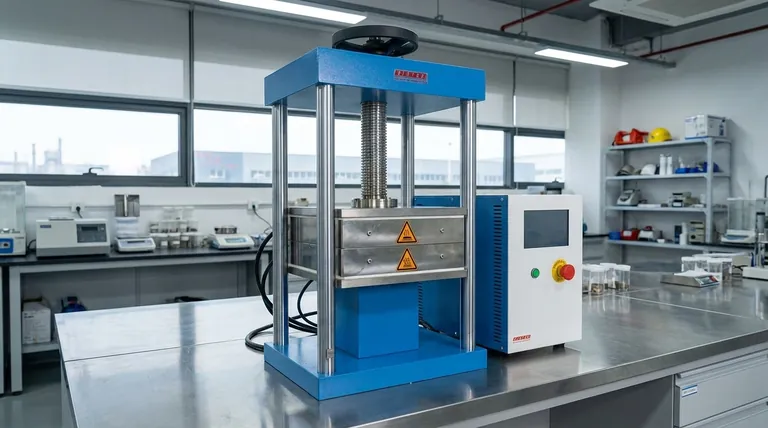
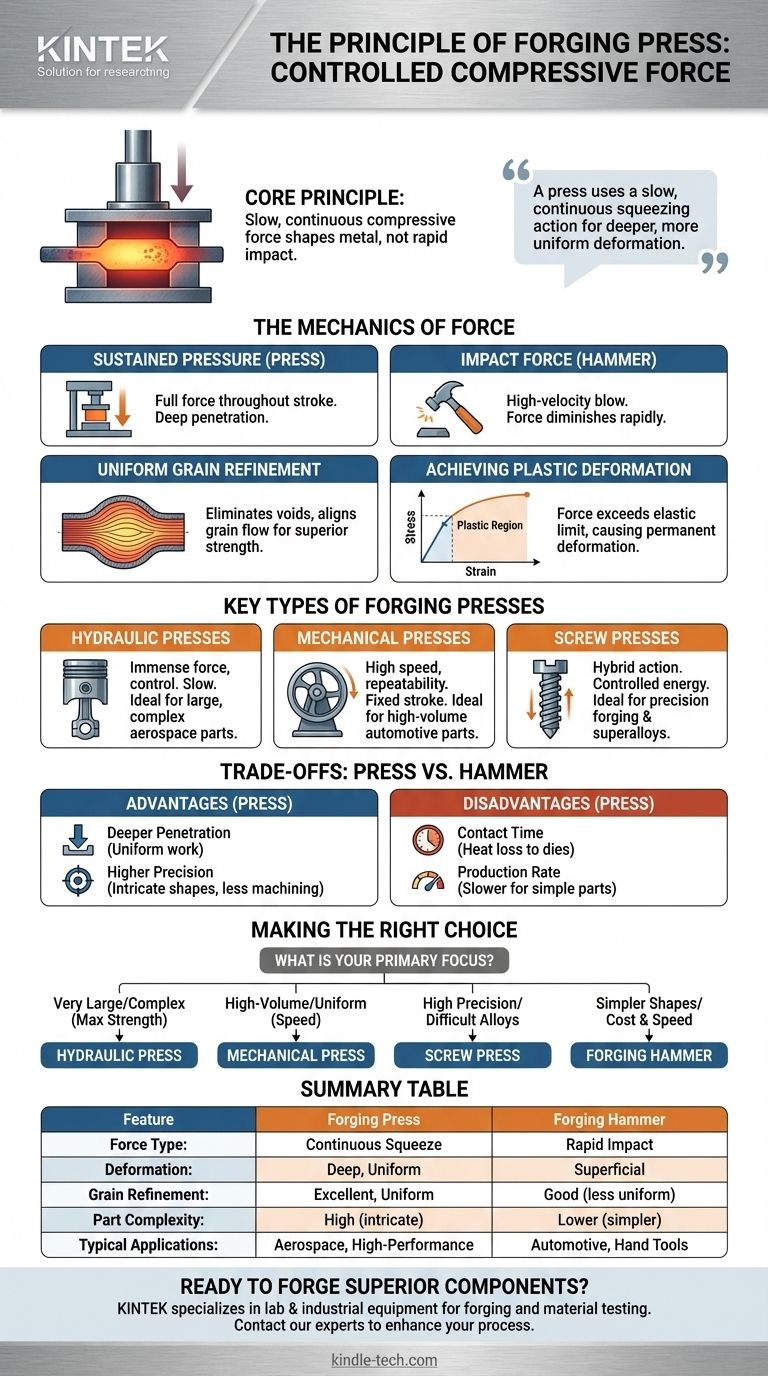
At its core, the principle of a forging press is the controlled application of slow, continuous compressive force to shape metal. Unlike the rapid, sharp impacts of a forging hammer, a press uses a mechanical or hydraulic ram to gradually squeeze a heated metal workpiece between two dies. This sustained pressure forces the metal to undergo plastic deformation, filling the die cavity and refining its internal grain structure for superior strength and integrity.
The fundamental difference between a forging press and other methods lies in its method of force application. A press uses a slow, continuous squeezing action, which allows for deeper and more uniform deformation throughout the entire volume of the metal, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties and the ability to create highly complex parts.

The Mechanics of Force: How a Press Achieves Deformation
Sustained Pressure vs. Impact Force
A forging hammer's energy is kinetic, delivered in a single, high-velocity blow. Its force is greatest at the moment of impact and diminishes rapidly.
A forging press, conversely, applies its full rated force throughout the entire length of its stroke. This slow, controlled squeeze ensures the deforming force penetrates deep into the center of the workpiece.
Uniform Grain Refinement
The slow application of pressure allows the metal's internal crystal structure (its "grain") to deform and recrystallize in a highly uniform manner.
This process eliminates internal voids and aligns the grain flow with the shape of the part, which is the primary source of a forged component's exceptional strength, ductility, and resistance to fatigue.
Achieving Plastic Deformation
Every metal has an elastic limit. Force applied below this limit will cause it to temporarily deform and then spring back to its original shape.
A forging press is engineered to apply force that far exceeds the metal's elastic limit, causing it to deform permanently—or plastically—into the new shape dictated by the dies.
Key Types of Forging Presses
Hydraulic Presses
Powered by high-pressure hydraulic fluid and large pistons, these presses are the titans of the forging world.
They are slower than other types but offer immense force and unparalleled control. The ram's speed and pressure can be varied at any point during the stroke, making them ideal for massive and highly complex components, such as those used in aerospace.
Mechanical Presses
These presses use a flywheel to store energy, which is then transferred to the ram via a crank mechanism (an eccentric shaft).
Mechanical presses are faster than hydraulic presses and offer high repeatability, making them perfect for high-volume production of smaller to medium-sized parts like automotive components. Their stroke length and force profile, however, are fixed by their mechanical design.
Screw Presses
A screw press is a hybrid, combining characteristics of both hammers and presses. An electric motor turns a large screw to accelerate the ram.
It delivers a controlled amount of energy in a single stroke, much like a hammer, but with the full-press action of a press. This makes them highly suitable for precision forging and forming high-temperature superalloys that require specific energy inputs.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Press vs. Hammer
Advantage: Deeper Material Penetration
The slow squeeze of a press ensures the entire volume of the metal is worked evenly. A hammer's impact can sometimes have a more superficial effect, especially on parts with large cross-sections, potentially leaving the core less refined.
Advantage: Higher Precision and Complexity
Because the force is applied slowly and controllably, presses can create parts with more intricate shapes, thinner walls, and tighter dimensional tolerances. This often reduces the need for extensive and costly post-forging machining.
Disadvantage: Contact Time and Heat Loss
The dies in a press remain in contact with the hot workpiece for a longer duration compared to a hammer blow. This prolonged contact allows more heat to transfer from the workpiece to the cooler dies, which can sometimes necessitate higher initial heating temperatures or even reheating between forging stages.
Disadvantage: Production Rate and Cost
For simple, standardized parts, the faster cycle time of a forging hammer or a mechanical press can make them more cost-effective. The slower, more deliberate action of a large hydraulic press is better reserved for parts where ultimate performance justifies the cycle time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct forging method is critical to achieving the desired balance of performance, precision, and cost for your component.
- If your primary focus is producing very large or complex components with maximum internal strength (e.g., aircraft landing gear, turbine disks): A hydraulic press is the only choice due to its immense, controllable force.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of uniform parts where speed is critical (e.g., automotive connecting rods, hand tools): A mechanical press provides the necessary speed and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is achieving high precision on difficult-to-form alloys or parts requiring exact energy input: A screw press offers a unique balance of impact energy and press-like control.
- If your primary focus is creating simpler shapes where ultimate internal refinement is secondary to cost and speed: A traditional forging hammer remains a viable and economical solution.
Understanding these principles allows you to specify the correct manufacturing process, ensuring your component possesses the precise mechanical properties required for its function.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Forging Press | Forging Hammer |
|---|---|---|
| Force Type | Continuous, compressive squeeze | Rapid, high-impact blow |
| Deformation | Deep, uniform throughout the part | Can be more superficial |
| Grain Refinement | Excellent, highly uniform | Good, but less uniform in thick sections |
| Part Complexity | High (intricate shapes, thin walls) | Lower (simpler shapes) |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace components, high-performance parts | Automotive parts, hand tools |
Ready to forge superior components with precision and strength?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab and industrial equipment to meet your forging and material testing needs. Whether you're developing high-performance aerospace parts or producing high-volume automotive components, our expertise in forging technology can help you achieve the mechanical properties and precision your application demands.
Let us help you select the perfect equipment for your project. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















