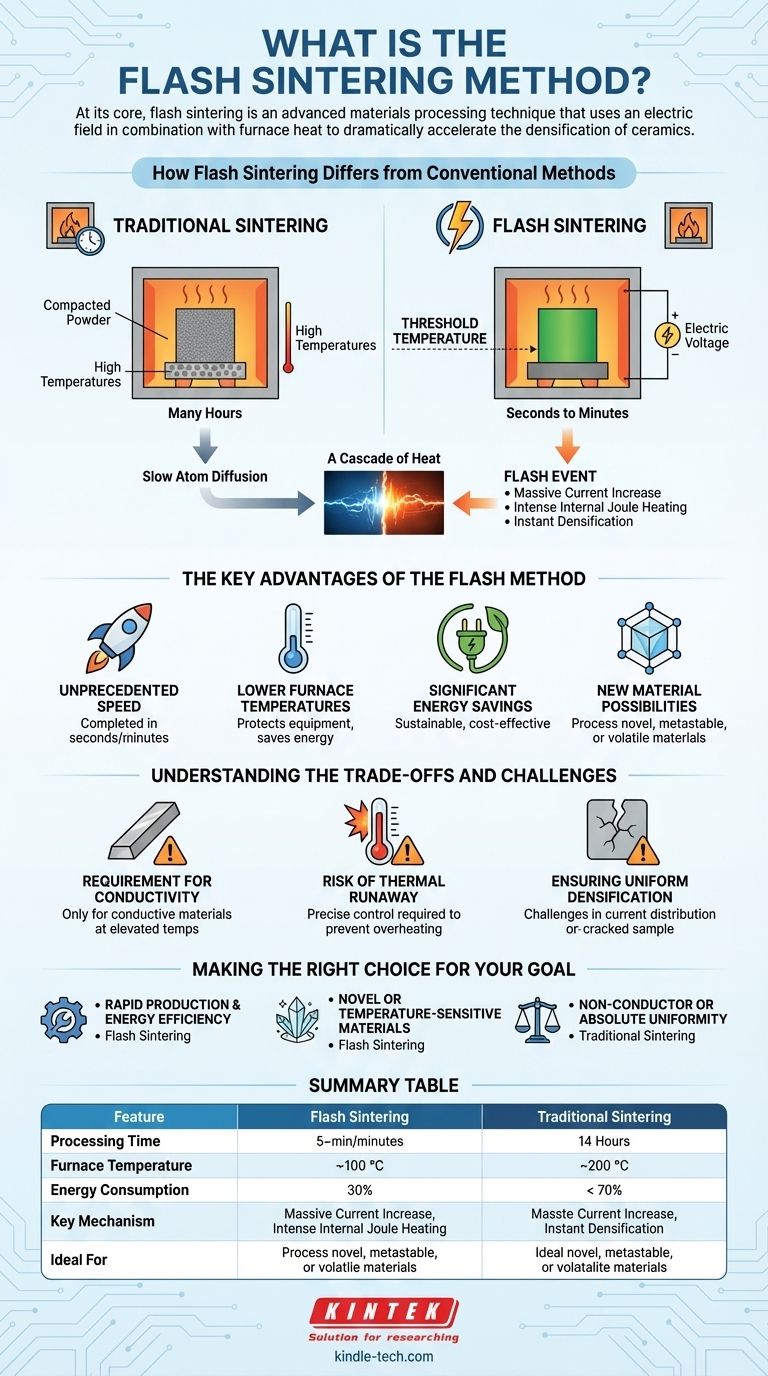
At its core, flash sintering is an advanced materials processing technique that uses an electric field in combination with furnace heat to dramatically accelerate the densification of ceramics. Once the material reaches a specific threshold temperature, the applied voltage causes a sudden, massive increase in electrical current, which generates intense internal heat (Joule heating) and consolidates the material into a dense solid in mere seconds.
By departing from the slow, brute-force heating of traditional methods, flash sintering uses electricity as a catalyst to trigger a rapid, internal heating event. This fundamentally changes the energy and time required to process advanced materials.
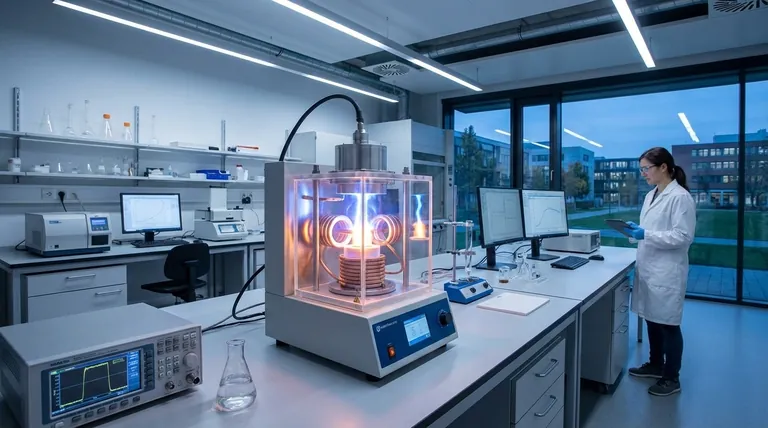

How Flash Sintering Differs from Conventional Methods
To understand the innovation of flash sintering, it's essential to first understand the process it improves upon.
The Slow Pace of Traditional Sintering
Traditional sintering works by heating a compacted powder ("green part") in a furnace for an extended period.
The high temperature causes atoms to slowly diffuse across the boundaries of individual particles, fusing them together and eliminating the porous spaces between them. This process is effective but often requires many hours and extremely high temperatures, consuming significant energy.
The Introduction of an Electric Field
Flash sintering begins like the traditional method, with the material being heated in a furnace. However, it introduces a critical difference: an electric voltage is applied directly across the sample.
Initially, not much happens, as most ceramics are poor electrical conductors at room temperature.
The "Flash" Event: A Cascade of Heat
As the furnace heats the material, it reaches a threshold temperature where its electrical conductivity begins to rise.
At this point, a feedback loop is triggered. The increasing conductivity allows more current to flow, which generates internal Joule heating. This internal heat further increases the material's temperature and conductivity, causing a sudden, nonlinear surge of current—the "flash."
This intense, internally generated heat densifies the material almost instantaneously, often in less than a minute.
The Key Advantages of the Flash Method
This unique mechanism provides several transformative benefits over conventional sintering processes.
Unprecedented Speed
The most significant advantage is speed. Processes that traditionally take many hours can be completed in seconds or minutes, dramatically increasing throughput.
Lower Furnace Temperatures
Because the "flash" event generates most of the required heat internally, the external furnace does not need to reach the extreme temperatures required for traditional sintering. This protects the equipment and saves energy.
Significant Energy Savings
The combination of drastically shorter processing times and lower furnace temperatures results in a substantial reduction in overall energy consumption, making it a more sustainable and cost-effective method.
New Material Possibilities
The rapid heating and short duration at high temperatures allow for the densification of materials that would otherwise decompose, change phase, or coarsen during long conventional cycles. This opens the door to processing novel metastable, volatile, or finely structured materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
No technique is universally superior, and flash sintering has specific requirements and potential pitfalls that must be managed.
Requirement for Conductivity
The core mechanism relies on the material becoming sufficiently electrically conductive at an elevated temperature. Materials that remain highly insulating even when hot are not suitable candidates for this method.
Risk of Thermal Runaway
The "flash" event is a powerful thermal cascade. If not precisely controlled by limiting the current, it can lead to thermal runaway, overheating, and damage or destruction of the sample.
Ensuring Uniform Densification
Achieving a perfectly uniform current distribution through the sample can be challenging. Any non-uniformities can lead to "hot spots" and result in a part with inconsistent density and mechanical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering method depends entirely on your material, application, and production goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid production and energy efficiency: Flash sintering is an exceptional choice for suitable ceramic materials, drastically cutting down processing time and costs.
- If you are working with novel or temperature-sensitive materials: The ability to densify at lower external temperatures makes this method ideal for preserving unique microstructures or preventing decomposition.
- If your material is a non-conductor or requires absolute uniformity on a large scale: A traditional furnace or an alternative like microwave sintering might offer more predictable and scalable results without the electrical constraints.
Ultimately, flash sintering represents a powerful paradigm shift in materials processing, trading conventional thermal reliance for precise electrical control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Flash Sintering | Traditional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | Seconds to minutes | Many hours |
| Furnace Temperature | Lower | Extremely high |
| Energy Consumption | Significantly lower | High |
| Key Mechanism | Electric field + Joule heating | Thermal diffusion |
| Ideal For | Conductive ceramics, novel materials | Broad range of materials |
Ready to accelerate your materials processing with advanced sintering techniques?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need to implement cutting-edge methods like flash sintering. Whether you're developing novel ceramics or optimizing production for energy efficiency, our solutions are designed to meet the precise demands of your laboratory.
Contact us today to discover how KINTEK can support your research and production goals with reliable, high-performance equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication



















