Increasing the substrate temperature during film deposition is a primary method for improving film quality. A higher temperature provides depositing atoms with more kinetic energy, allowing them to arrange into a denser, more ordered structure with fewer defects. This directly enhances the film's structural, optical, and electrical properties.
The core principle is simple: higher substrate temperature increases the surface mobility of deposited atoms. This allows them to move around on the surface, find more stable energy sites, and form a higher-quality film, but this benefit must be balanced against thermal constraints and induced stress.
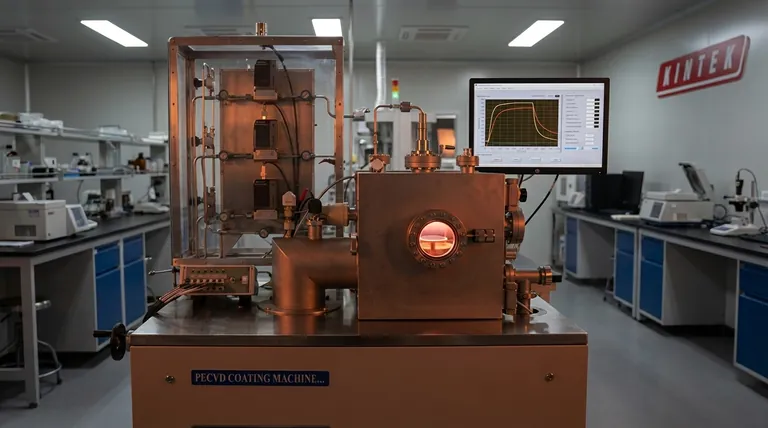
The Core Mechanism: Enhancing Atomic Mobility
The fundamental reason substrate temperature is so influential is its effect on the energy of the atoms as they land on the surface.
What is Surface Mobility?
When atoms or molecules arrive at the substrate during deposition, they are called adatoms.
Surface mobility is the ability of these adatoms to diffuse or move across the surface before locking into their final position.
Higher substrate temperature directly translates to higher thermal energy, which fuels this movement.
Finding Lower-Energy States
A rough, porous film with many defects is in a high-energy, unstable state. A dense, well-ordered crystalline film is in a much lower-energy, stable state.
By increasing surface mobility, you give adatoms the energy needed to escape from less-than-ideal positions and settle into these preferred low-energy sites. This process effectively "self-anneals" the film as it grows.
Key Improvements in Film Properties
This increase in atomic mobility leads to several measurable and highly desirable improvements in the final thin film.
Increased Film Density
With greater mobility, adatoms can more effectively fill microscopic voids and gaps. This migration results in a film that is physically denser and less porous.
Reduced Defect Density
Many film defects are the result of atoms getting "stuck" in the wrong place. Higher temperatures help compensate for dangling bonds and other structural imperfections.
This reduction in the density of local states creates a more ordered, and often more crystalline, structure.
Improved Adhesion and Crystallinity
Enhanced surface mobility at the film-substrate interface promotes better chemical bonding and mechanical interlocking, which significantly improves adhesion.
Furthermore, the ability of atoms to arrange themselves properly encourages the formation of larger, more uniform crystalline grains.
Altered Electrical and Optical Properties
The structural improvements are not just mechanical. A film with fewer defects and a more ordered structure will typically exhibit higher electron mobility and different optical properties (like refractive index or transparency).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While higher temperature is generally beneficial, it is not a universal solution and comes with critical constraints.
Thermal Mismatch Stress
As the substrate and newly deposited film cool down after deposition, they shrink. If the film and substrate have different coefficients of thermal expansion, one will shrink more than the other.
This mismatch induces significant mechanical stress in the film, which can be strong enough to cause cracking, peeling, or warping.
Substrate Material Constraints
The choice of substrate often places a hard limit on the maximum process temperature.
Polymeric substrates for flexible electronics, for example, have low melting or glass transition temperatures. Similarly, some compound semiconductors like GaAs can degrade or decompose if heated excessively.
Matching Temperature to Your Objective
The optimal substrate temperature is a function of the materials involved and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum film quality and density: Use the highest temperature that your substrate and film materials can tolerate without damage or unwanted chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is minimizing film stress: You must carefully balance the benefits of higher temperature with the stress induced by thermal expansion mismatch.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive substrates: You are forced to use lower temperatures and may need to compensate by using other deposition techniques to add energy to the growing film.
Ultimately, controlling substrate temperature is about intentionally managing the energy available to depositing atoms to build the desired film structure.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Impact on Film Properties |
|---|---|
| Increased Temperature | Higher density, fewer defects, improved crystallinity & adhesion |
| Decreased Temperature | Higher porosity, more defects, amorphous structure, lower stress |
| Key Trade-off | Higher quality vs. thermal stress & substrate limitations |
Achieve precise control over your thin film properties with KINTEK.
Whether you are developing advanced semiconductors, optical coatings, or flexible electronics, the substrate temperature is a critical parameter. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including deposition systems with precise temperature control, to help you optimize film density, crystallinity, and minimize stress for your specific substrate and material requirements.
Let our experts help you build a better film. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the ideal solution for your laboratory's thin film deposition needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















