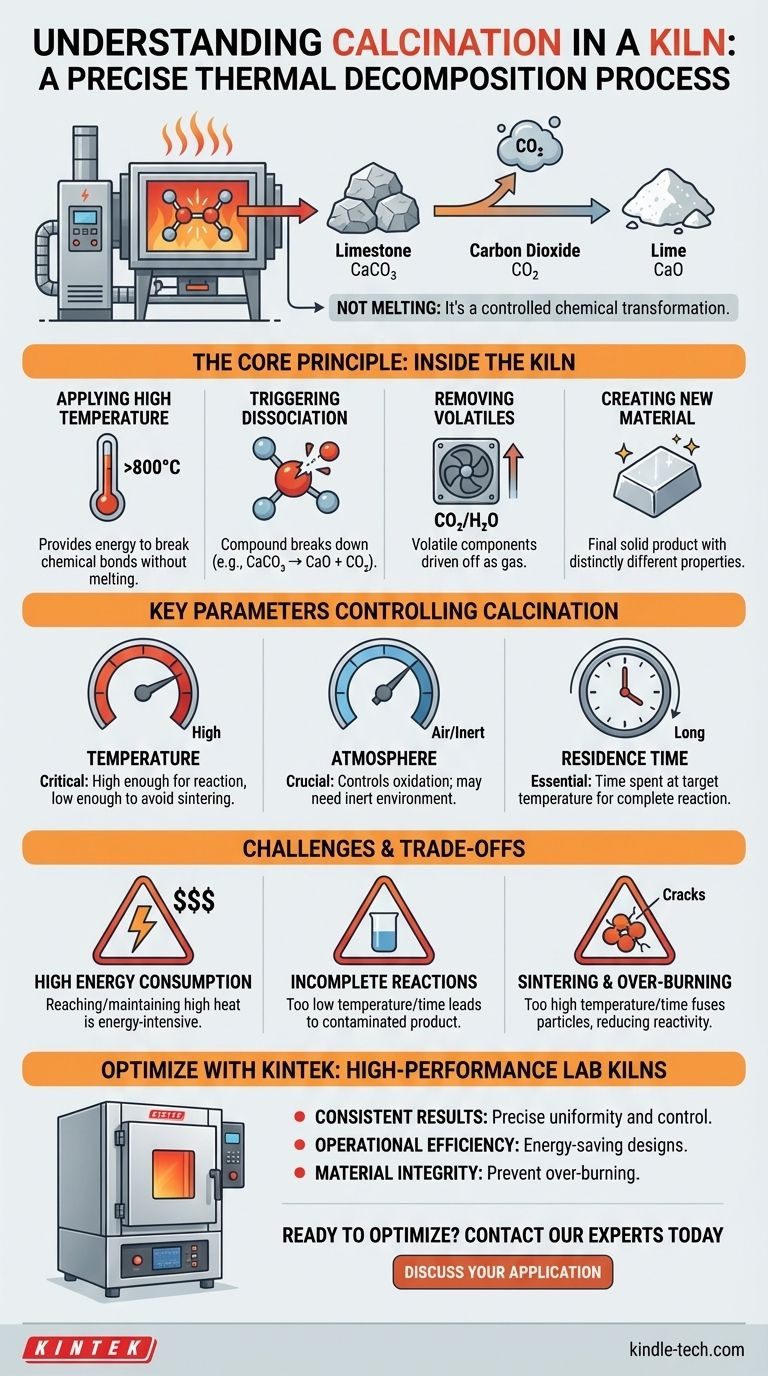
At its core, calcination in a kiln is a high-temperature thermal treatment process designed to induce a chemical change in a solid material. It uses controlled heat, typically below the material's melting point, to break chemical bonds, drive off volatile components, and produce a new, stable substance. The most common example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) and release carbon dioxide gas.
Calcination is not about melting; it is a precise thermal decomposition process. The kiln provides the controlled environment—temperature, atmosphere, and time—necessary to break down a compound into a desired new material and a volatile byproduct that is driven off.
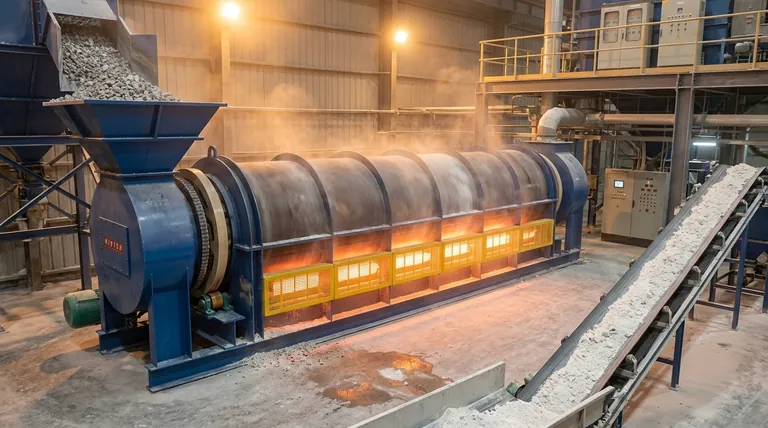

The Core Principle: What's Happening Inside the Kiln?
To understand calcination, you must look at it as a controlled chemical transformation. The kiln is simply the industrial vessel where the right conditions are created to make this reaction happen reliably and at scale.
Applying High Temperature
The fundamental input for calcination is thermal energy. The kiln heats the material to a specific temperature, known as the dissociation or decomposition temperature, which provides the energy needed to break internal chemical bonds.
Triggering Chemical Dissociation
Once the target temperature is reached, the compound begins to break down. For limestone (CaCO₃), this means the bonds holding it together break, resulting in the formation of solid calcium oxide (CaO) and gaseous carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Removing Volatile Substances
The process is defined by the removal of a volatile component. In the limestone example, the CO₂ gas is driven off and removed from the kiln, leaving the solid product behind. This principle also applies to removing chemically bound water (water of crystallization) from hydrates, such as when processing borax or bauxite.
Creating a New Material
The final solid product, often called the "calcine," is a new substance with distinctly different physical and chemical properties from the original material. Quicklime (CaO) is highly reactive, whereas the original limestone (CaCO₃) is relatively inert.
Key Parameters Controlling Calcination
Achieving a successful and efficient calcination process depends on precise control over several key variables within the kiln.
Temperature
Temperature is the most critical parameter. It must be high enough to initiate and sustain the decomposition reaction but low enough to avoid melting the material or causing unwanted side reactions like sintering (fusing of particles).
Atmosphere Control
The composition of the gas inside the kiln is crucial. While many processes occur in air, some require an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen) to prevent oxidation or other unwanted reactions with the material being processed.
Residence Time
This refers to the amount of time the material spends inside the kiln at the target temperature. The residence time must be long enough to ensure the chemical reaction proceeds to completion throughout the entire volume of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, calcination is a demanding industrial process with inherent challenges that must be managed for quality and efficiency.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for calcination is extremely energy-intensive. This represents a significant operational cost and environmental consideration for any large-scale process.
Incomplete Reactions
If the temperature is too low or the residence time is too short, the calcination will be incomplete. This results in a final product contaminated with the original, unreacted material, which can severely impact its quality and performance.
Sintering and Over-burning
Conversely, if the temperature is too high or the material is heated for too long, it can lead to "over-burning." This causes particles to fuse together (sinter), reducing the surface area and reactivity of the final product, which is often undesirable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters you prioritize will depend entirely on the material you are processing and the desired properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is producing a pure oxide (like lime): Your goal is to precisely achieve the dissociation temperature to drive off all CO₂ without over-burning the material, which would reduce its reactivity.
- If your primary focus is removing bound water from a hydrate: Your goal is careful temperature ramping and control to drive off the water molecules without causing a thermal shock or decomposing the valuable underlying compound.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and cost-reduction: Your goal is to optimize heat transfer and residence time within the kiln to ensure complete calcination using the minimum amount of energy possible.
Ultimately, mastering calcination is about using heat to precisely control chemical decomposition.
Summary Table:
| Key Calcination Parameter | Role in the Process |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Provides energy to break chemical bonds without melting the material. |
| Atmosphere | Controls the gas environment (e.g., air or inert) to prevent unwanted reactions. |
| Residence Time | Ensures the material is heated long enough for the reaction to complete fully. |
| Goal | To drive off volatile components (e.g., CO₂, water) and create a new, stable material. |
Ready to Optimize Your Calcination Process?
Precise temperature control and efficient thermal processing are critical for producing high-quality materials like lime, ceramics, or specialized oxides. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory kilns and furnaces designed for reliable calcination, sintering, and heat treatment.
Our equipment helps you achieve:
- Consistent Results: Precise temperature uniformity and control for complete, predictable reactions.
- Operational Efficiency: Energy-efficient designs to reduce costs and environmental impact.
- Material Integrity: Prevent over-burning or sintering to maintain product reactivity and quality.
Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, KINTEK has the laboratory equipment and expertise to support your goals.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific application and find the right kiln solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















