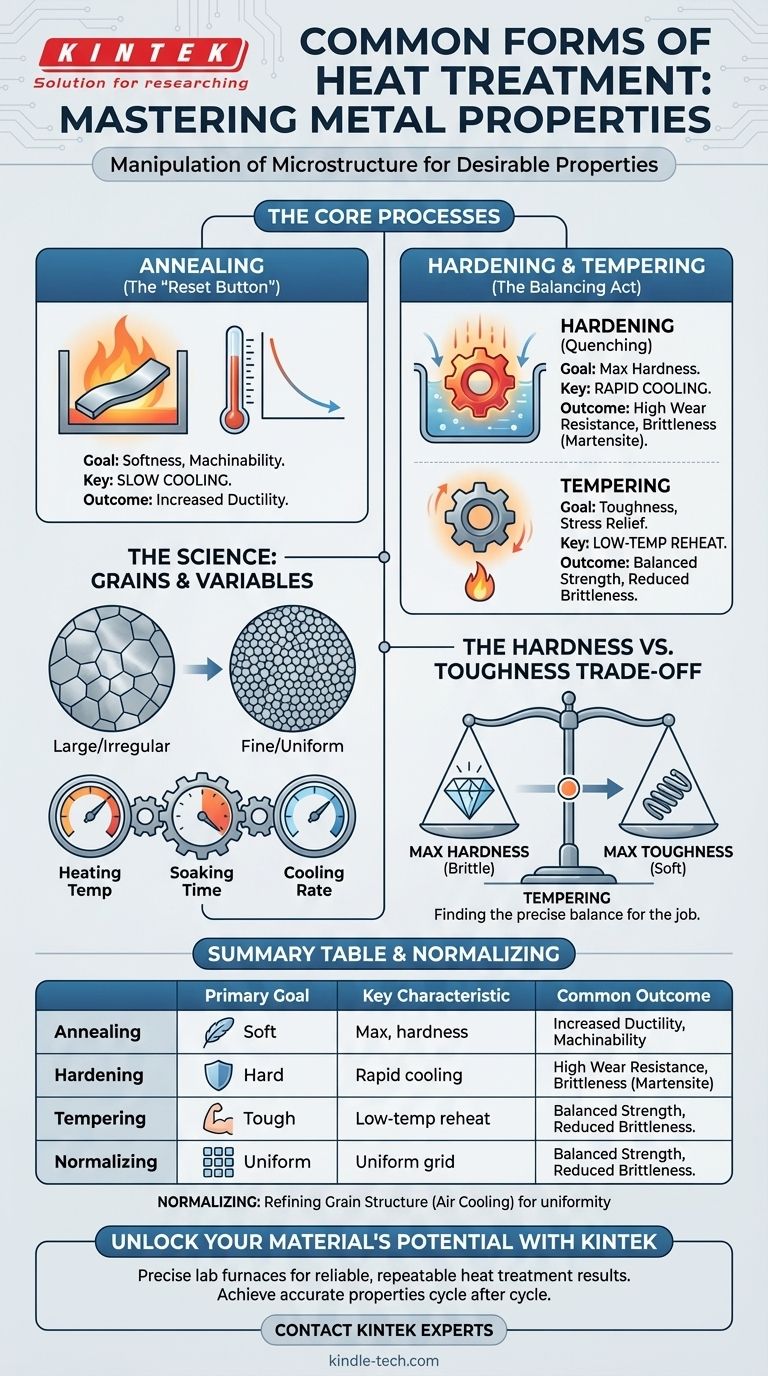
While there is no single "most common" heat treatment that applies to every industry, the processes of annealing and the combination of hardening (quenching) followed by tempering are the most fundamental and widely used across metallurgy. These methods form the foundation for manipulating the properties of metals, particularly steel.
The core purpose of heat treatment is not just to heat metal, but to execute a precisely controlled cycle of heating and cooling. This cycle intentionally alters the metal's internal microstructure to achieve specific, desirable properties like softness, extreme hardness, or a durable balance of strength and toughness.

The Goal of Heat Treatment: Manipulating Microstructure
Heat treatment is the controlled process of altering a material's physical and mechanical properties without changing its shape. It is a metallurgical tool used to make a material better suited for its intended application.
The Science of Grains
At a microscopic level, most metals are made of crystalline structures called grains. The size, shape, and composition of these grains—the metal's microstructure—dictate its macroscopic properties like hardness, ductility, and strength.
Heat treatment works by heating a metal to a specific temperature where its grain structure becomes malleable. The subsequent rate of cooling then locks in a new, desired microstructure.
The Critical Variables
Success in heat treatment depends on three factors:
- Heating Temperature: The peak temperature the metal reaches.
- Soaking Time: The amount of time the metal is held at that peak temperature.
- Cooling Rate: How quickly or slowly the metal is returned to room temperature.
The Most Common Heat Treatment Processes
While dozens of specialized treatments exist, a few core processes represent the vast majority of applications. They are best understood by their intended outcome.
Annealing: The "Reset Button" for Softness and Machinability
Annealing is a process used to make a metal as soft as possible, relieve internal stresses, and improve its ductility (ability to be formed). It is often performed on materials that have been "work-hardened" from processes like bending or drawing.
The key to annealing is slow cooling. The metal is heated to a specific temperature, held there, and then cooled very slowly, often by leaving it inside the turned-off furnace. This slow cooling allows the grain structure to reform in a very uniform and low-stress state.
Hardening (Quenching): The Pursuit of Maximum Hardness
Hardening is used to make steels and other alloys extremely hard and wear-resistant. This process is essential for tools, knives, bearings, and gears.
It involves heating the steel to a high temperature and then cooling it as rapidly as possible. This rapid cooling, known as quenching, is done by submerging the hot part in a medium like water, oil, or even forced air. Quenching traps the steel in a very hard but brittle microstructure called martensite.
Tempering: Trading Hardness for Toughness
A part that has only been hardened (quenched) is often too brittle for practical use; a sharp impact could cause it to shatter. Tempering is a secondary process performed after hardening to reduce that brittleness and increase toughness.
Tempering involves reheating the hardened part to a much lower temperature and holding it for a specific time. This process relieves some of the internal stresses from quenching, sacrificing a small amount of hardness for a significant gain in toughness—the ability to resist fracture. The combination of quenching and tempering is extremely common.
Normalizing: Refining the Grain Structure
Normalizing is similar to annealing but uses a faster cooling rate, typically by letting the part cool in open air. This results in a grain structure that is more uniform and fine than an annealed part.
The goal of normalizing is not maximum softness but structural uniformity. It provides a predictable starting point and improves the mechanical properties of materials that have been worked through processes like forging or casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process is always an exercise in balancing competing properties. There is no single "best" state for a metal; there is only the best state for a specific job.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
This is the most fundamental trade-off in heat treatment.
- Maximum Hardness (achieved through quenching) results in high wear resistance but makes the material brittle and prone to shattering.
- Maximum Toughness (often achieved through annealing) makes a material ductile and resistant to fracture but leaves it soft and easily deformed.
Tempering is the primary tool used to find a precise balance between these two opposing properties.
Process Control is Everything
Minor deviations in temperature or cooling rate can have a major impact. Quenching too slowly may fail to harden the part, while cooling too quickly can cause it to warp or crack due to thermal shock and internal stresses. This is why professional heat treatment requires precise furnace controls and well-understood quenching media.
Material Limitations
Not all metals are equally responsive to heat treatment. The ability of steel to be hardened, for instance, is almost entirely dependent on its carbon content. Low-carbon steels cannot be significantly hardened through quenching, while high-carbon steels can achieve extreme hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of heat treatment must be driven by the final application of the part.
- If your primary focus is making a metal easier to machine or form: Annealing is your go-to process for achieving maximum softness and relieving internal stresses.
- If your primary focus is creating a strong and wear-resistant part: A combination of hardening (quenching) followed by tempering is the standard approach to achieve high strength while retaining necessary toughness.
- If your primary focus is improving structural uniformity for predictable performance: Normalizing is often used to refine the grain structure after processes like forging or casting.
By understanding these core processes, you can begin to unlock the full engineering potential hidden within a material.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic | Common Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Softness, Stress Relief | Slow Cooling | Increased Ductility & Machinability |
| Hardening (Quenching) | Maximum Hardness | Rapid Cooling | High Wear Resistance, Brittleness |
| Tempering | Toughness, Stress Relief | Low-Temperature Reheating | Reduced Brittleness, Balanced Strength |
| Normalizing | Grain Refinement | Air Cooling | Uniform Microstructure, Predictable Properties |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Materials with KINTEK
Choosing the right heat treatment process is critical for achieving the precise mechanical properties your application demands. Whether you need the softness of annealing for easy machining or the balanced strength and toughness from quenching and tempering, the quality of your results depends on precise temperature control and consistent process execution.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed for reliable and repeatable heat treatment. Our solutions help metallurgy labs, R&D departments, and quality control teams achieve accurate results cycle after cycle.
Ready to enhance your material testing and processing? Contact our experts today via our contact form to discuss your specific heat treatment challenges and discover how KINTEK's equipment can help you achieve superior material properties.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between hot air oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Thermal Needs
- What is the difference between sintering and fusing? Master the Key Thermal Processes for Your Materials
- What is the hottest temperature a furnace can be? Exploring Limits from 3,000°C+ to Your Application



















