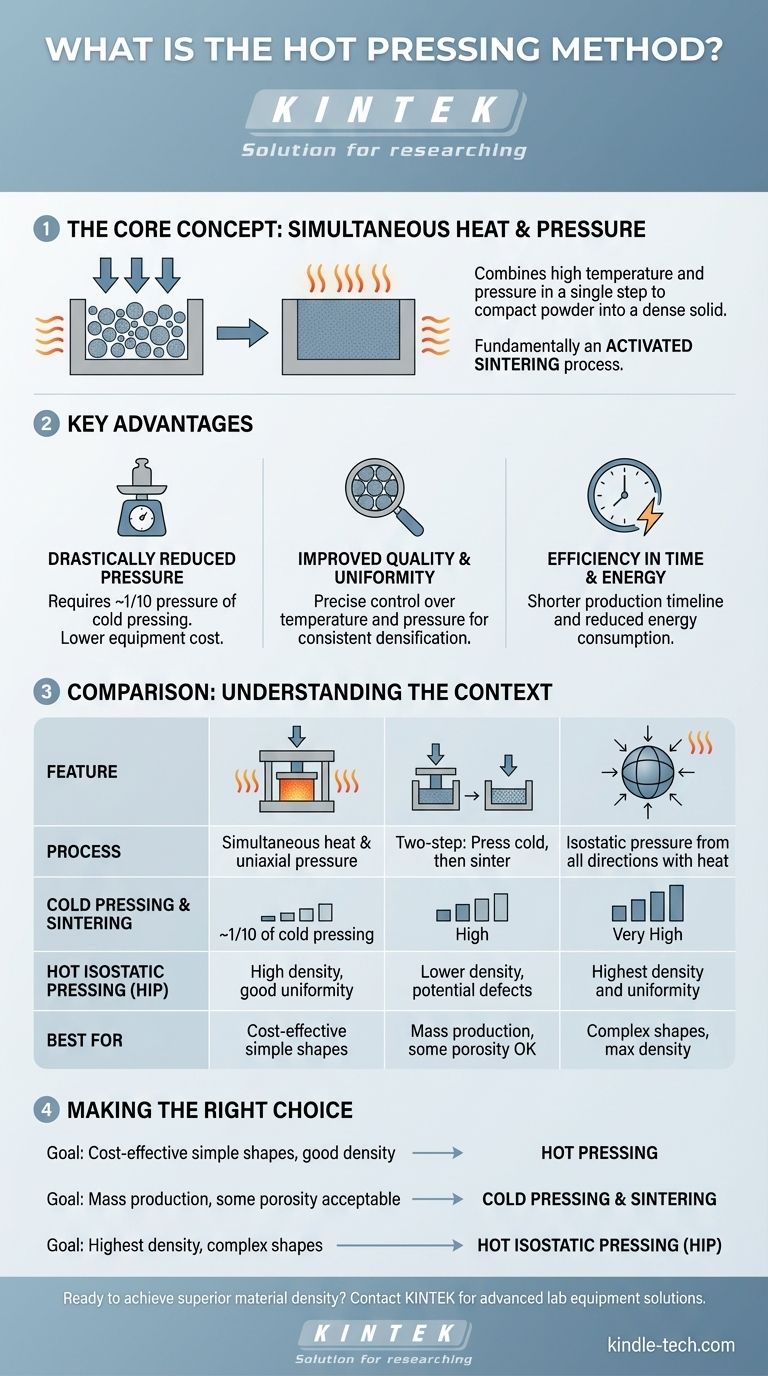
In short, hot pressing is a material processing method that simultaneously applies high temperature and pressure to a powder or material. This combination fundamentally changes the material's behavior, allowing it to be compacted into a dense, solid part in a single, efficient step. Unlike traditional methods that press material when cold and heat it later, hot pressing performs both actions at the same time.
The central advantage of hot pressing is its efficiency. By heating the material during compaction, it becomes more pliable, achieving superior density and material properties with significantly less pressure and in less time than conventional cold pressing and sintering methods.

The Core Principle: Activated Sintering
Hot pressing is fundamentally a form of activated sintering. The term "sintering" refers to the process of bonding particles together using heat, just below their melting point.
How Heat Activates the Process
Applying heat makes the material particles softer and more plastic. This allows them to deform and fit together more easily under pressure, eliminating the empty spaces, or pores, between them.
Combining Pressure and Heat
By applying directional pressure at the same time, the process is accelerated dramatically. This simultaneous action reduces the time needed for atomic diffusion and phase changes within the material, leading to a denser and more uniform final product.
Key Advantages of Hot Pressing
The unique combination of heat and pressure provides several distinct operational and material advantages over other methods.
Drastically Reduced Pressure Requirements
The unit pressing pressure needed for hot pressing is only about one-tenth of that required for cold pressing. This has a significant impact on equipment needs.
Because less force is required, the machinery can be smaller and represents a lower capital investment.
Improved Material Quality and Uniformity
The process allows for excellent control over the final material properties. Modern hot presses use advanced technology to precisely measure and control the temperature and pressure.
This control ensures a uniform temperature field across the workpiece, resulting in consistent densification and higher-quality materials with fewer internal defects.
Efficiency in Time and Energy
Combining the pressing and sintering steps into a single operation significantly shortens the overall production timeline.
This streamlined process, coupled with the ability to use thinner pressure-bearing materials, also leads to a notable reduction in total energy consumption.
Understanding the Method in Context
To fully grasp the value of hot pressing, it's useful to compare it to related manufacturing techniques.
Hot Pressing vs. Cold Pressing & Sintering
The most common alternative is a two-step process: cold pressing followed by sintering. In this method, powder is first compacted at room temperature into a "green" part, which is then heated in a furnace to achieve final density.
Hot pressing consolidates these two steps into one, achieving better results with lower pressure.
Hot Pressing vs. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a more advanced variation. While standard hot pressing typically applies pressure along a single axis (uniaxial), HIP applies equal pressure from all directions using a high-pressure gas.
This isostatic pressure results in exceptional uniformity and can produce parts with highly complex geometries. It is particularly effective for creating advanced alloys and minimizing segregation, where different elements in a material separate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for performance, complexity, and cost.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of simple shapes with good density: Hot pressing is an excellent choice due to its lower equipment costs and energy usage compared to cold pressing for similar quality.
- If your primary focus is mass production of simple parts where some porosity is acceptable: Traditional cold pressing followed by sintering may be the most economical route.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density and uniformity in complex shapes: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the superior, albeit more complex, technology.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal-mechanical process is key to achieving your desired material outcomes with maximum efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Pressing | Cold Pressing & Sintering | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Simultaneous heat and uniaxial pressure | Two-step: press cold, then sinter | Isostatic pressure from all directions with heat |
| Pressure Required | ~1/10 of cold pressing | High | Very High |
| Density/Uniformity | High density, good uniformity | Lower density, potential for defects | Highest density and uniformity |
| Best For | Cost-effective production of simple shapes | Mass production where some porosity is acceptable | Complex shapes requiring maximum density |
Ready to achieve superior material density and efficiency in your lab?
The hot pressing method can transform your material processing, but selecting the right equipment is crucial for your specific application. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including hot press systems, to help you streamline production and enhance material properties. Our experts will work with you to identify the perfect solution for your needs.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and see how KINTEK's solutions can benefit your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- Why is a high vacuum preferred over argon for sintering VC/Cu composites? Achieve Superior Wetting and Bond Strength
- Why must a high vacuum be maintained during Cu-CNT sintering? Ensure Optimal Bonding and Material Integrity



















