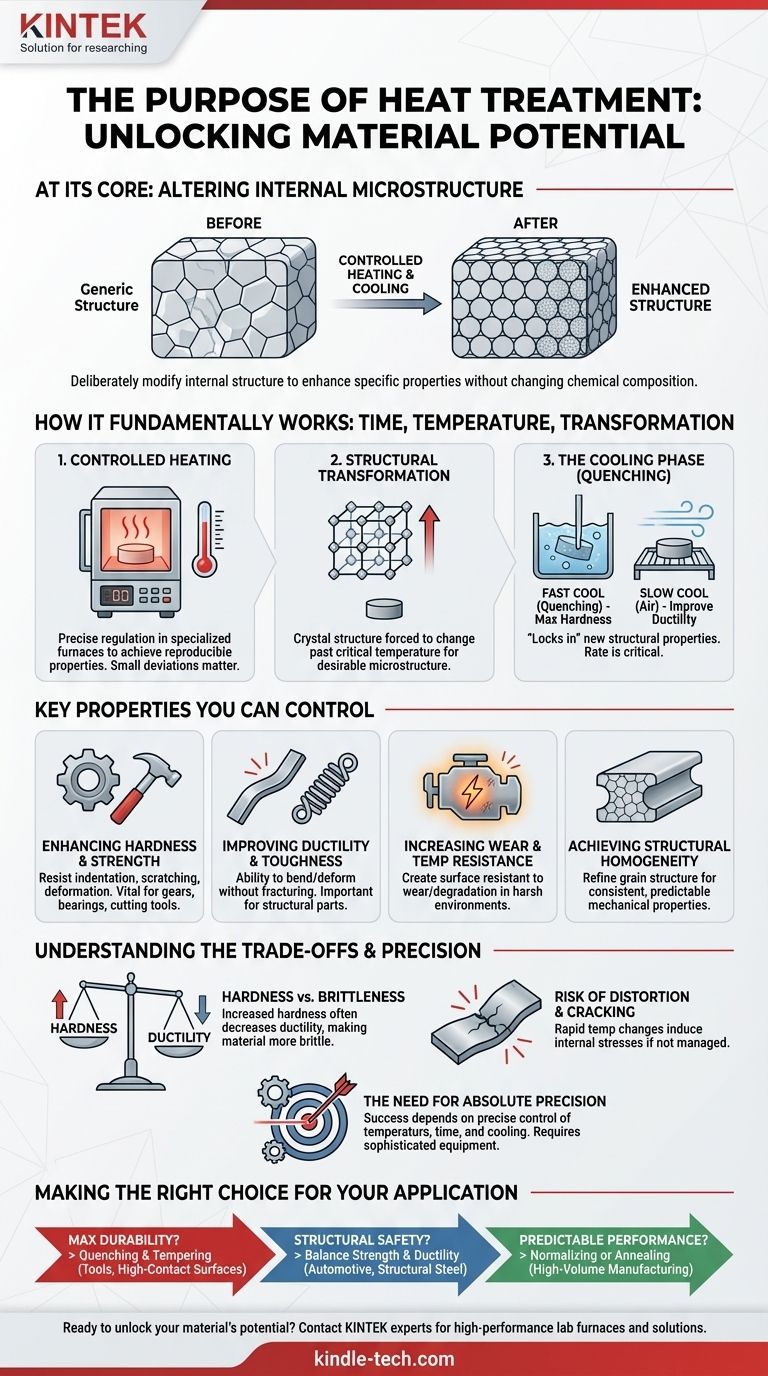
At its core, the primary purpose of any heat treatment operation is to deliberately alter a material's internal microscopic structure through a highly controlled process of heating and cooling. This manipulation is not done arbitrarily; it is performed to enhance specific physical and mechanical properties like strength, hardness, or ductility, thereby making the material suitable for its intended industrial application.
The ultimate goal of heat treatment is not just to change a material, but to unlock its full potential. It is a precise engineering process that tailors a raw metal's properties to meet the specific performance demands of a final component.

How Heat Treatment Fundamentally Works
Heat treatment is a powerful metallurgical tool because it allows us to modify a material's performance without changing its chemical composition. The entire process hinges on the principles of time, temperature, and transformation.
The Principle of Structural Transformation
Most metals have a crystalline structure. By heating a metal past a critical temperature, we can force this internal crystal structure to change into a different, often more refined, configuration.
The goal is to create a more desirable microstructure. This could mean making the internal grains of the metal smaller and more uniform, or creating new structural phases with unique properties.
The Critical Role of Controlled Heating
The process begins in a specialized heat treatment furnace. These devices are engineered to regulate and maintain specific temperatures with high precision.
This control is essential for achieving reproducible and useful properties. Even small deviations in temperature or the duration of heating can lead to a completely different, and often undesirable, outcome in the final product.
The Cooling Phase (Quenching)
After the material has been held at the target temperature, the cooling process is what "locks in" the new structural properties.
The rate of cooling—whether it's done rapidly in water or oil (quenching) or slowly in the air—is just as critical as the heating. A fast cool might maximize hardness, while a slower cool might improve ductility.
The Key Properties You Can Control
By manipulating the material's microstructure, engineers can fine-tune a range of properties to meet the demands of an application.
Enhancing Hardness and Strength
This is one of the most common goals. Heat treatment can significantly increase a material's ability to resist indentation, scratching, and deformation under load. This is vital for components like gears, bearings, and cutting tools.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
While hardness is important, some applications require a material that can bend or deform without fracturing. Certain heat treatment processes, like annealing, are used to soften a material, relieve internal stresses, and improve its overall toughness.
Increasing Wear and Temperature Resistance
For parts that experience friction or operate in high-heat environments, heat treatment can create a surface that is exceptionally resistant to wear and degradation. This extends the service life of critical components.
Achieving Structural Homogeneity
Processes like normalizing are used to refine a material's internal grain structure, making it uniform throughout the entire component. This ensures consistent and predictable mechanical properties, eliminating weak spots and improving overall reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a balancing act; improving one property often comes at the expense of another. Understanding these compromises is key to successful application.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Dilemma
The most common trade-off is between hardness and brittleness. As you increase a metal's hardness, you almost always decrease its ductility, making it more brittle and prone to shattering under sudden impact.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid temperature changes involved, especially during aggressive quenching, induce significant internal stresses within the material. If not managed properly, these stresses can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack.
The Need for Absolute Precision
Heat treatment is not a forgiving process. Success depends entirely on the precise control of temperature, time, and cooling rates. This requires sophisticated equipment and deep expertise, as small errors can easily ruin an entire batch of components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The specific heat treatment process you choose should be driven entirely by the primary requirement of your final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and wear resistance: You will need a process that prioritizes hardness, such as quenching and tempering, often used for tools and high-contact surfaces.
- If your primary focus is structural safety and reliability: You should choose a process that creates a good balance of strength and ductility to prevent catastrophic failure, common for structural steel and automotive parts.
- If your primary focus is predictable, uniform performance: You should use a process like normalizing or annealing to ensure the material behaves consistently throughout, which is critical for high-volume manufacturing.
Ultimately, heat treatment transforms a generic piece of metal into a precisely engineered, high-performance component fit for its purpose.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Heat Treatment | Key Properties Enhanced | Common Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Hardness & Strength | Resistance to wear, indentation, and deformation | Gears, bearings, cutting tools |
| Improve Ductility & Toughness | Ability to bend or deform without fracturing | Structural steel, automotive parts |
| Achieve Structural Homogeneity | Uniform and predictable mechanical properties | High-volume manufacturing components |
| Enhance Wear & Temperature Resistance | Extended service life in harsh environments | High-friction and high-heat components |
Ready to unlock your material's full potential? The precise control required for successful heat treatment starts with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for exact temperature regulation and uniform heating. Whether you're hardening tools, annealing metals, or normalizing structures, our solutions ensure reproducible results and enhanced component performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific heat treatment challenges and help you achieve superior material properties.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the optimal temperature for ashing in a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Efficient Results
- What is the maximum temperature of muffle furnace? A Guide from 1100°C to 1800°C
- How do you calibrate a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What is a muffle furnace in the environment? Achieve Clean, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What are the parts of a muffle furnace? Uncover the Core Components for Precision Heating



















