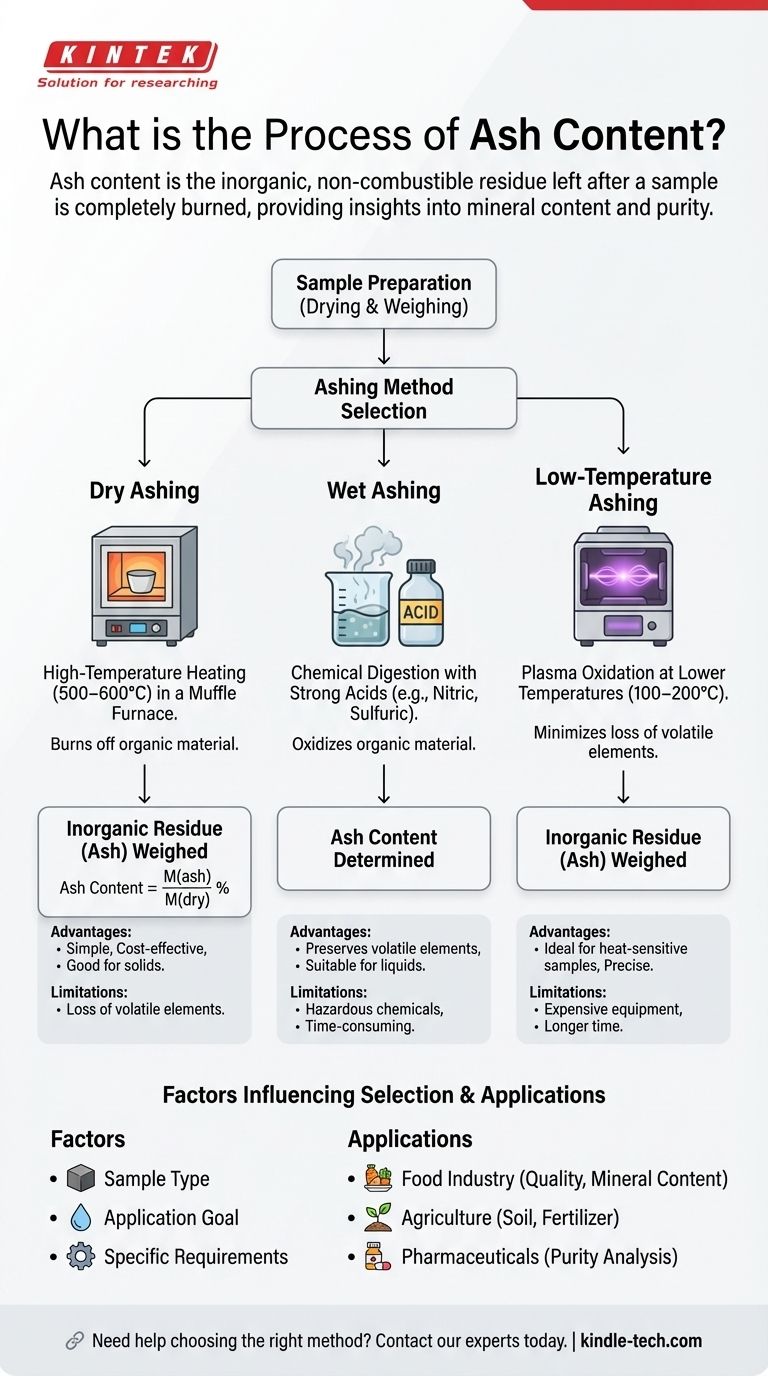
The process of ash content determination involves measuring the inorganic, non-combustible material in a sample, typically food products. The most common methods for this analysis are dry ashing, wet ashing, and low-temperature ashing. The choice of method depends on the sample type, application, and specific requirements. Dry ashing, the most widely used method, involves heating the sample in a furnace to burn off organic material, leaving behind inorganic residues (ash). The ash content is calculated using the formula: Ash content = M(ash)/M(dry) %, where M(ash) is the weight of the sample after ashing and M(dry) is the weight before ashing. Wet ashing uses chemical digestion, while low-temperature ashing employs plasma oxidation. The method selection is critical and depends on the analysis goals and sample characteristics.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Ash Content:
- Ash content refers to the inorganic, non-combustible residue left after a sample is completely burned. This residue typically consists of oxides of inorganic elements present in the original sample.
- It is a critical parameter in food analysis, as it provides insights into the mineral content and purity of the product.
-
Methods for Ash Content Determination:
-
Dry Ashing:
- The most common method, involving heating the sample in a muffle furnace at high temperatures (500–600°C) to burn off organic material.
- The remaining inorganic residue (ash) is weighed to determine the ash content.
- Formula: Ash content = M(ash)/M(dry) %, where M(ash) is the weight after ashing and M(dry) is the weight before ashing.
-
Wet Ashing:
- Involves digesting the sample with strong acids (e.g., nitric acid or sulfuric acid) to oxidize organic material.
- Suitable for samples that may volatilize at high temperatures or contain elements that form volatile compounds.
-
Low-Temperature Ashing:
- Uses plasma oxidation at lower temperatures (100–200°C) to minimize the loss of volatile elements.
- Ideal for heat-sensitive samples or those requiring precise mineral analysis.
-
Dry Ashing:
-
Factors Influencing Method Selection:
- Sample Type: The physical and chemical properties of the sample determine the most suitable method. For example, dry ashing is ideal for solid food samples, while wet ashing is better for liquid or heat-sensitive samples.
- Application: The purpose of the analysis (e.g., regulatory compliance, quality control, or research) influences the choice of method.
- Specifications: Specific analytical requirements, such as the need to preserve volatile elements or achieve high precision, guide the selection.
-
Process of Dry Ashing:
- Sample Preparation: The sample is dried to remove moisture and weighed accurately.
- Combustion: The sample is placed in a crucible and heated in a muffle furnace until all organic material is burned off.
- Cooling and Weighing: The crucible is cooled in a desiccator to prevent moisture absorption, and the ash is weighed.
- Calculation: The ash content is calculated using the formula mentioned above.
-
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method:
-
Dry Ashing:
- Advantages: Simple, cost-effective, and suitable for most solid samples.
- Limitations: May lead to loss of volatile elements and is unsuitable for heat-sensitive samples.
-
Wet Ashing:
- Advantages: Preserves volatile elements and is suitable for liquid samples.
- Limitations: Requires hazardous chemicals and is more time-consuming.
-
Low-Temperature Ashing:
- Advantages: Minimizes loss of volatile elements and is ideal for heat-sensitive samples.
- Limitations: Expensive equipment and longer processing times.
-
Dry Ashing:
-
Applications of Ash Content Analysis:
- Food Industry: Determines mineral content, assesses product quality, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
- Agriculture: Evaluates soil and fertilizer composition.
- Pharmaceuticals: Analyzes the purity of raw materials and finished products.
By understanding these key points, a purchaser of equipment or consumables for ash content analysis can make informed decisions about the most suitable methods and tools for their specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Inorganic, non-combustible residue left after burning a sample. |
| Common Methods | Dry ashing, wet ashing, low-temperature ashing. |
| Dry Ashing | High-temperature heating (500–600°C) in a muffle furnace. |
| Wet Ashing | Chemical digestion using strong acids. |
| Low-Temperature Ashing | Plasma oxidation at 100–200°C. |
| Applications | Food industry, agriculture, pharmaceuticals. |
| Key Factors | Sample type, application, and analytical requirements. |
Need help choosing the right method for ash content analysis? Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is melting point affected by heating rate? Avoid Inaccurate Measurements in Your Lab
- What is the specific heat capacity for melting? Clarifying Latent Heat vs. Specific Heat
- What are the conditions for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety, Performance, and Longevity
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a normal furnace? Ensuring Sample Purity with Indirect Heating



















