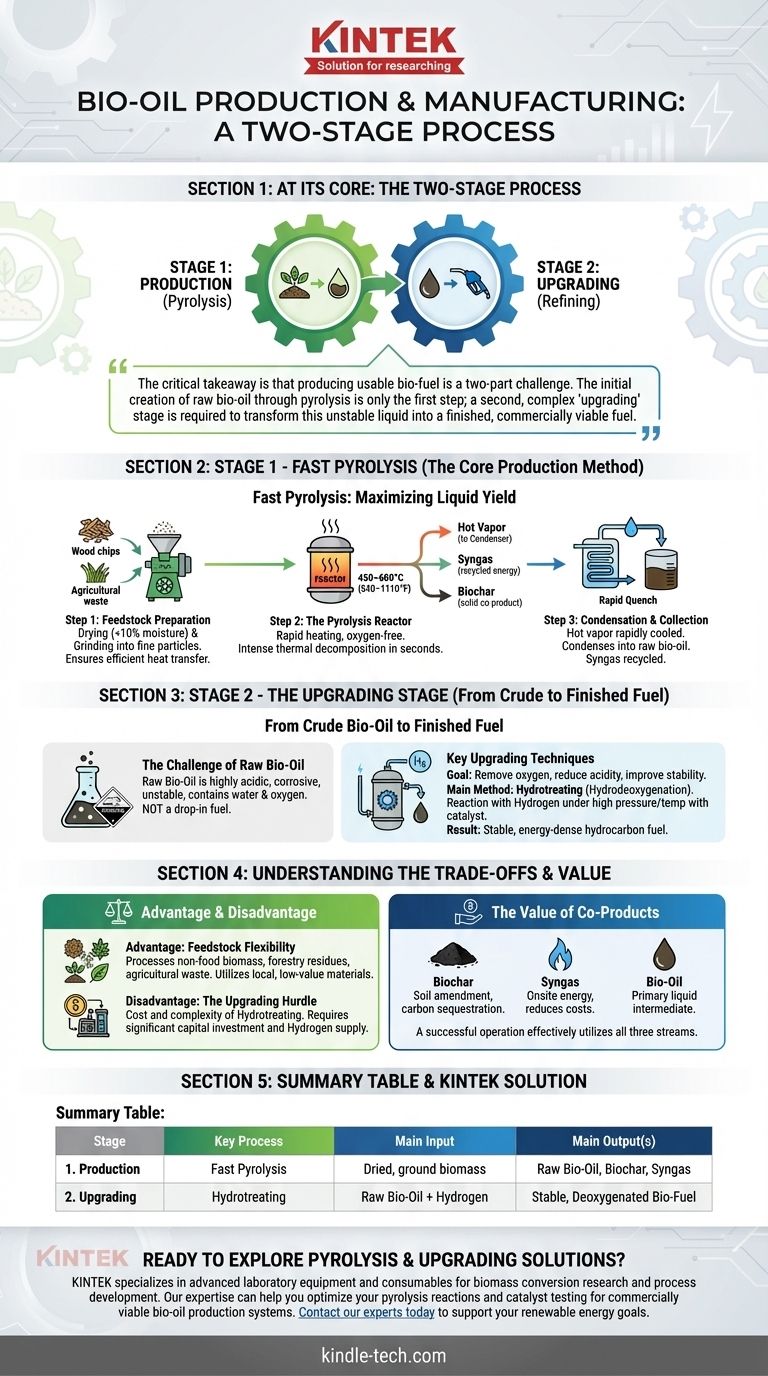
At its core, bio-oil production is a two-stage process. First, biomass like wood or agricultural waste is rapidly heated in an oxygen-free environment in a process called pyrolysis, which breaks it down into a vapor. This vapor is then rapidly cooled and condensed into a liquid known as raw bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
The critical takeaway is that producing usable bio-fuel is a two-part challenge. The initial creation of raw bio-oil through pyrolysis is only the first step; a second, complex "upgrading" stage is required to transform this unstable liquid into a finished, commercially viable fuel.

The Core Production Method: Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis is the central technology for converting solid biomass into liquid bio-oil. The entire process is designed to maximize the liquid yield by heating the feedstock extremely quickly and then cooling the resulting vapors just as fast.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
Before entering the reactor, the raw biomass must be prepared. This involves drying the material to a low moisture content (typically below 10%) and grinding it into fine, uniform particles.
Proper preparation is crucial for ensuring efficient heat transfer and consistent chemical reactions within the pyrolysis reactor.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reactor
The prepared biomass is fed into a reactor heated to 450–600°C (840–1110°F) in the near-total absence of oxygen. The intense heat causes thermal decomposition, breaking down the complex polymers in the biomass in a matter of seconds.
This rapid decomposition yields three primary products: a hot vapor (which becomes bio-oil), non-condensable gases (syngas), and a solid carbon-rich material (biochar).
Step 3: Condensation and Collection
The hot vapor stream is immediately directed away from the solid char and passed through a condenser. Here, it is rapidly cooled (quenched), causing the condensable portions of the vapor to turn into a dark, dense liquid.
This liquid is the raw bio-oil. The non-condensable gases are often recycled to provide the energy needed to heat the reactor, making the process more energy-efficient.
From Crude Bio-Oil to Finished Fuel: The Upgrading Stage
The liquid collected directly from the pyrolysis process is not a "drop-in" fuel. It is an intermediate product that requires significant processing before it can be used in conventional engines or refineries.
The Challenge of Raw Bio-Oil
Raw bio-oil is highly acidic, corrosive, and unstable. It contains a significant amount of water (15-30%) and oxygen, which makes it chemically different from conventional hydrocarbon fuels.
If left untreated, it will thicken and can even phase-separate over time, making it difficult to store and transport.
Key Upgrading Techniques
Upgrading aims to remove oxygen, reduce acidity, and improve the stability of the oil. The most common method is hydrotreating (or hydrodeoxygenation).
In this process, the bio-oil is reacted with hydrogen gas under high pressure and temperature in the presence of a catalyst. This removes oxygen atoms (as water) and saturates unstable chemical bonds, resulting in a more stable, energy-dense hydrocarbon fuel similar to diesel or gasoline.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While promising, the pyrolysis-to-bio-oil pathway involves clear technical and economic challenges that must be considered.
Advantage: Feedstock Flexibility
A major benefit of pyrolysis is its ability to process a wide variety of non-food biomass. This includes forestry residues, agricultural waste (like corn stover), and dedicated energy crops.
This flexibility allows bio-oil production to utilize locally available, low-value materials, avoiding competition with food production.
Disadvantage: The Upgrading Hurdle
The primary bottleneck is the cost and complexity of upgrading. Hydrotreating requires significant capital investment for high-pressure reactors and a continuous supply of hydrogen, which is often produced from natural gas.
The efficiency and cost of this upgrading step are the most critical factors determining the economic viability of a bio-oil facility.
The Value of Co-Products
Pyrolysis does not just produce oil. The solid biochar is a valuable co-product that can be sold as a soil amendment to improve fertility and sequester carbon.
As mentioned, the syngas stream provides onsite energy, reducing external energy costs and improving the overall process carbon footprint. A successful operation must effectively utilize all three output streams.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your evaluation of the bio-oil process depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is on renewable energy potential: Recognize that pyrolysis is a powerful technology for converting low-value, bulky biomass into an energy-dense, transportable liquid intermediate.
- If your primary focus is on technology investment: Focus your due diligence almost entirely on the cost, efficiency, and scalability of the back-end upgrading process, as this is the key to producing a fungible, market-ready fuel.
- If your primary focus is on process engineering: The key to an efficient system lies in optimizing reactor heat transfer and developing an integrated strategy for utilizing all three outputs: the oil, the biochar, and the syngas.
Understanding this two-part process of pyrolysis and upgrading is the key to evaluating the true potential of any bio-oil technology.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Main Input | Main Output(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Production | Fast Pyrolysis | Dried, ground biomass (wood, agricultural waste) | Raw Bio-Oil, Biochar, Syngas |
| 2. Upgrading | Hydrotreating (Hydrodeoxygenation) | Raw Bio-Oil + Hydrogen | Stable, Deoxygenated Bio-Fuel |
Ready to explore pyrolysis and upgrading solutions for your biofuel project? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for biomass conversion research and process development. Our expertise can help you optimize your pyrolysis reactions and catalyst testing to create efficient, commercially viable bio-oil production systems. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your renewable energy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















