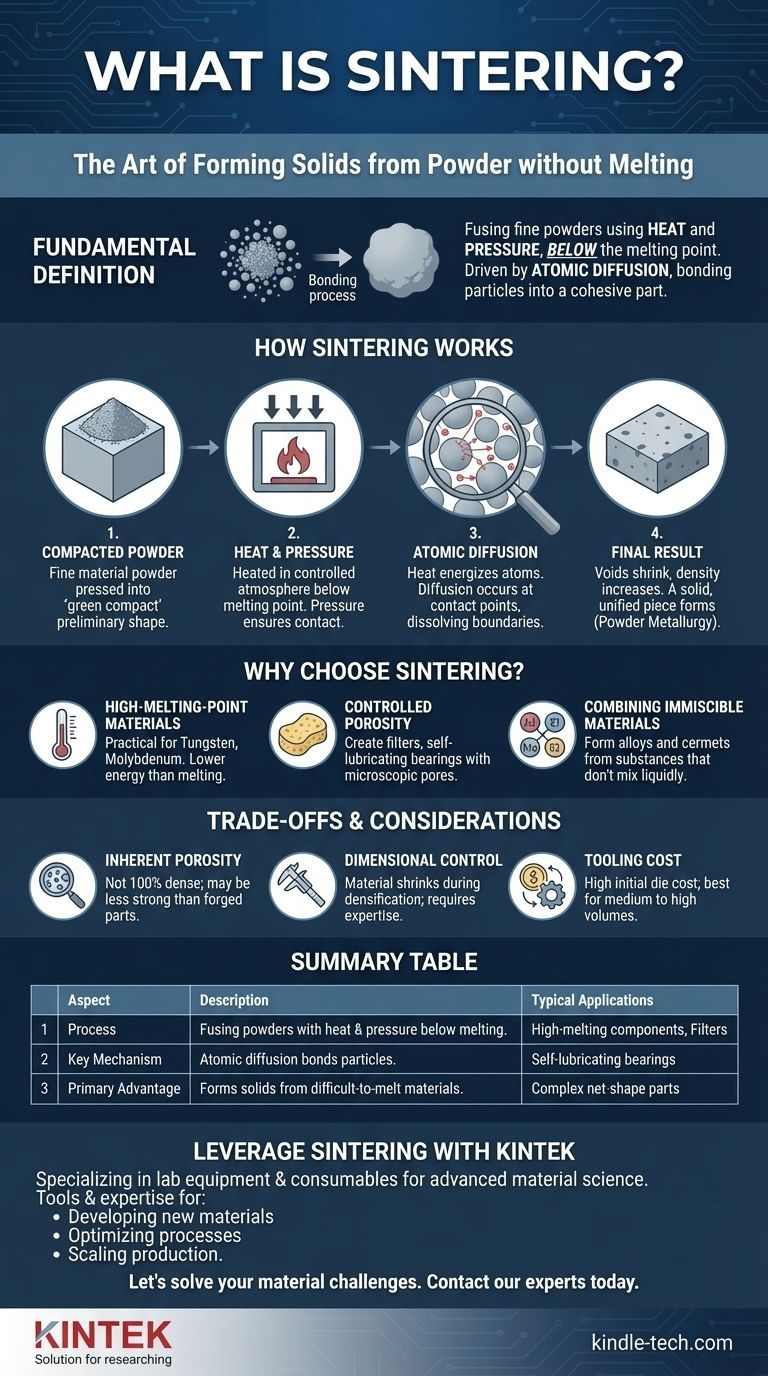
In material science and manufacturing, the term "sintered" describes a material or part that has been formed by fusing fine powders together using heat and pressure. Crucially, this process occurs without melting the material into a liquid state. Instead, atoms from adjacent particles migrate across their boundaries, bonding the powder into a solid, cohesive mass.
The core problem sintering solves is how to form a solid object from materials that are difficult or impractical to melt. It provides a method to create strong, often complex parts by bonding powders at temperatures below their melting point, unlocking unique material properties and manufacturing efficiencies.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
To understand what "sintered" means, you must first understand the process. It transforms a loose powder into a solid component through a specific sequence of physical changes driven by energy.
The Starting Point: A Compacted Powder
The process begins with a fine powder of a specific material, such as metal, ceramic, or plastic. This powder is typically placed into a die or mold and compacted under high pressure to form a "green compact," which is a fragile, preliminary shape.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
The green compact is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below the material's melting point. This heat provides the thermal energy necessary to initiate bonding, while pressure ensures the particles remain in intimate contact.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
This is the key to sintering. The applied heat energizes the atoms within the powder particles. At the points where particles touch, atoms begin to migrate, or diffuse, across the boundaries. This diffusion effectively dissolves the boundaries between individual particles, fusing them together.
The Final Result: A Solid, Unified Part
As this process continues, the voids between the particles shrink, and the material becomes denser and stronger. The final result is a single, solid piece that has been formed directly from powder, a core technique in the field of powder metallurgy.
Why Choose Sintering Over Melting?
Sintering is not simply an alternative to melting and casting; it is chosen for specific strategic advantages that traditional methods cannot offer.
Working with High-Melting-Point Materials
Some materials, like tungsten and molybdenum, have exceptionally high melting points. Reaching these temperatures is incredibly energy-intensive and technically challenging. Sintering allows for the creation of solid parts from these materials at much lower, more manageable temperatures.
Creating Controlled Porosity
Because sintering starts with individual particles, the final part naturally contains microscopic pores. This can be precisely controlled to create components like filters, which rely on a porous structure to function. It is also used to make self-lubricating bearings, where the pores are impregnated with oil.
Combining Immiscible Materials
Sintering makes it possible to create composite materials from substances that would not mix in a liquid state (like oil and water). By mixing their powders and sintering them, you can create alloys and cermets (ceramic-metal composites) with unique combined properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that represent trade-offs compared to other manufacturing methods.
Inherent Porosity and Mechanical Strength
Unless secondary operations are performed, sintered parts are almost never 100% dense. The remaining porosity can act as a stress concentration point, meaning sintered parts are often less strong than parts forged or machined from a solid billet of the same material.
Dimensional Control
The material shrinks as it densifies during sintering. Predicting and controlling this shrinkage to achieve tight dimensional tolerances requires significant process expertise and control.
Tooling and Production Volume
Creating the precision dies used to compact the powder can be expensive. This high initial tooling cost means sintering is most cost-effective for medium to high-volume production runs where the cost can be amortized over many parts.
Key Applications of Sintering
Understanding when to leverage sintering is key to using it effectively.
- If your primary focus is creating components like filters or self-lubricating bearings: Sintering is ideal because it allows for precise control over the final part's porosity.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing parts from extremely high-melting-point metals like tungsten: Sintering is the most practical and energy-efficient method, avoiding the challenges of liquefaction.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, near-net-shape parts in high volumes: Powder metallurgy using sintering minimizes material waste and secondary machining, making it highly cost-effective at scale.
Ultimately, sintering is a foundational process that enables the creation of advanced materials and components that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to manufacture.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Fusing fine powders using heat and pressure, below the material's melting point. |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion bonds particles together, densifying the material. |
| Primary Advantage | Forms solid objects from materials that are difficult or impractical to melt. |
| Common Materials | Metals (e.g., tungsten), ceramics, plastics, and composite materials. |
| Typical Applications | High-melting-point components, porous filters, self-lubricating bearings, complex net-shape parts. |
Ready to Leverage Sintering for Your Lab or Production Needs?
Sintering unlocks unique material properties and manufacturing efficiencies, but it requires precise control and the right equipment to be successful. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that support advanced material science processes like sintering.
We provide the tools and expertise to help you:
- Develop new materials with controlled porosity and composite structures.
- Optimize your sintering process for consistent, high-quality results.
- Scale your production from R&D to manufacturing.
Let's discuss how sintering can solve your specific material challenges. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace used for high-temperature calcination? Maximize Adsorbent Porosity and Surface Area
- What is the temperature range for annealing hardening? Master the Key to Metal Properties
- Why is a high-precision muffle furnace required for the thermal decomposition of siderite to produce nano-iron oxide?
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to LATP ceramics post-heat treatment? Optimize Your Microstructure Repair
- Why is a 1100°C sintering furnace required for delafossite-type catalysts? Unlock High-Performance Atomic Diffusion
- Which of the following are the important temperature controls used in sintering furnace? Mastering Precise Thermal Profiles for Superior Materials
- What is the role of a high-temperature box furnace in 9Cr-1Mo steel normalizing? Achieve Precise Microstructure Control
- What is the difference between an oven and a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Thermal Equipment



















