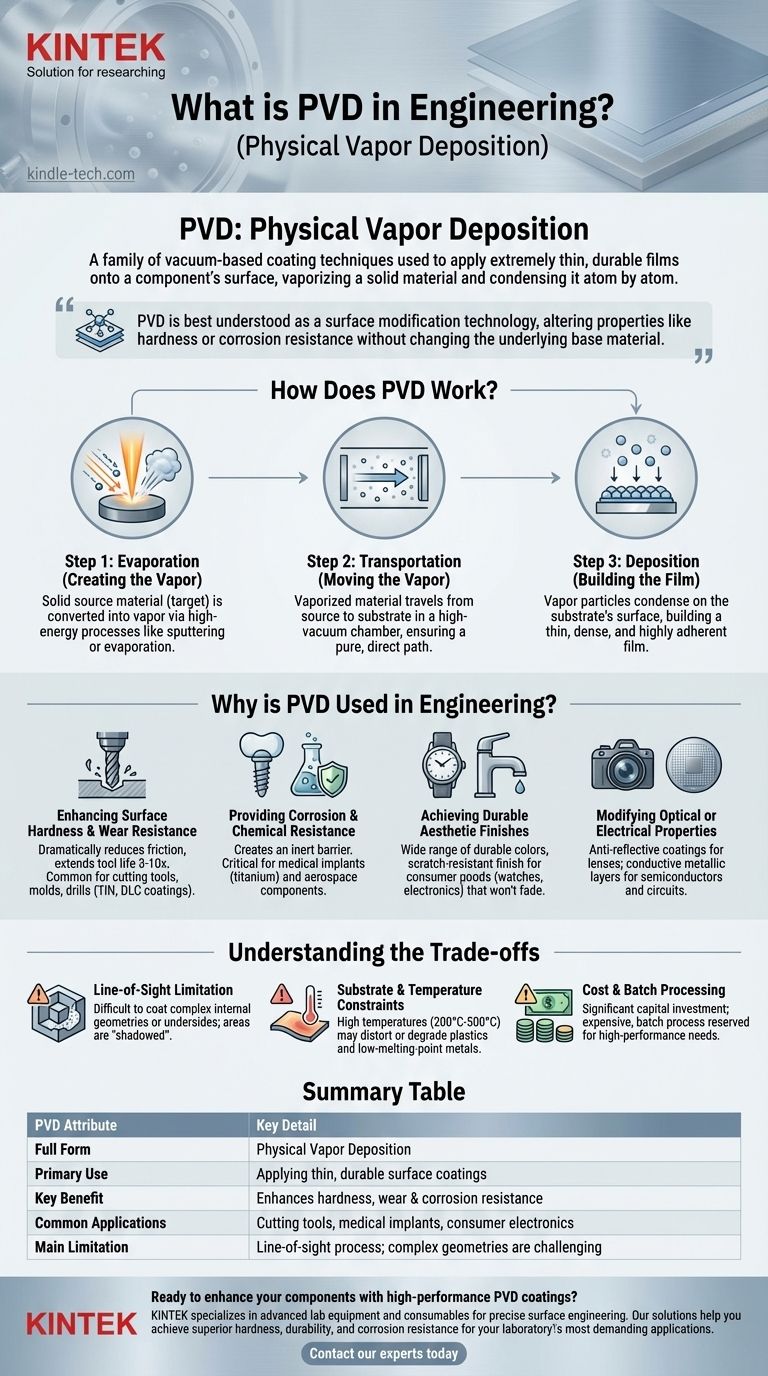
In engineering, PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. It is not a single process, but a family of vacuum-based coating techniques used to apply an extremely thin yet durable film onto a component's surface. This process vaporizes a solid material in a vacuum chamber, which then condenses onto the target object, creating a high-performance coating atom by atom.
PVD is best understood as a surface modification technology. It fundamentally alters the properties of a component's surface—such as hardness or corrosion resistance—without changing the underlying base material.

How Does Physical Vapor Deposition Work?
At its core, PVD is a three-step process that takes place inside a high-vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is critical to ensure the purity and quality of the final coating.
Step 1: Evaporation (Creating the Vapor)
First, a solid source material, often called the "target," is converted into a vapor. This is typically achieved through high-energy processes like bombarding the target with ions (sputtering) or heating it with an electron beam or arc (evaporation).
Step 2: Transportation (Moving the Vapor)
The vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the components being coated (the "substrates"). The vacuum is essential here, as it eliminates air molecules that could otherwise react with or deflect the vapor, ensuring a pure and direct path.
Step 3: Deposition (Building the Film)
When the vapor particles reach the substrate, they condense on its surface. This builds a thin, highly adherent, and dense film. The thickness of this film can be controlled with extreme precision, often ranging from a few microns down to nanometers.
Why is PVD Used in Engineering?
Engineers specify PVD coatings to achieve specific performance goals that the base material alone cannot meet. The applications are vast and driven by the unique properties these films provide.
Enhancing Surface Hardness and Wear Resistance
This is a primary application. Hard coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) are applied to cutting tools, drills, and molds. The PVD layer dramatically reduces friction and increases surface hardness, extending tool life by 3 to 10 times.
Providing Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
PVD films create an inert barrier between the component and its environment. This is critical for medical implants (like those made of titanium) to ensure biocompatibility and for aerospace components exposed to harsh conditions.
Achieving Durable Aesthetic Finishes
PVD allows for the deposition of a wide range of colors that are far more durable than paint or plating. This is widely used on consumer goods like watches, faucets, and high-end electronics to provide a scratch-resistant finish that will not fade or tarnish.
Modifying Optical or Electrical Properties
The process is used to apply anti-reflective coatings on lenses and optics. In the semiconductor industry, PVD is a fundamental step for depositing the conductive metallic layers that form circuits on silicon wafers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Line-of-Sight Limitation
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, PVD is best suited for coating external surfaces. It is very difficult to coat complex internal geometries or the undersides of features, as these areas are "shadowed" from the vapor source.
Substrate and Temperature Constraints
PVD processes can involve high temperatures (from 200°C to 500°C). While this helps create a dense, well-adhered coating, it also means the substrate material must be able to withstand this heat without warping or degrading, limiting its use on many plastics and low-melting-point metals.
Cost and Batch Processing
PVD requires significant capital investment in vacuum equipment and is a batch process, not a continuous one. This makes it more expensive than bulk treatments like painting or electroplating, and it is generally reserved for components where high performance justifies the cost.
When to Consider PVD for Your Project
Use this guidance to determine if PVD is the right choice for your specific engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is extending the life of high-wear components: PVD is an exceptional choice for adding a hard, lubricious surface to cutting tools, molds, and engine parts.
- If your primary focus is achieving a durable, decorative finish: Consider PVD for consumer products where both aesthetics and scratch resistance are critical, such as watches, faucets, or sporting goods.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight geometries: You should investigate alternative methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or electroless nickel plating, which are better suited for uniform coverage on intricate parts.
By understanding PVD as a strategic surface modification tool, you can unlock new levels of performance and durability in your engineered designs.
Summary Table:
| PVD Attribute | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Full Form | Physical Vapor Deposition |
| Primary Use | Applying thin, durable surface coatings |
| Key Benefit | Enhances hardness, wear & corrosion resistance |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, consumer electronics |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight process; complex geometries are challenging |
Ready to enhance your components with high-performance PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise surface engineering. Our solutions help you achieve superior hardness, durability, and corrosion resistance for your laboratory's most demanding applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















