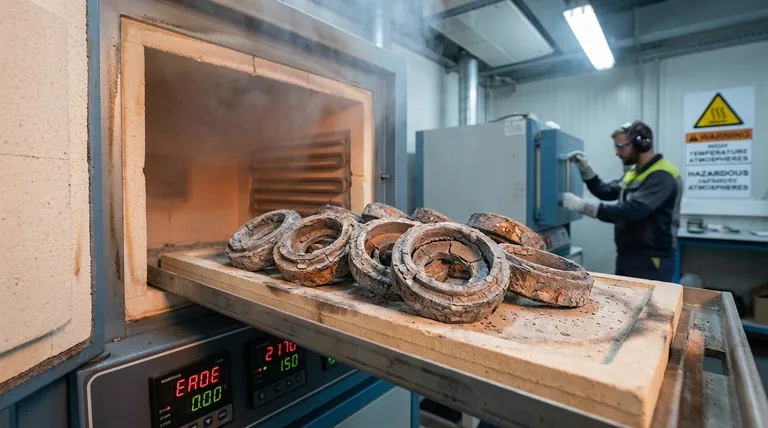
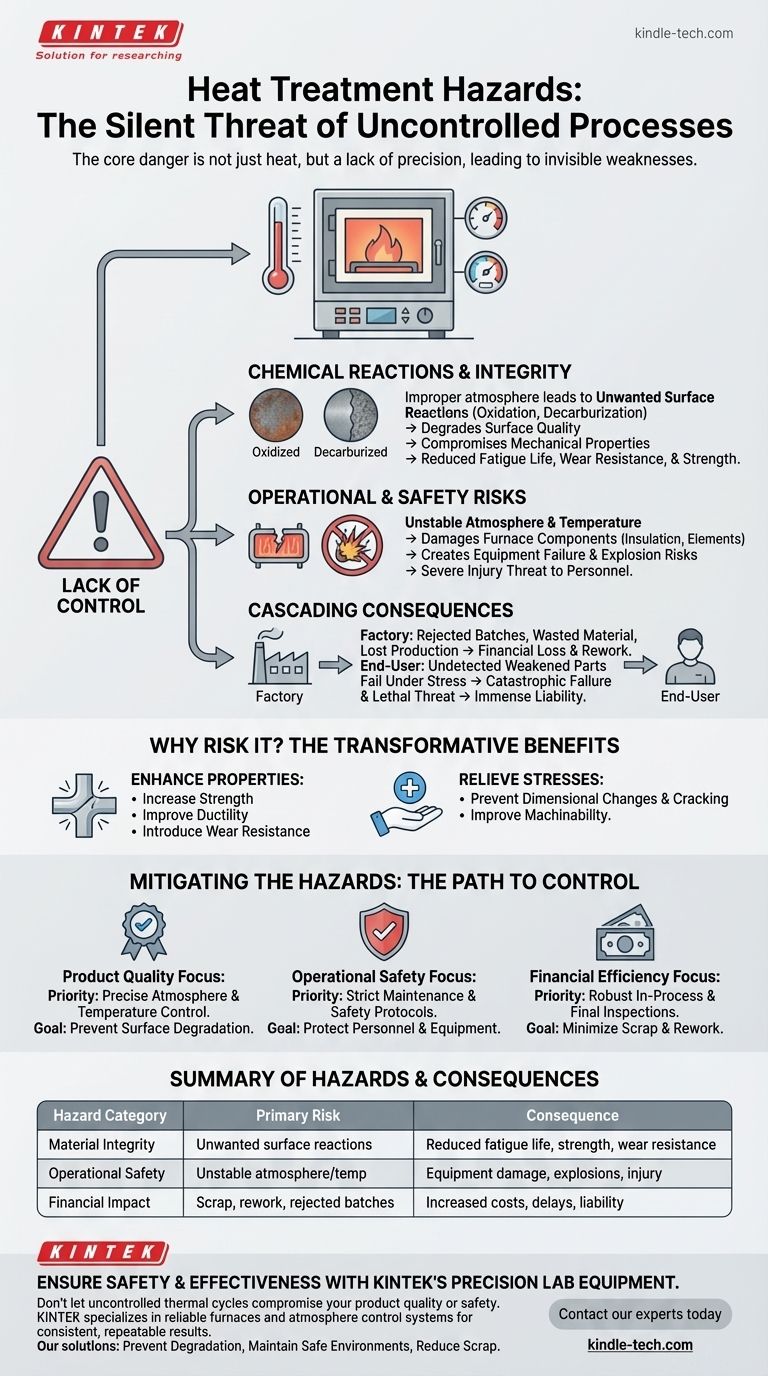
The primary hazards of heat treatment are not just related to high temperatures; they stem from a lack of control over the process. When the thermal cycle or furnace atmosphere is improperly managed, it can trigger unwanted chemical reactions on the metal's surface, fundamentally compromising the part's integrity, damaging equipment, and creating significant safety risks for personnel.
The core danger in heat treatment is subtle: an improperly controlled process can silently create internal weaknesses in a metal part. This undetected flaw can lead to catastrophic failure in the field, turning a routine manufacturing step into a major liability.

The Source of the Hazard: Lack of Process Control
Heat treatment is a precise science. The hazards arise when that precision is lost, leading to unintended and often invisible consequences for the material and the surrounding environment.
Chemical Reactions and Surface Integrity
An improperly controlled furnace atmosphere is a primary source of risk. The gases present can react with the hot surface of the metal alloy.
This can cause conditions like oxidation (scaling) or decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface layer of steel), which degrade the material's surface quality.
Compromised Mechanical Properties
These unwanted surface reactions directly undermine the purpose of heat treatment. Instead of strengthening the part, they can create a weak surface layer.
This invisible weakness can lead to a drastic reduction in fatigue life, wear resistance, and overall strength, making the part unreliable and unfit for its intended application.
Operational and Safety Risks
Beyond the material itself, a poorly managed process poses direct physical threats.
An unstable or improperly controlled atmosphere can damage the furnace's internal components, such as insulation or heating elements. In worst-case scenarios, it can create conditions that lead to equipment failure or even explosions, posing a severe risk of injury to employees.
Understanding the Consequences
The failures caused by improper heat treatment have cascading effects, moving from the factory floor to the end-user.
Product Failure and Financial Loss
Parts that fail inspection due to flawed heat treatment result in rejected batches, wasted material, and lost production time.
This directly translates to significant financial loss and requires costly rework or complete remanufacturing, impacting project timelines and budgets.
Catastrophic End-User Risk
The most dangerous repercussion occurs when a weakened part is not detected before use.
A component that has been unknowingly compromised by poor heat treatment can fail unexpectedly under operational stress. This poses a direct and potentially lethal threat to customers and the public, creating immense liability.
Why Heat Treatment is Worth the Risk
Despite these hazards, heat treatment is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing because its benefits are transformative when the process is correctly controlled.
Enhancing Material Properties
The primary goal is to fundamentally change a material's physical and mechanical properties.
Proper heat treatment can dramatically increase strength, improve ductility (the ability to deform without fracturing), and introduce critical wear-resistant characteristics.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, or hot forming introduce internal stresses into a material.
Heat treatment is used to relieve these stresses, which makes parts easier to machine and prevents dimensional changes or cracking later in the part's life.
How to Mitigate Heat Treatment Hazards
Managing the risks of heat treatment is about enforcing rigorous control over every variable of the process.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Your priority must be precise control over the furnace atmosphere and temperature to prevent unwanted surface chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Implement and enforce strict furnace maintenance schedules and operator safety protocols to protect personnel and equipment.
- If your primary focus is financial efficiency: Invest in robust in-process and final inspection methods to detect deviations early, minimizing scrap and rework.
Ultimately, mastering control over the heat treatment process is the key to unlocking its immense benefits while neutralizing its significant risks.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Primary Risk | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Material Integrity | Unwanted surface reactions (oxidation, decarburization) | Reduced fatigue life, strength, and wear resistance |
| Operational Safety | Unstable furnace atmosphere or temperature | Equipment damage, explosions, and personnel injury |
| Financial Impact | Scrap, rework, and rejected batches | Increased costs, delays, and liability |
Ensure your heat treatment process is safe and effective with KINTEK's precision lab equipment.
Don't let uncontrolled thermal cycles compromise your product quality or operator safety. KINTEK specializes in reliable furnaces and atmosphere control systems designed to deliver consistent, repeatable results. Our solutions help you:
- Prevent surface degradation and material weaknesses.
- Maintain a stable, safe furnace environment.
- Reduce scrap rates and protect your bottom line.
Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your laboratory's heat treatment needs and transform a high-risk step into a reliable advantage.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an industrial oven in slate waste ceramsite production? Ensure Dryness & Process Stability
- Why is a high-purity argon protection system required in a vacuum arc furnace? Protect Ti-Zr-Hf-V-Ta Alloy Integrity
- What is a sintering kiln? The Essential Tool for Transforming 3D Printed Parts into Durable Components
- What is the role of an arc-melting furnace in the synthesis of uranium silicide? Master Nuclear Fuel Composition
- What heat transfer happens in a vacuum? Master Thermal Radiation for Your Lab Equipment
- What are the benefits of annealing metal? Enhance Ductility and Relieve Internal Stresses
- What is a furnace reline? A Strategic Guide to Extending Industrial Furnace Life
- Why are vacuum furnaces or high-purity inert atmosphere furnaces required for joining refractory metals?



















