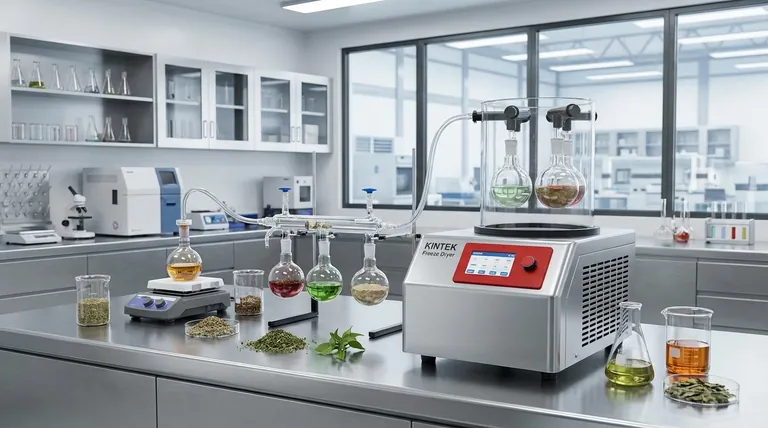
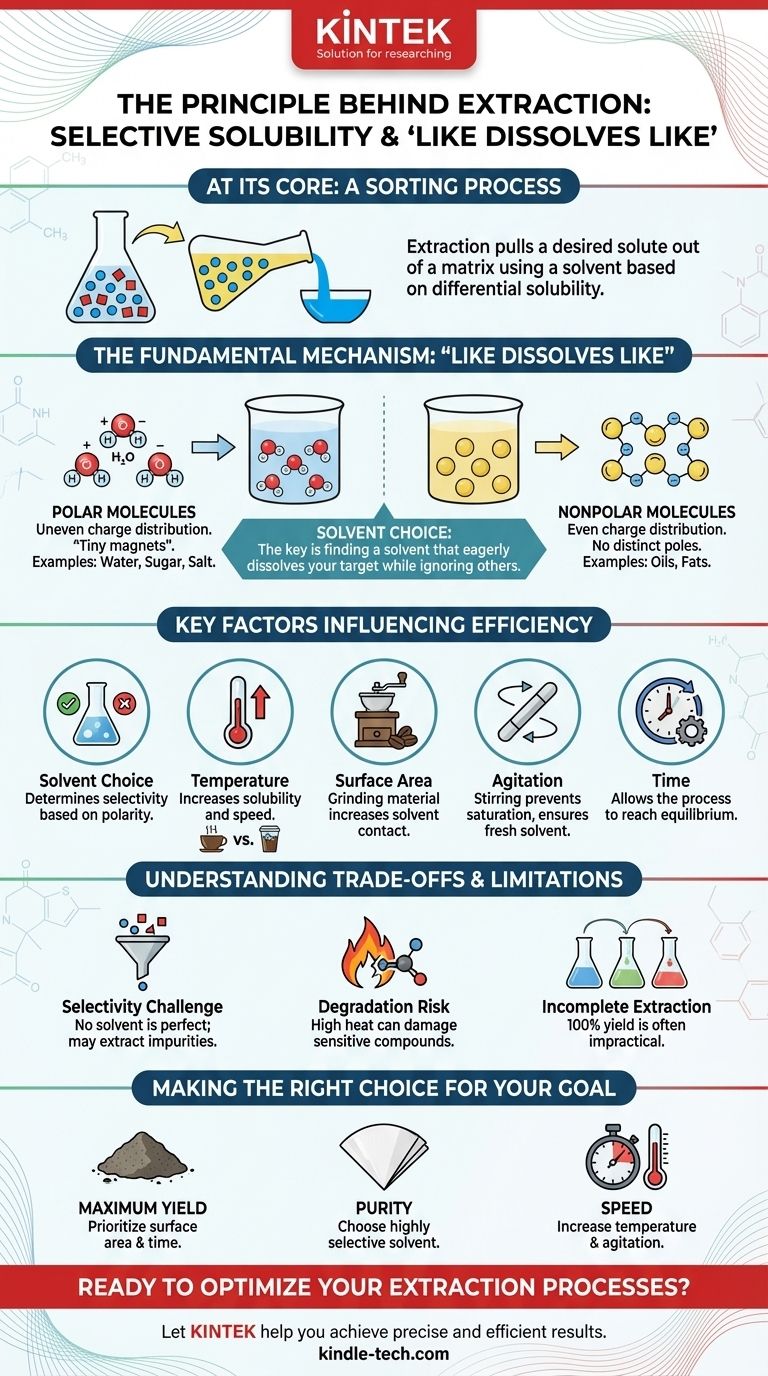
At its core, extraction is a sorting process based on a simple principle of selective solubility. It is the technique of pulling a specific desired substance (a solute) out of a mixture by using a liquid or gas (a solvent) that dissolves the target substance but leaves the other components behind. This is the fundamental mechanism behind everything from brewing coffee to creating medicines.
The effectiveness of any extraction hinges on a single concept: differential solubility. The goal is to find a solvent that eagerly dissolves the substance you want while ignoring, as much as possible, the other materials it is mixed with.

The Fundamental Mechanism: "Like Dissolves Like"
Extraction works because of how molecules interact with each other. The guiding rule is one of the most foundational in chemistry: "like dissolves like." This refers to the polarity of the molecules involved.
Polarity: The Driving Force
Every molecule has an electrical charge distribution. In polar molecules, like water (H₂O), this charge is unevenly distributed, creating positive and negative ends, much like a tiny magnet.
Nonpolar molecules, like oils and fats, have an even charge distribution and lack these distinct positive and negative poles.
How Solvents and Solutes Interact
A polar solvent, with its magnetic-like ends, will readily attract and surround other polar molecules, pulling them away from the mixture and into the solution. This is why polar sugar and salt dissolve in polar water.
Conversely, a nonpolar solvent will effectively dissolve nonpolar solutes. This is why oil-based stains are removed with nonpolar solvents like turpentine, not water.
The Role of the Matrix
The substance you are extracting from is called the matrix. The solvent must be able to penetrate this matrix to get to the target compound. The efficiency of the extraction depends on how easily the solvent can access the solute within this matrix.
Key Factors Influencing Extraction Efficiency
Several variables can be adjusted to control the speed and completeness of an extraction process. Understanding them allows you to optimize your results.
Choice of Solvent
This is the single most important decision. The ideal solvent strongly dissolves your target compound (solute) but poorly dissolves the other components of the matrix. It should also be easily separable from the solute after extraction (e.g., through evaporation).
Temperature
Increasing the temperature generally increases the solubility of a substance and the speed of the extraction. Think of how hot water brews coffee or tea much faster and more intensely than cold water.
Surface Area
Breaking the matrix into smaller pieces dramatically increases the surface area exposed to the solvent. This allows the solvent to penetrate the material more quickly and completely. This is why ground coffee extracts far more efficiently than whole beans.
Agitation
Stirring, shaking, or mixing the matrix and solvent is crucial. It ensures that fresh, unsaturated solvent is always in contact with the matrix, preventing a saturated layer from forming and halting the process.
Time
Extraction is not instantaneous. The solvent needs sufficient time to penetrate the matrix, dissolve the solute, and reach an equilibrium. The required time depends on all the factors above.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, extraction is a balancing act with inherent compromises. Acknowledging these is key to troubleshooting and setting realistic expectations.
The Challenge of Selectivity
No solvent is perfectly selective. It's common to accidentally extract other, unwanted compounds that have similar polarity to your target. This leads to an impure final product that may require further purification steps.
The Risk of Degradation
Using high temperatures to speed up extraction can be a double-edged sword. Heat can damage or chemically alter heat-sensitive compounds, like delicate flavors or bioactive molecules, destroying the very substance you're trying to isolate.
Incomplete Extraction
It is often impractical or impossible to extract 100% of a solute from its matrix. Each "wash" with a solvent removes a percentage of the remaining solute, meaning subsequent extractions yield diminishing returns.
Post-Extraction Separation
The process isn't over once the substance is in the solvent. You are then left with a new problem: separating your desired solute from the solvent itself. This often requires another process like evaporation or distillation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, you must first define your priority. Your primary objective will dictate your approach.
- If your primary focus is maximum yield: Prioritize increasing surface area by grinding the material and allowing sufficient extraction time, potentially using multiple washes with fresh solvent.
- If your primary focus is purity: Your choice of the most selective solvent is the single most important decision, even if it results in a lower yield or a slower process.
- If your primary focus is speed: Increase the temperature and use vigorous agitation, but remain aware that this can compromise purity and potentially degrade sensitive compounds.
By mastering these principles, you can transform extraction from a simple procedure into a precise and powerful tool for separation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Extraction Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Solvent Choice | Determines selectivity based on the 'like dissolves like' principle (polarity). |
| Temperature | Increases solubility and speed, but risks degrading heat-sensitive compounds. |
| Surface Area | Grinding material increases contact with the solvent for faster, more complete extraction. |
| Agitation | Stirring or mixing prevents saturation and ensures fresh solvent contact. |
| Time | Allows the process to reach equilibrium for maximum yield. |
Ready to Optimize Your Extraction Processes?
Whether your goal is maximum yield, high purity, or rapid processing, the right lab equipment is crucial. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment and consumables to support your extraction needs—from solvent selection to post-extraction separation.
Let us help you achieve precise and efficient results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a freeze dryer in a laboratory setting? Preserve Delicate Materials with Sublimation
- What is the freeze drying or lyophilisation process? A Guide to Gentle, High-Quality Dehydration
- What role do laboratory freeze dryers play in the food industry? Unlock Superior Food Preservation
- Why are laboratory freeze dryers considered economical tools? Maximize Value and Minimize Loss
- What are some common uses of freeze drying? Preserve Delicate Materials with Precision



















