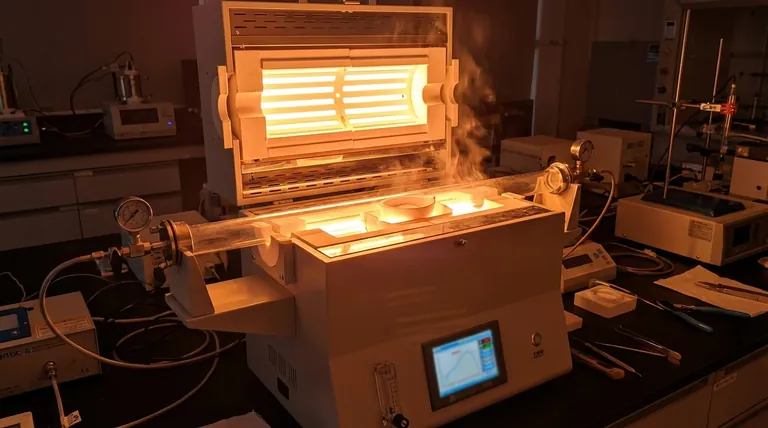
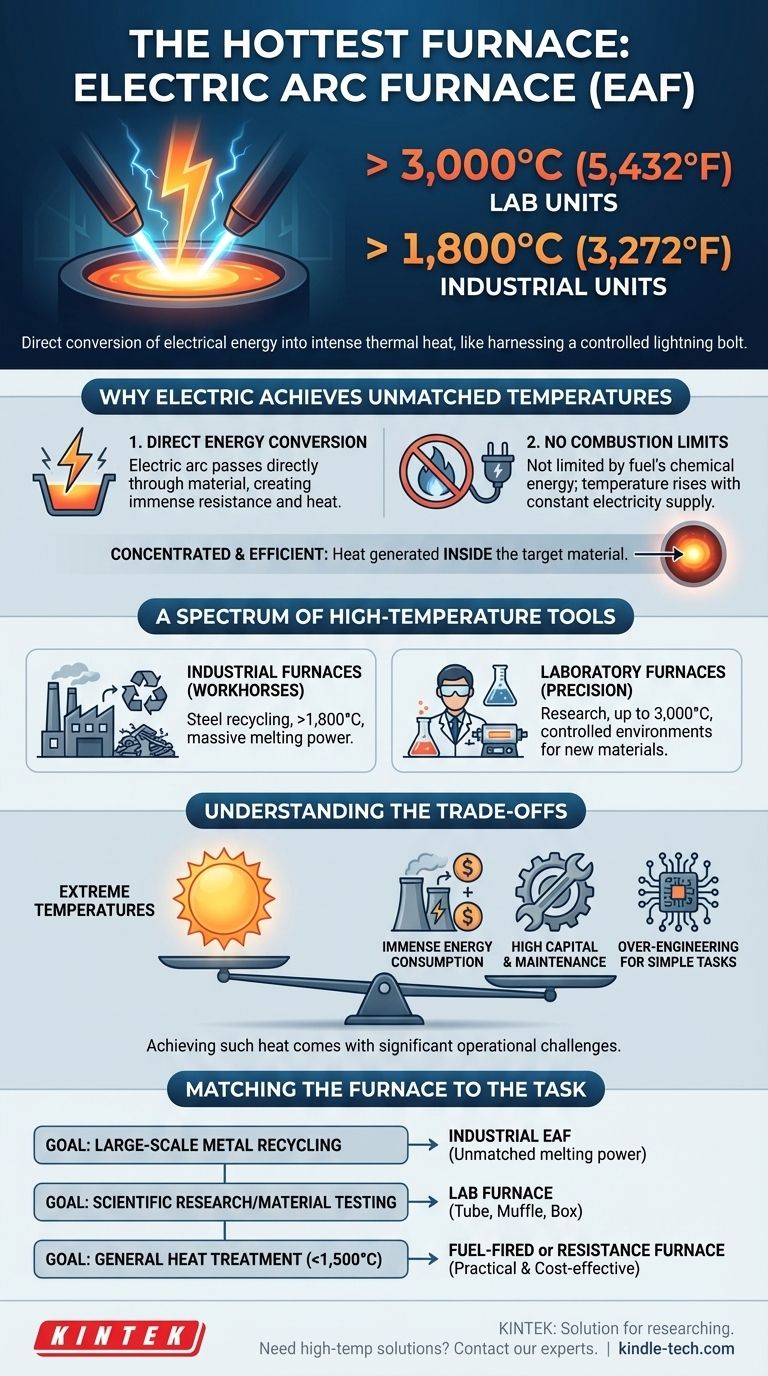
By a significant margin, the hottest type of furnace is the electric furnace, specifically the electric arc furnace (EAF). While industrial versions consistently operate above 1,800°C (3,272°F) for applications like steelmaking, specialized laboratory units can exceed an astonishing 3,000°C (5,432°F).
The core reason electric furnaces achieve these extreme temperatures is their method of heat generation. Instead of being limited by the chemical energy of a fuel, they convert electrical energy directly into thermal energy, allowing for a far higher and more concentrated temperature ceiling.

Why Electric Furnaces Achieve Unmatched Temperatures
To understand why electric furnaces get so hot, we must look at how they work compared to traditional fuel-fired systems. The difference is fundamental.
The Principle of Direct Energy Conversion
The most powerful electric furnaces use an electric arc—essentially a sustained, high-power spark that jumps between graphite electrodes.
This arc passes directly through the material to be heated (like scrap metal), creating immense resistance and releasing a tremendous amount of energy as intense heat. It is like harnessing a controlled lightning bolt.
Freedom from Combustion Limits
Fuel-fired furnaces, which burn natural gas, oil, or coal, are chemically limited. Their maximum temperature is dictated by the energy released when the fuel's chemical bonds are broken during combustion.
Electric furnaces have no such constraint. As long as a sufficient and constant supply of electricity is provided, the temperature can continue to rise, limited only by the physical properties of the furnace components themselves.
Concentrated and Efficient Heating
The heat in an electric arc furnace is generated inside the target material, not in a separate chamber. This direct transfer is incredibly efficient and allows for the rapid melting and processing of compounds with extremely high melting points.
A Spectrum of High-Temperature Tools
While the electric arc furnace holds the title for the absolute hottest, the term "furnace" covers a wide range of devices tailored for different tasks.
Industrial Furnaces (The Workhorses)
Industrial-scale electric furnaces are the backbone of modern steel recycling. They can melt enormous quantities of scrap metal at temperatures around 1,800°C, a task for which fuel-fired furnaces are far less efficient.
Laboratory Furnaces (The Precision Instruments)
For scientific research and materials testing, smaller, more controlled furnaces are used. These can include tube furnaces or muffle (box) furnaces.
Specialized versions of these lab furnaces, often using advanced heating elements, can reach or exceed 3,000°C to create new materials or test components for extreme environments like aerospace applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving such extreme temperatures comes with significant operational challenges. The hottest furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Immense Energy Consumption
The primary drawback is massive electricity consumption. Running an industrial electric arc furnace requires a dedicated electrical substation, and energy costs are a major factor in its operational budget.
High Capital and Maintenance Costs
These are complex, expensive machines. The graphite electrodes used to create the arc are consumed during operation and must be replaced regularly, adding a significant maintenance cost on top of the initial investment.
Over-engineering for Most Tasks
For countless applications, from home heating to many industrial processes like annealing or tempering, temperatures above 1,500°C are simply unnecessary. In these cases, a simpler and more cost-effective fuel-fired furnace is the superior choice.
Matching the Furnace to the Task
The "best" furnace is the one that most efficiently meets the temperature requirements of the specific goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale metal recycling and production: The industrial electric arc furnace is the unmatched standard for its raw melting power.
- If your primary focus is scientific research or material testing: A specialized laboratory furnace (tube, muffle, or box) provides the precise control needed for extreme temperature experiments.
- If your primary focus is general industrial heat treatment below 1,500°C: Fuel-fired or standard resistance-based electric furnaces offer a much more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of heat generation allows you to select the right tool for any thermal challenge.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | > 3,000°C (5,432°F) | Steelmaking, advanced materials research |
| Laboratory Furnace (Tube/Muffle) | Up to 3,000°C (5,432°F) | Scientific research, materials testing |
| Fuel-Fired Furnace (Gas/Oil) | < 1,800°C (3,272°F) | General industrial heat treatment |
Need a high-temperature solution for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust furnaces for demanding applications. Whether you're in materials science, metallurgy, or R&D, our expertise ensures you get the precise thermal performance you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How to clean an alumina tube furnace? Extend Tube Life and Ensure Experimental Purity
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















