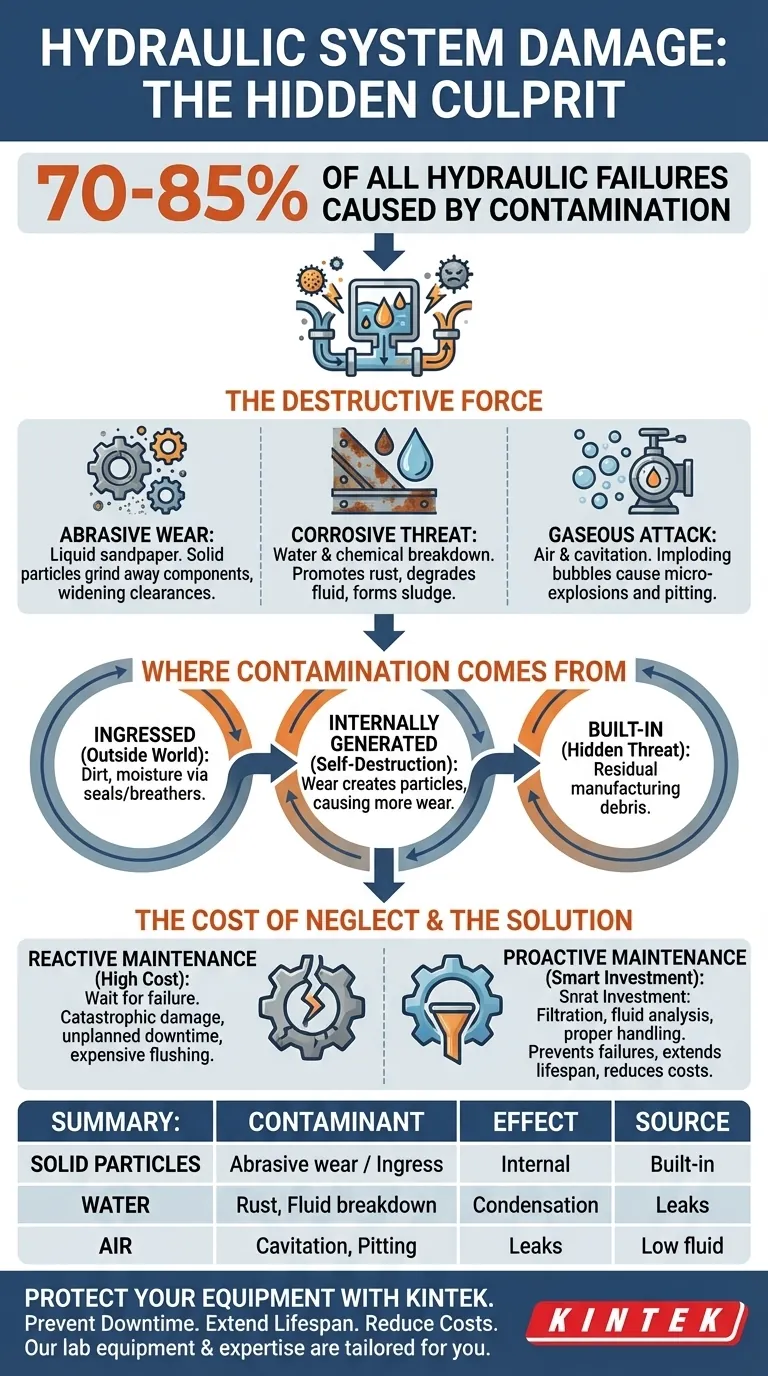
The single most destructive force in any hydraulic system is contamination. It is the direct or indirect cause of 70% to 85% of all hydraulic system failures. This isn't an isolated problem; it is the central challenge in maintaining the health and performance of hydraulic equipment.
The core issue is not a single component failing, but the hydraulic fluid itself becoming a destructive agent. Therefore, the goal shifts from simply repairing broken parts to proactively managing the cleanliness and condition of the fluid.

Why Contamination Is So Destructive
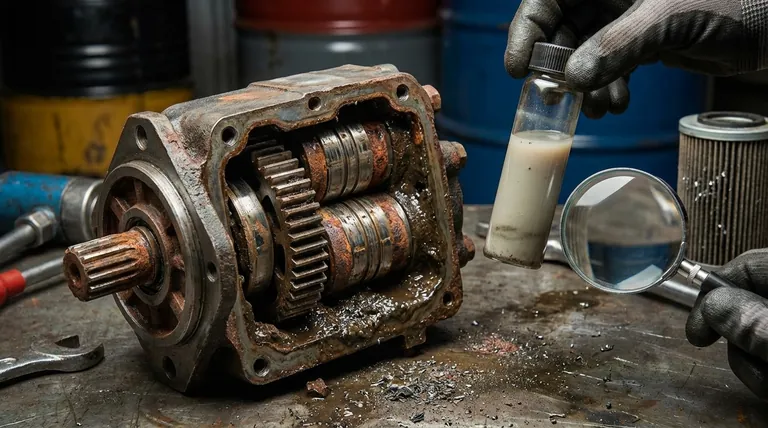
Hydraulic systems operate on the principle of transmitting force through an incompressible fluid, but they rely on extremely tight clearances between moving parts—often measured in microns. When foreign material is introduced into this high-pressure, high-precision environment, it systematically destroys components from the inside out.
The Abrasive Effect: Liquid Sandpaper
Solid particles, such as dirt, sand, and microscopic metal shavings, become suspended in the hydraulic fluid. As this contaminated fluid is forced through the system, these particles act like liquid sandpaper.
They grind away at the precisely machined surfaces of pumps, motors, valves, and cylinders. This process, known as abrasive wear, widens critical clearances, leading to internal leakage, loss of efficiency, and eventually, catastrophic component failure.
The Corrosive Threat: Water and Chemical Breakdown
Water is a devastating contaminant. It promotes rust and corrosion on metal surfaces, generating more abrasive particulate matter that feeds the cycle of wear.
Furthermore, water and excessive heat degrade the fluid itself, breaking down essential additives. This leads to the formation of sludge and varnish, which can clog small orifices in servo and proportional valves, causing components to stick and operate erratically.
The Gaseous Attack: Air and Cavitation
Air contamination can manifest as either aeration (dispersed bubbles) or cavitation (vapor bubbles forming and collapsing). When these bubbles are rapidly compressed in a pump, they implode with incredible force.
These micro-explosions generate intense, localized heat and shockwaves that blast small pits into metal surfaces. Over time, cavitation can erode and destroy critical pump components, leading to a rapid loss of performance.
Where Contamination Comes From
Understanding the source of contamination is the first step toward preventing it. These sources fall into three primary categories.
Ingressed Contaminants (The Outside World)
This is contamination that enters the system from the surrounding environment. It often enters through worn cylinder rod seals, faulty reservoir breather caps, or during maintenance when the system is opened. Dust, dirt, and moisture are the most common culprits.
Internally Generated Contaminants (The System Destroying Itself)
As components wear down from normal operation or from existing abrasive particles, they shed their own material into the fluid. This creates a destructive feedback loop: wear creates particles, which in turn cause more wear, generating even more particles at an accelerating rate.
Built-in Contaminants (The Hidden Threat)
New systems or newly repaired components often contain residual contamination from the manufacturing or assembly process. This can include casting sand, metal shavings, thread sealant, and paint flakes that were not properly flushed out before commissioning.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Cost of Neglect
The choice isn't whether to deal with contamination, but when. Addressing it proactively is always less expensive than dealing with it reactively after a failure.
Proactive vs. Reactive Maintenance
Proactive maintenance involves investing in high-quality filtration, regular fluid analysis, and proper fluid handling procedures. These are small, consistent operational costs.
Reactive maintenance means waiting for a component to fail. This path inevitably leads to catastrophic failure, unplanned downtime, expensive component replacement, and the high cost of flushing the entire system to remove the debris from the failed part.
The Limits of Filtration
A filter is not a one-time solution; it is a critical maintenance item. A filter that has become clogged will go into bypass mode, allowing contaminated fluid to flow unchecked through the system. Choosing the right filter for the application and replacing it on a set schedule is non-negotiable for system health.
Implementing a Contamination Control Strategy
A robust strategy isn't about a single action, but a comprehensive approach to managing the lifeblood of your system: the hydraulic fluid.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Uptime: Prioritize scheduled oil analysis to catch contamination, fluid degradation, and water ingress before they cause a failure.
- If your primary focus is Extending Component Lifespan: Focus on exclusion by maintaining seals, using high-quality breathers, and enforcing strict cleanliness procedures during all maintenance.
- If your primary focus is Cost Reduction: View effective filtration and clean fluid as the highest return-on-investment activity, as it prevents the far greater costs associated with downtime and component replacement.
Ultimately, controlling contamination is not an expense; it is the single most effective investment in the health and longevity of your hydraulic equipment.
Summary Table:
| Contaminant Type | Primary Effect | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Particles | Abrasive wear, grinding components | Ingressed dirt, internal metal shavings, built-in debris |
| Water | Rust, corrosion, fluid breakdown, sludge | Condensation, faulty seals, environmental ingress |
| Air | Cavitation, aeration, micro-pitting on surfaces | Leaky seals, low fluid levels, improper maintenance |
Protect your hydraulic equipment and maximize uptime.
Contamination is a relentless threat, but it can be managed. KINTEK specializes in the filtration systems, fluid analysis equipment, and consumables that form the foundation of an effective contamination control strategy. By partnering with us, you can:
- Prevent Costly Downtime: Catch issues early with regular oil analysis.
- Extend Component Lifespan: Protect your investment in pumps, valves, and motors.
- Reduce Operational Costs: Shift from reactive repairs to proactive, cost-saving maintenance.
Our lab equipment and expertise are tailored to the precise needs of industrial maintenance teams and fluid power engineers. Let us help you implement a strategy that turns your hydraulic fluid from a destructive agent into a protective asset.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific challenges and build a more reliable hydraulic system.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 304 316 Stainless Steel Vacuum Ball Valve Stop Valve for High Vacuum Systems
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What is the most efficient method of sterilization? Match the Right Method to Your Materials
- What are the different sterilization methods for a microbiology lab? Ensure Reliable and Safe Experiments
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization



















