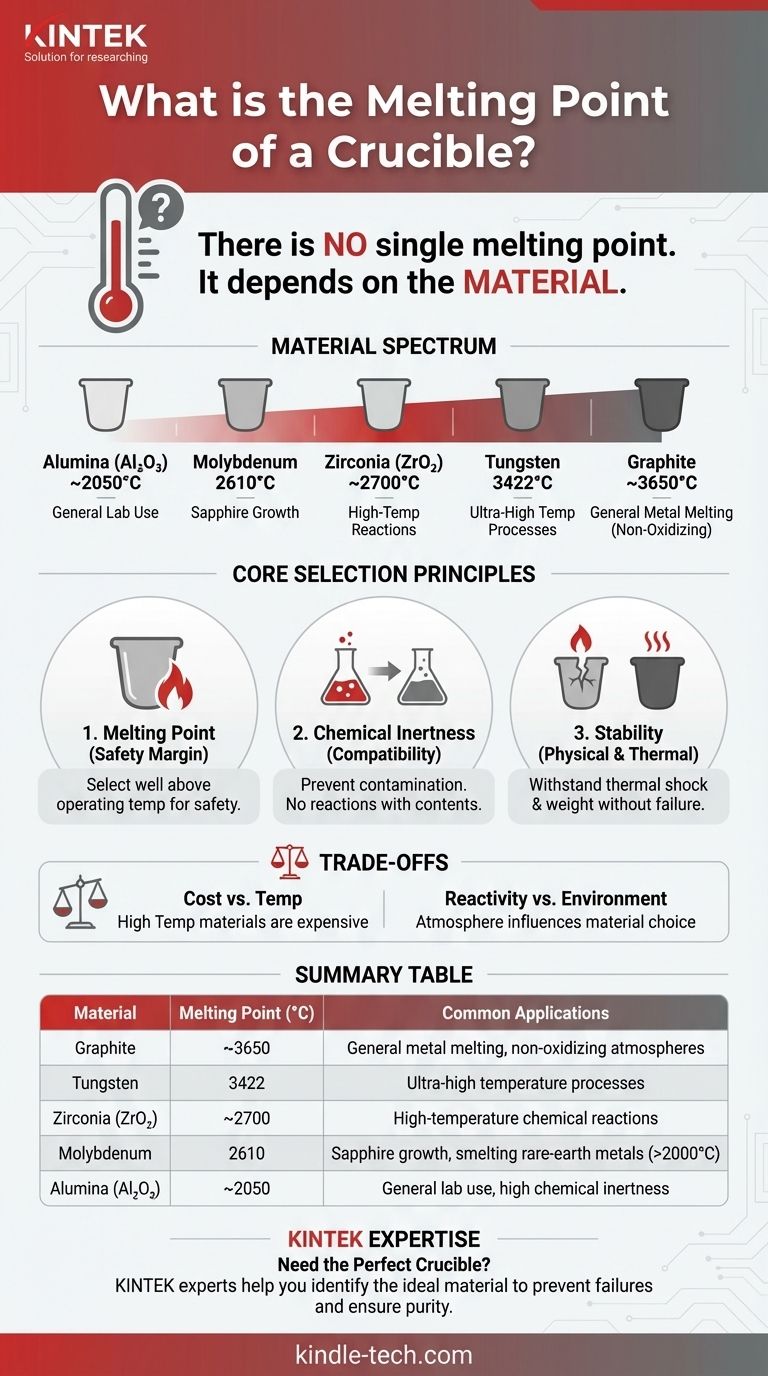
There is no single melting point for a crucible because the term "crucible" describes a type of container, not a specific material. The melting point is entirely determined by the material it is made from, which can range from clay and graphite to highly refractory metals like molybdenum, which has a melting point of up to 2610°C (4730°F).
A crucible's most important characteristic is having a melting point significantly higher than the substance it is intended to contain. The choice of crucible material is therefore dictated by the specific temperature and chemical requirements of the application.

Why Material Defines the Crucible
A crucible is simply a container designed to withstand extremely high temperatures for processes like melting metals, growing crystals, or conducting high-temperature chemical reactions. Because these applications vary so widely, crucibles are made from a diverse range of materials.
The Function Defines the Tool
The primary job of a crucible is to remain stable and inert at extreme temperatures. It must hold its shape and not react with the contents it holds, which would cause contamination and equipment failure.
A Spectrum of Materials
Different tasks demand different materials. For example, a molybdenum crucible, with its 2610°C melting point, is used in industrial furnaces that operate above 2000°C for applications like sapphire crystal growth or smelting rare-earth metals. Other common materials include alumina, zirconia, graphite, and tungsten, each with its own unique melting point and chemical properties.
Core Principles for Crucible Selection
Choosing the right crucible involves more than just looking at the melting point. It requires a holistic assessment of the entire high-temperature process to ensure reliability and prevent catastrophic failure.
Melting Point is the First Step
The rule of thumb is to select a crucible with a maximum service temperature well above your planned operating temperature. The gap between the operating temperature and the melting point provides a critical safety margin.
Chemical Inertness is Critical
A crucible must be chemically compatible with the substance being heated. If the crucible reacts with its contents, it can introduce impurities into the melt and degrade the crucible itself, leading to cracks or leaks.
Physical and Thermal Stability
The chosen material must be able to withstand rapid changes in temperature (thermal shock) without cracking. It must also be physically strong enough at high temperatures to hold the weight of the molten material without deforming.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible is always a balance between performance requirements and practical constraints. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
Materials with the highest melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum, are typically far more expensive than materials like clay-graphite or alumina, which are suitable for lower-temperature applications.
Reactivity vs. Environment
The environment inside the furnace (e.g., vacuum, inert gas, or open air) can influence material choice. For instance, a graphite crucible offers a very high temperature limit but will oxidize and burn away rapidly if used in an oxygen-rich atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate crucible, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures: You must select a crucible made from a refractory metal like molybdenum (up to 2610°C) or tungsten (up to 3422°C), ensuring your furnace atmosphere is compatible.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose metal melting: Materials like clay-graphite or silicon carbide often provide the best balance of performance, thermal shock resistance, and cost for temperatures up to around 1600°C.
- If your primary focus is preventing product contamination: You must prioritize chemical compatibility, selecting an inert ceramic like high-purity alumina or zirconia that will not react with your specific molten material.
Ultimately, choosing the right crucible is about precisely matching the material's properties to the demands of your specific high-temperature task.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Melting Point (°C) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | ~3650 | General metal melting, non-oxidizing atmospheres |
| Molybdenum | 2610 | Sapphire growth, smelting rare-earth metals (>2000°C) |
| Tungsten | 3422 | Ultra-high temperature processes |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | ~2050 | General lab use, high chemical inertness |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | ~2700 | High-temperature chemical reactions |
Need the Perfect Crucible for Your Application?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for the success and safety of your high-temperature processes. The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, offering a wide range of crucibles in various materials to meet your specific needs for temperature, chemical resistance, and budget.
We can help you:
- Identify the ideal material (graphite, ceramic, refractory metal) for your temperature and chemical requirements.
- Prevent contamination and ensure the purity of your melts.
- Avoid costly failures by matching the crucible's properties to your application.
Let's find your solution together. Contact our technical experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Can you melt copper in a ceramic crucible? Yes, with the right crucible choice.
- What is the role of a crucible in testing the hydration activity of calcined boron mud clinker? Ensure Data Precision
- What is the difference between clay graphite crucible and silicon carbide crucible? A Guide to Maximizing Your Melt Efficiency
- How do you maintain a crucible? Maximize Lifespan & Ensure Melt Purity with Proper Care
- Why must alumina crucibles be configured inside static experimental tanks? Ensure Accuracy in Liquid Lead Tests
- What are the benefits of using ceramic crucibles in hydrothermal oxidation? Ensure Pure Reaction Integrity
- What can I use as a crucible for melting gold? Choose the Right Material for a Clean, Efficient Melt
- Why must high-purity graphite crucibles be treated in a vacuum oven and pre-baked? Ensure Pure Molten Salt Experiments



















