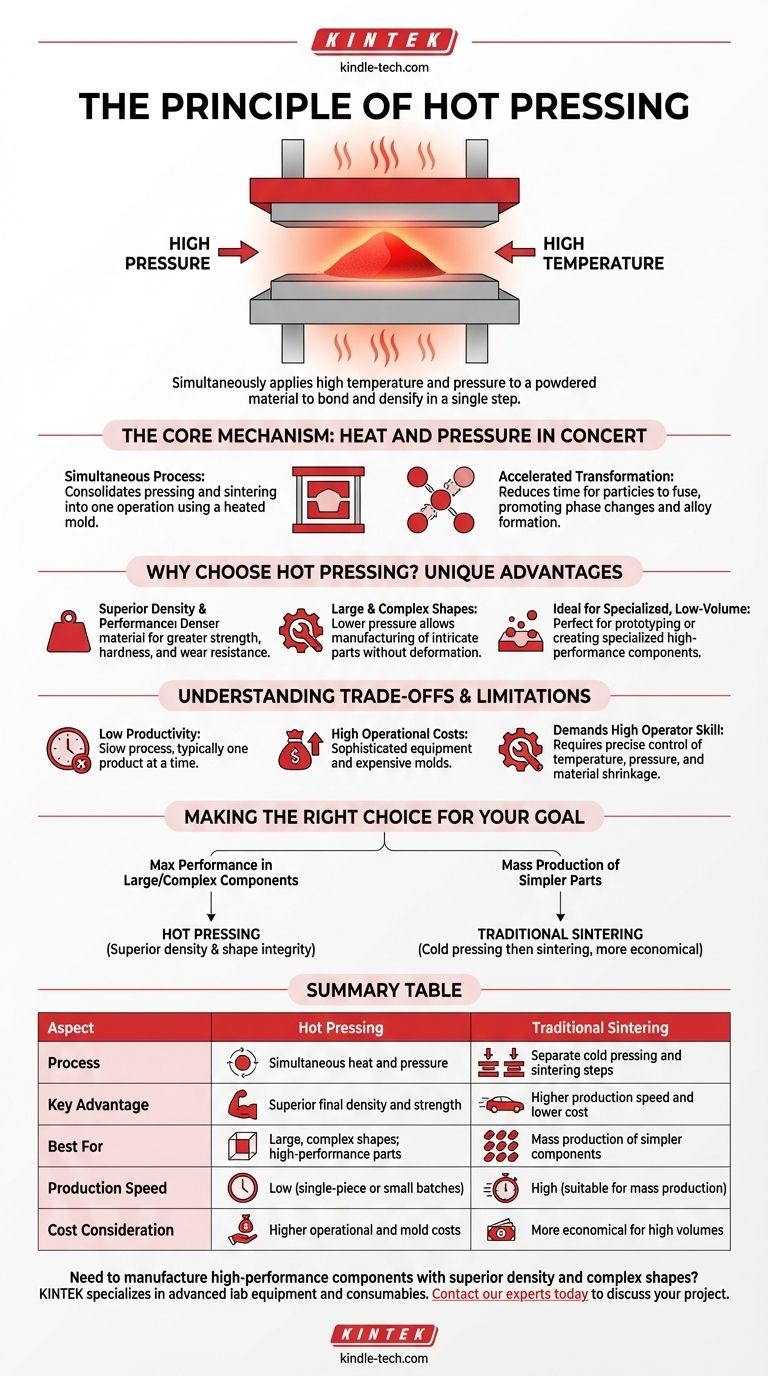
At its core, the principle of hot pressing is a manufacturing process that simultaneously applies high temperature and pressure to a powdered material. This combination forces the powder particles to bond and densify, forming a solid, high-performance final product in a single step.
The central concept behind hot pressing is achieving superior material density and performance by combining the pressing and sintering stages. This approach is ideal for creating complex, large, or high-quality components, but it comes at the cost of lower production speed and higher operational expense.

The Core Mechanism: Heat and Pressure in Concert
Hot pressing is fundamentally an "activated sintering process." By applying heat and pressure at the same time, it accelerates the material transformations that are crucial for creating a strong, dense final product.
The Simultaneous Process
Unlike traditional methods that first cold-press a powder into a shape and then sinter it in a separate furnace, hot pressing consolidates these into one operation. The powder is placed into a mold, often made of graphite, which is then heated while under mechanical pressure.
Accelerated Material Transformation
This simultaneous action significantly reduces the time required for the material's particles to fuse together. The combination of heat and pressure promotes phase changes and alloy formation much more efficiently than sintering alone.
Why Choose Hot Pressing? The Unique Advantages
The decision to use hot pressing is driven by the need for specific product characteristics that are difficult to achieve with other methods.
Superior Density and Performance
The primary benefit is achieving exceptionally high density in the final product. A denser material almost always translates to superior mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
Production of Large and Complex Shapes
The process can operate with relatively lower pressing pressures compared to cold pressing. This allows for the successful manufacturing of large components or parts with intricate shapes without causing deformation or internal stress.
Ideal for Specialized, Low-Volume Production
Because setup is intensive, hot pressing is well-suited for single-piece or small-batch production runs. It is often the go-to method for prototyping or creating specialized components like high-performance cemented carbides.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. Its disadvantages are directly linked to its specialized nature.
Low Productivity
The process is inherently slow. Molds can typically produce only one or a few products at a time, making it unsuitable for high-volume, mass-production scenarios.
High Operational Costs
The equipment is sophisticated and the molds, which must withstand extreme heat and pressure, have a high cost and a relatively short service life. This contributes to a higher cost per part.
Demands High Operator Skill
Successfully managing a hot pressing cycle is a technical challenge. Operators must precisely control the interplay of temperature, pressure, heating and cooling speeds, and material shrinkage to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right manufacturing process requires balancing product requirements with production realities. Hot pressing offers a unique capability for specific, demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance in large or complex components: Hot pressing is the superior choice, as it delivers the high density and shape integrity required for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is mass production of simpler parts: The low productivity and high costs make hot pressing impractical; traditional cold pressing followed by sintering is the more economical path.
Ultimately, hot pressing is a specialized tool for achieving material properties and geometric forms that other processes simply cannot deliver.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Pressing | Traditional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Simultaneous heat and pressure | Separate cold pressing and sintering steps |
| Key Advantage | Superior final density and strength | Higher production speed and lower cost |
| Best For | Large, complex shapes; high-performance parts | Mass production of simpler components |
| Production Speed | Low (single-piece or small batches) | High (suitable for mass production) |
| Cost Consideration | Higher operational and mold costs | More economical for high volumes |
Need to manufacture high-performance components with superior density and complex shapes?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for material processing. Our expertise can help you determine if hot pressing is the right solution for your specific laboratory or R&D needs, ensuring you achieve the material properties required for demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with the right equipment and insights.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What processing conditions does a vacuum hot press furnace provide? Optimize GNPs-Cu/Ti6Al4V Fabrication
- Why is vacuum sintering equipment essential for hot pressing sub-micron metal powders? Ensure Purity and Conductivity
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot-pressing furnace? Superior Copper-Graphite Composite Production
- How does the high vacuum environment benefit RuTi alloy preparation? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in RuTi alloys? Achieve High-Density Reactive Synthesis



















