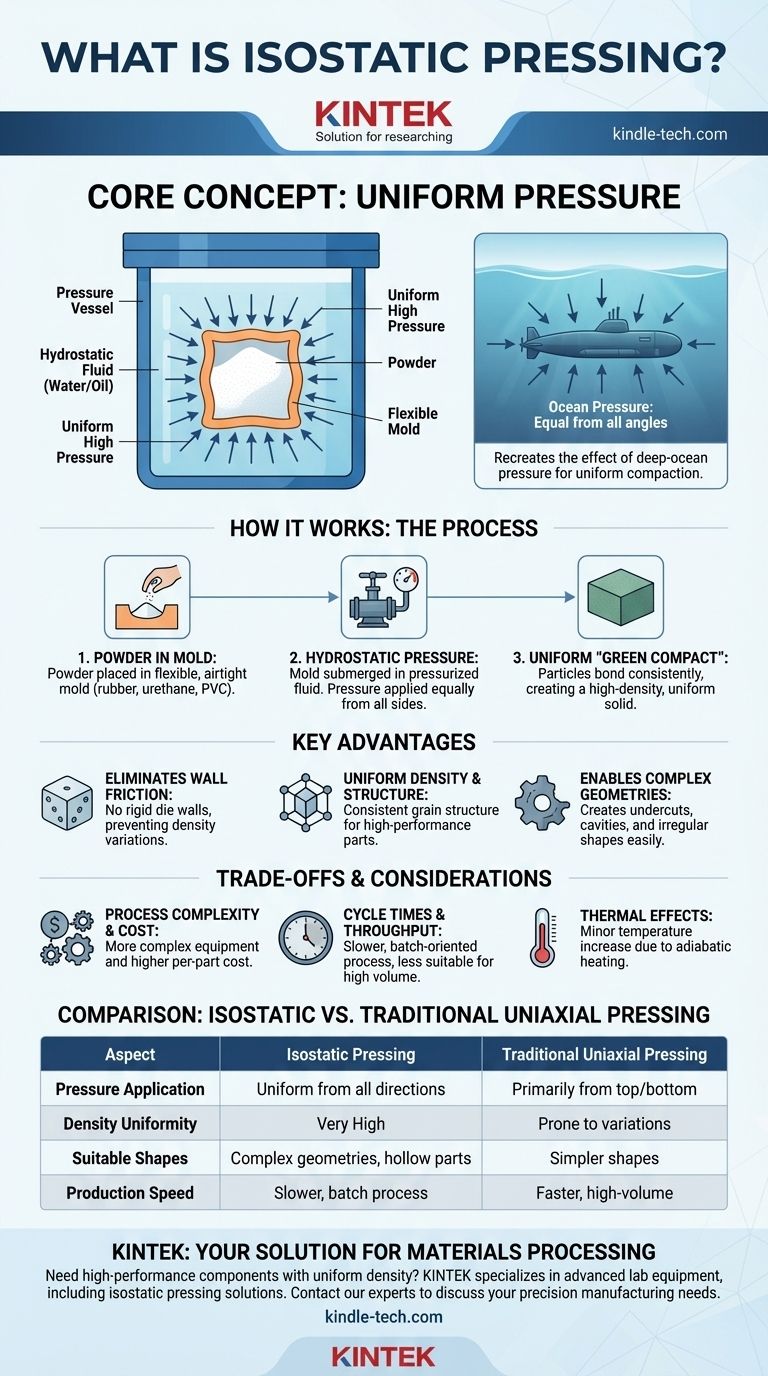
In essence, isostatic pressing is a materials processing technique that compacts a powder into a solid object by subjecting it to uniform, high pressure from all directions simultaneously. Imagine an object submerged deep in the ocean—the water pressure acts on it equally from every angle. Isostatic pressing recreates this effect by placing the powder in a flexible mold and then immersing that mold in a fluid that is pressurized, ensuring the powder is compacted with exceptional uniformity.
The core value of isostatic pressing is its ability to overcome the fundamental limitations of traditional pressing methods. By applying pressure equally in all directions, it eliminates density variations caused by friction, resulting in highly uniform, high-density parts, even those with complex shapes.

How Isostatic Pressing Works: The Core Mechanism
Isostatic pressing is chosen when the final component's integrity and uniformity are paramount. The process is elegant in its simplicity and effectiveness.
The Setup: Powder in a Flexible Mold
The process begins with a powder, typically a metal or ceramic, which is the raw material for the final part. This powder is poured into a flexible, airtight mold, often made of rubber, urethane, or PVC, that is shaped into the desired final geometry.
The Application of Hydrostatic Pressure
This sealed, flexible mold is then placed inside a high-pressure chamber. The chamber is filled with a liquid, such as water or oil. A pump then pressurizes this liquid, creating immense hydrostatic pressure that is transmitted uniformly through the flexible mold walls and onto the powder inside.
The Result: A Uniform "Green Compact"
Because the pressure is isostatic (equal from all directions), the powder particles are forced together with incredible consistency. This creates a uniformly dense object known as a "green compact"—a part that is solid and can be handled but has not yet been sintered (heated) to achieve its final strength.
Why Choose Isostatic Pressing? Key Advantages
The method's primary benefits stem directly from its use of uniform pressure, solving problems inherent in other compaction techniques.
Eliminating Wall Friction
In traditional uniaxial pressing, where pressure is applied from one or two directions (top and bottom), friction between the powder and the rigid die walls prevents pressure from being transmitted evenly. This leads to significant density variations within the part, creating weak spots. Isostatic pressing has no rigid die walls, completely eliminating this problem.
Achieving Uniform Density and Structure
By removing friction as a variable, isostatic pressing produces parts with a practically uniform grain structure and density. This consistency is critical for high-performance applications where predictable mechanical properties, like strength and wear resistance, are non-negotiable.
Enabling Complex Geometries
Uniaxial presses are limited to relatively simple shapes that can be ejected from a rigid die. Isostatic pressing allows for the creation of far more complex geometries, including parts with undercuts, internal cavities, or irregular contours, because the flexible mold can be easily removed from the compacted part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, isostatic pressing is not the universal solution for all applications. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Process Complexity and Cost
The equipment required for isostatic pressing—high-pressure vessels, pumps, and fluid-handling systems—is more complex and expensive than a conventional mechanical press. This often translates to a higher cost per part, especially for simple geometries.
Cycle Times and Throughput
Isostatic pressing is generally a slower, batch-oriented process compared to the high-speed, continuous nature of automated uniaxial pressing. This makes it less suitable for extremely high-volume production of simple components.
Thermal Effects
The rapid application of immense pressure can cause a slight temperature increase in the material due to adiabatic heating. While often minor, this effect may need to be managed with chamber cooling for temperature-sensitive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct compaction method depends entirely on the technical requirements and economic constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple shapes: Traditional uniaxial pressing is often the more cost-effective and faster solution.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and uniform material properties: Isostatic pressing is the superior choice for creating reliable, high-performance components.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing parts with complex or hollow geometries: Isostatic pressing provides the design freedom that other powder compaction methods cannot match.
By understanding its principle of uniform pressure, you can leverage isostatic pressing to engineer components that overcome the fundamental limits of conventional manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Isostatic Pressing | Traditional Uniaxial Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Application | Uniform from all directions | Primarily from top/bottom |
| Density Uniformity | Very High | Prone to variations |
| Suitable Shapes | Complex geometries, hollow parts | Simpler shapes |
| Production Speed | Slower, batch process | Faster, high-volume |
Need to produce high-performance components with uniform density and complex geometries?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for materials processing like isostatic pressing. Our expertise can help you achieve superior part integrity and reliability for your most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's precision manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
















