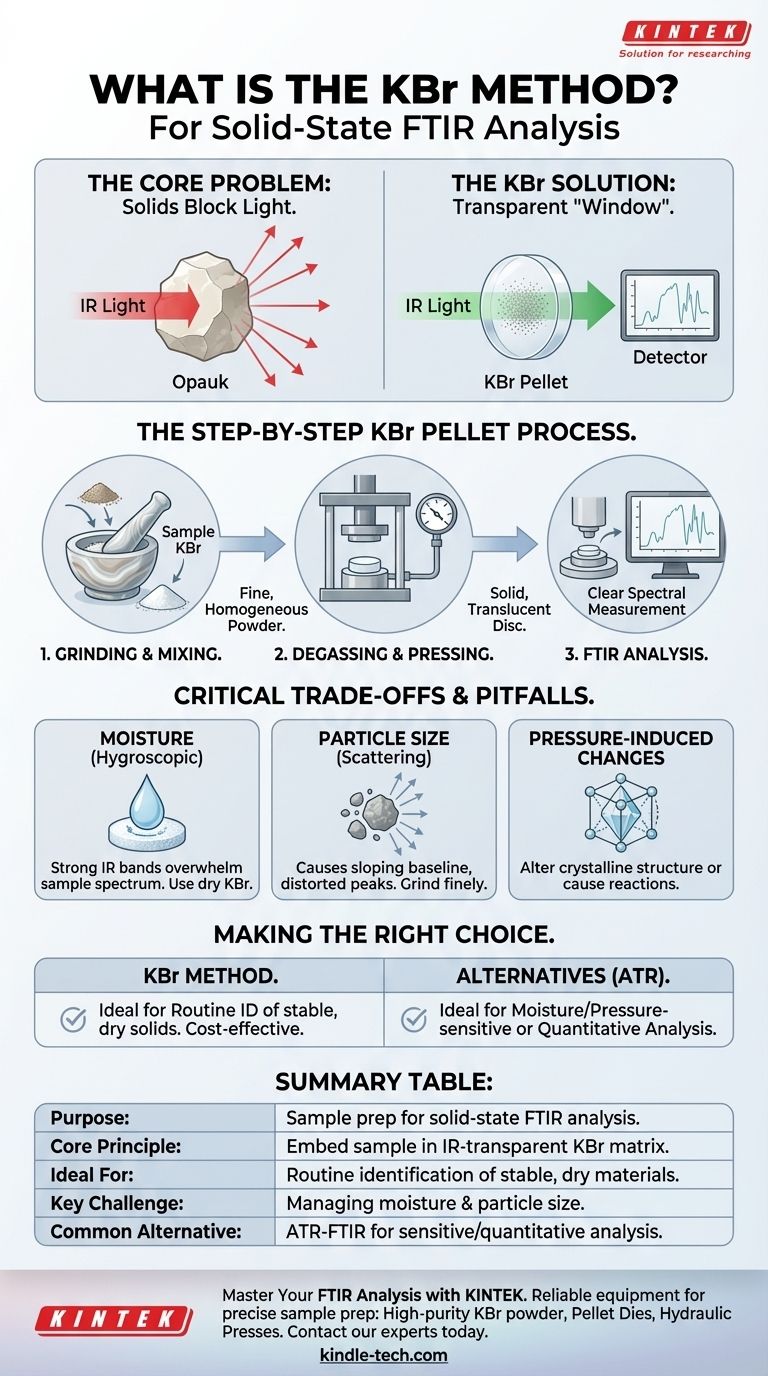
The KBr method is a widely used sample preparation technique for analyzing solid-state materials using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It involves finely grinding a sample with potassium bromide (KBr) powder and compressing the mixture under high pressure to form a small, transparent disc, or "pellet." This pellet can then be placed directly in the path of the spectrometer's infrared beam for analysis.
The core principle is simple: potassium bromide is transparent to infrared radiation. By embedding a small amount of a solid sample within a transparent KBr matrix, you create a "window" that allows the spectrometer's light to pass through and interact only with your sample, revealing its unique chemical fingerprint.

The Core Problem: Analyzing Solids with Light
Infrared spectroscopy works by passing infrared light through a substance and measuring which wavelengths are absorbed. This process is straightforward for liquids and gases, but presents a fundamental challenge for solid materials.
Why Solids Are Challenging
Most solid samples are opaque in their natural state. Attempting to pass an IR beam through a solid chunk or even a coarse powder will result in the light being completely blocked or scattered in all directions, making a useful measurement impossible.
The KBr Solution
The KBr method solves this problem by using potassium bromide (KBr) as an ideal matrix material. Under immense pressure, the crystalline KBr powder becomes plastic and fuses into a solid, glass-like sheet that is almost perfectly transparent to infrared light. The sample, ground into tiny particles, becomes evenly dispersed within this transparent medium, allowing for a clear spectral measurement.
The Step-by-Step KBr Pellet Process
Creating a high-quality KBr pellet is a precise process where each step is critical for an accurate result.
Grinding and Mixing
First, a tiny amount of the sample (typically less than 1%) is mixed with pure, dry KBr powder. The mixture is then ground extensively, usually with an agate mortar and pestle, to reduce the sample's particle size to a fine powder. This step is crucial to minimize light scattering and ensure the sample is distributed homogeneously.
Degassing and Pressing
The fine powder is placed into a pellet die. The die is briefly put under a vacuum to remove trapped air and, most importantly, adsorbed water moisture. It is then placed in a hydraulic press and subjected to high pressure (several tons per square inch), which causes the KBr to fuse into a solid, translucent disc.
The Final Product
The ideal result is a thin, uniform pellet that looks like a small, clear or slightly cloudy piece of glass. This pellet is then carefully removed from the die and placed in a sample holder for immediate analysis in the FTIR spectrometer.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While effective, the KBr method is sensitive and requires careful technique to avoid common errors that can compromise the quality of the spectrum.
The Critical Role of Moisture
Potassium bromide is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Water has very strong IR absorption bands that can easily overwhelm the spectrum of your actual sample. Using dry KBr, working quickly, and storing pellets in a desiccator are essential.
Particle Size and Scattering
If the sample is not ground finely enough, its particles will scatter the IR light rather than absorb it. This results in a poor-quality spectrum with a sloping baseline and distorted peak shapes, an issue known as the Christiansen effect.
Pressure-Induced Changes
The high pressures used to form the pellet can sometimes alter the crystalline structure of the sample itself. This can cause shifts in the spectral peaks compared to the material's native state. Furthermore, some samples may react with the KBr under pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The KBr method is a powerful tool, but it's one of several available for solid-state analysis. Your choice should depend on your sample and your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is routine identification of stable solids: The KBr method is a cost-effective and well-established technique that provides high-quality results when performed correctly.
- If your sample is sensitive to moisture or pressure: You should consider alternative methods like creating a Nujol mull or, more commonly, using Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) spectroscopy.
- If your goal is quantitative analysis: The KBr method is difficult to use for quantitation due to unavoidable variations in pellet thickness and sample concentration; ATR is almost always the superior choice here.
Ultimately, mastering sample preparation is the key to obtaining a meaningful infrared spectrum.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Sample preparation for solid-state FTIR analysis. |
| Core Principle | Embed sample in a transparent KBr matrix to create an IR-transparent pellet. |
| Ideal For | Routine identification of stable, dry solid materials. |
| Key Challenge | Managing moisture (KBr is hygroscopic) and achieving fine particle size. |
| Common Alternative | ATR-FTIR for moisture-sensitive or quantitative analysis. |
Master Your FTIR Analysis with KINTEK
Obtaining a clear, high-quality FTIR spectrum starts with perfect sample preparation. Whether you're using the classic KBr pellet method or exploring modern ATR techniques, having the right equipment is crucial for success.
KINTEK specializes in supplying reliable laboratory equipment and consumables, including high-purity KBr powder, pellet dies, and hydraulic presses, to ensure your sample prep is precise and reproducible.
Let us help you achieve accurate and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific lab needs and find the perfect solution for your analytical challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy



















