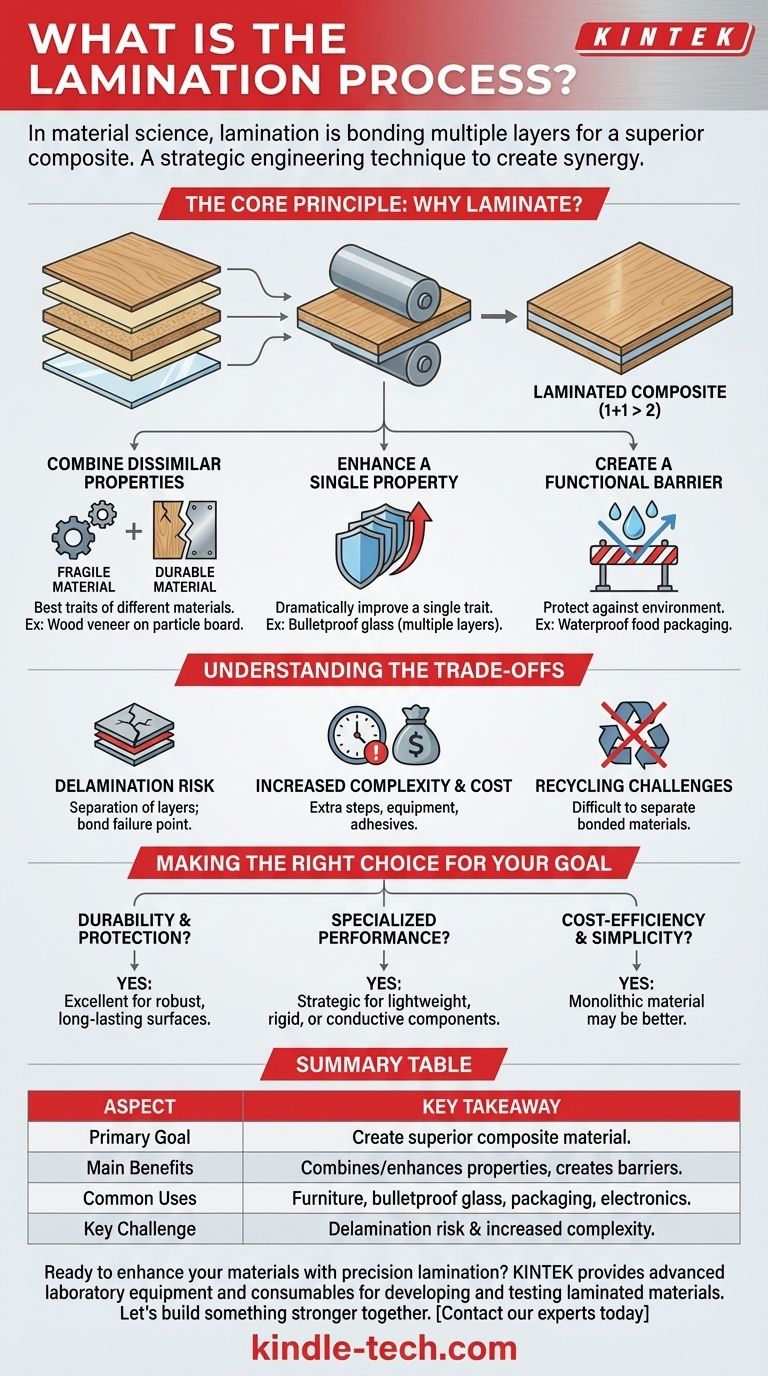
In material science and manufacturing, lamination is the process of bonding two or more layers of material together to create a single, improved composite sheet or object. The fundamental goal is to combine the distinct properties of different layers—such as strength, appearance, or stability—into a final product that is superior to any of its individual components.
Lamination is not simply about stacking materials; it's a strategic engineering technique used to create a new, composite material that is functionally greater than the sum of its parts. It allows designers to overcome the limitations of a single material by layering others with it.
The Core Principle: Why Laminate?
The decision to laminate a material is driven by the need to achieve a specific performance characteristic that a single material cannot provide on its own. The process is about creating synergy between layers.
Combining Dissimilar Properties
The most common reason for lamination is to combine the best traits of different materials. A thin, brittle material can be laminated with a flexible, durable one to create a final product that is both strong and resilient.
For example, a decorative wood veneer (which is fragile) can be laminated onto a core of particle board (which is stable but unattractive) to create a piece of furniture that is both beautiful and structurally sound.
Enhancing a Single Property
Sometimes, lamination involves layering the same material repeatedly. This is often done to dramatically enhance a single property, such as impact resistance.
Bulletproof glass is a perfect example. It consists of multiple layers of glass laminated with a clear polymer like polyvinyl butyral (PVB). A single, thick sheet of glass would shatter on impact, but the laminated layers absorb and distribute the energy, preventing penetration.
Creating a Functional Barrier
Lamination is highly effective for creating a barrier against environmental factors. By bonding a non-porous layer, like a plastic film, to a porous one, like paper, you can make the material waterproof, airtight, or resistant to grease.
This is the principle behind food packaging that keeps products fresh, restaurant menus that can be wiped clean, and floor coverings that resist stains and moisture.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, lamination is a specific engineering choice with its own set of challenges that must be considered.
The Risk of Delamination
The single greatest weakness of a laminated material is delamination—the separation of its constituent layers. This can be caused by a failure of the adhesive, exposure to moisture or heat, or physical stress. The bond between layers is the most common point of failure.
Increased Complexity and Cost
Lamination is an additional manufacturing step. It requires specialized equipment, adhesives, and process controls (for heat, pressure, and curing time), all of which add complexity and cost to the final product. For simple applications, a single monolithic material is almost always cheaper.
Recycling and Environmental Challenges
Composite materials created through lamination are notoriously difficult to recycle. Because they are made of different materials permanently bonded together (e.g., plastic and aluminum foil in a juice pouch), separating them for recycling is often economically or technically unfeasible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use a laminated material depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for performance, cost, and longevity.
- If your primary focus is durability and protection: Lamination is an excellent choice for creating robust, long-lasting surfaces that can withstand wear, moisture, or UV exposure.
- If your primary focus is specialized performance: Use lamination to strategically combine properties, such as creating lightweight-yet-rigid structural components or integrating conductive layers within electronics like circuit boards.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and simplicity: A single, monolithic material may be a better choice, as lamination adds manufacturing expense and complexity that may not be justified.
Ultimately, lamination empowers engineers and designers to create materials with precision, overcoming inherent limitations by combining the best attributes of multiple layers.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Create a composite material superior to its individual layers. |
| Main Benefits | Combines dissimilar properties, enhances single properties, creates functional barriers. |
| Common Uses | Furniture, bulletproof glass, food packaging, electronics. |
| Key Challenge | Risk of delamination and increased manufacturing complexity. |
Ready to enhance your materials with precision lamination?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables needed to develop, test, and perfect laminated materials. Whether you're working on high-performance composites, durable packaging, or innovative electronics, our solutions help you achieve superior bonding and reliable results.
Let's build something stronger together. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials
- Why is a heated laboratory hydraulic press necessary for composite laminates? Achieve Void-Free Structural Integrity



















