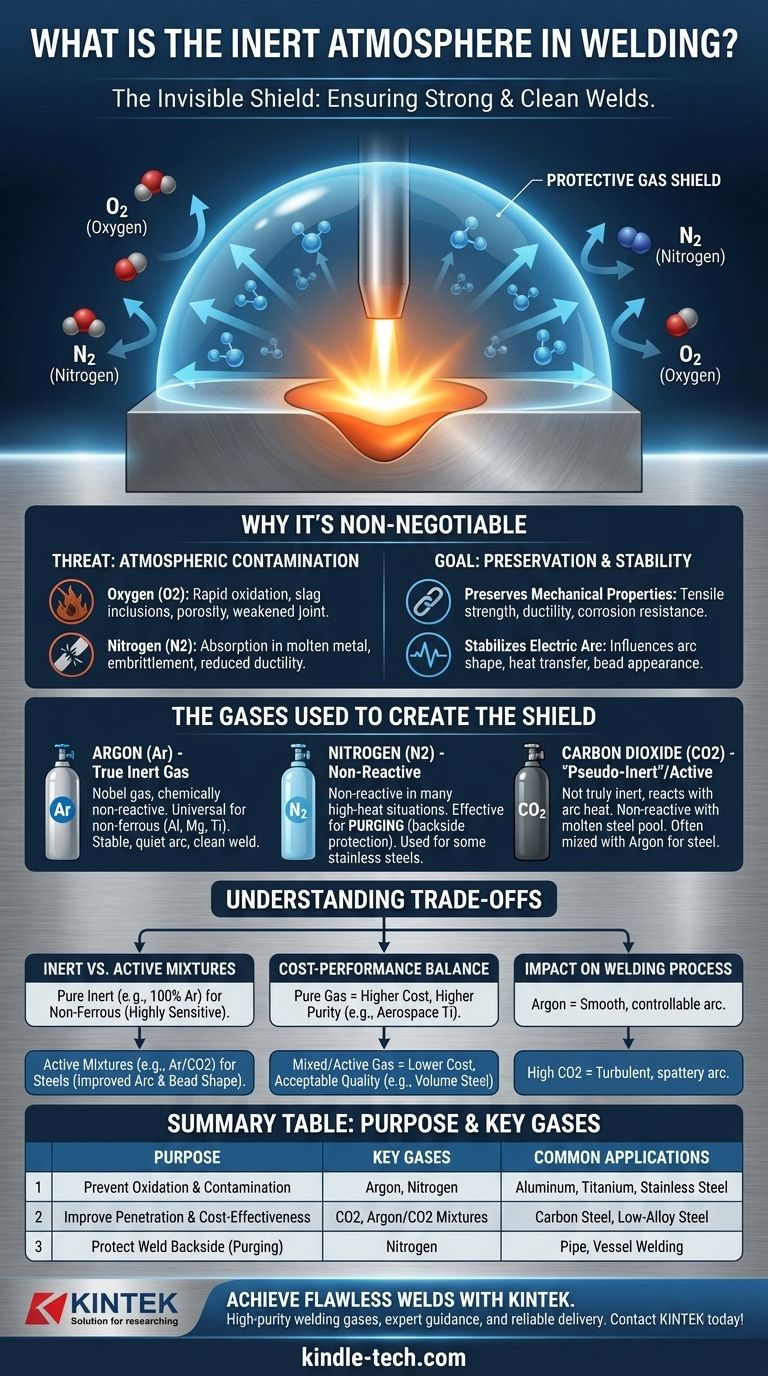
In welding, an inert atmosphere is a protective shield of gas deliberately flooded around the welding arc and the molten metal pool. This gaseous shield displaces the surrounding air, specifically oxygen and nitrogen, which are highly reactive with hot metal. By creating this controlled environment, the inert atmosphere prevents contamination and defects, ensuring the finished weld is strong and clean.
The core purpose of an inert atmosphere is not the gas itself, but its function: to create a sterile zone around the molten weld. By physically pushing away reactive atmospheric gases, this shield preserves the chemical integrity and structural strength of the final weldment.

Why a Protective Atmosphere is Non-Negotiable
To understand the role of an inert atmosphere, one must first appreciate the vulnerability of molten metal. It is in a highly reactive state, ready to combine with any element it touches.
The Threat of Atmospheric Contamination
Without a protective shield, the intense heat of the welding arc would cause the molten metal to react instantly with the air.
Oxygen is the primary enemy, causing rapid oxidation (like rust) that creates slag inclusions and porosity (tiny gas bubbles trapped in the weld), both of which severely weaken the joint.
Nitrogen, while often thought of as stable, can be absorbed by some molten metals, leading to embrittlement and a dramatic reduction in the weld's ductility and toughness.
Preserving Mechanical Properties
A proper inert atmosphere ensures the weld metal cools and solidifies with the intended chemical composition.
This preserves critical mechanical properties like tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. A contaminated weld is, by definition, a failed weld.
Stabilizing the Electric Arc
Beyond just protection, the shielding gas itself becomes part of the electrical circuit.
The type of gas used influences the arc's stability, the shape of the weld bead, and the way heat is transferred from the arc to the workpiece.
The Gases Used to Create the Shield
While many gases exist, only a select few have the right properties for creating a welding atmosphere. They are broadly categorized as inert, non-reactive, or part of an active mixture.
True Inert Gases: Argon (Ar)
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically non-reactive under any welding condition.
It is the universal standard for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, magnesium, and titanium. It produces a very stable, quiet arc and a clean weld appearance.
Non-Reactive Gases: Nitrogen (N2)
While not technically a noble gas, nitrogen is often used to create an inert atmosphere because it is non-reactive in many high-heat situations.
It is particularly effective and economical for purging—the process of filling the inside of a pipe or vessel with gas to protect the backside of a weld from oxygen. It can also be used as a primary shielding gas for certain stainless steels.
"Pseudo-Inert" and Active Gases: Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Some gases are not truly inert but behave as such in specific contexts. Carbon Dioxide is the most common example.
While it can react with the high temperature of the arc, it is largely non-reactive with the molten weld pool in steel welding. It is often mixed with Argon to improve weld penetration and is significantly less expensive.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of gas is a critical decision driven by metallurgy, cost, and the desired outcome. No single gas is perfect for every application.
Inert vs. Active Gas Mixtures
Pure inert gases like Argon are mandatory for non-ferrous metals that are highly sensitive to any form of oxidation.
Active gas mixtures, typically Argon with a small percentage of CO2 or Oxygen, are used for welding steels. The "active" component can actually improve arc stability and bead shape for these materials, offering better performance than a pure inert gas.
The Cost-Performance Balance
There is a direct correlation between gas purity and cost. Pure Argon is significantly more expensive than crude Carbon Dioxide.
For high-volume steel fabrication, using an Ar/CO2 mix or even pure CO2 provides an acceptable weld quality at a much lower operational cost. For aerospace or medical applications involving titanium, the high cost of pure Argon is a non-negotiable requirement.
Impact on the Welding Process
The gas choice directly affects the welder's experience. An Argon-shielded arc is smooth and easy to control.
A process shielded with a high concentration of CO2 tends to produce a more turbulent, spattery arc that requires greater operator skill to manage.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Weld
Your choice of shielding gas must be a deliberate one, aligned with the material you are welding and your quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is welding non-ferrous metals (like aluminum or titanium): A pure inert gas, typically 100% Argon, is required to prevent any chemical reaction and ensure a clean weld.
- If your primary focus is welding carbon or low-alloy steel: An active gas mixture, such as 75% Argon and 25% Carbon Dioxide, often provides the best balance of weld quality, deep penetration, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on the backside of a weld (purging): Nitrogen is an excellent and economical choice for creating an inert backing atmosphere, especially for stainless steels.
Ultimately, understanding the role of the atmosphere transforms welding from a simple process into a controlled science.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Gases | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation & Contamination | Argon (Inert), Nitrogen (Non-Reactive) | Aluminum, Titanium, Stainless Steel |
| Improve Penetration & Cost-Effectiveness | Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Argon/CO2 Mixtures | Carbon Steel, Low-Alloy Steel |
| Protect Weld Backside (Purging) | Nitrogen | Pipe, Vessel Welding |
Achieve Flawless Welds with the Right Atmosphere
Selecting the correct inert atmosphere is critical for weld integrity and performance. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-purity welding gases and equipment to meet your specific laboratory and industrial needs.
We provide:
- High-purity Argon, Nitrogen, and specialized gas mixtures.
- Expert guidance to match the gas to your material and application.
- Reliable delivery and support for your lab's consumables.
Ensure your welds are strong, clean, and defect-free. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your welding gas requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What does a heat treatment do? Unlock Your Material's Full Potential
- What are the factors of powder metallurgy? Master the Key to High-Performance Parts
- Why argon is used in magnetron sputtering? The Ideal Gas for Efficient Thin Film Deposition
- Can metals be sintered? A Guide to Manufacturing Strong, Complex Metal Parts
- What does the acronym CVD stand for? Decoding Its Meaning in Medicine and Technology
- What machine is used for cutting diamond? Discover the Laser Technology That Shapes Gems
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production



















