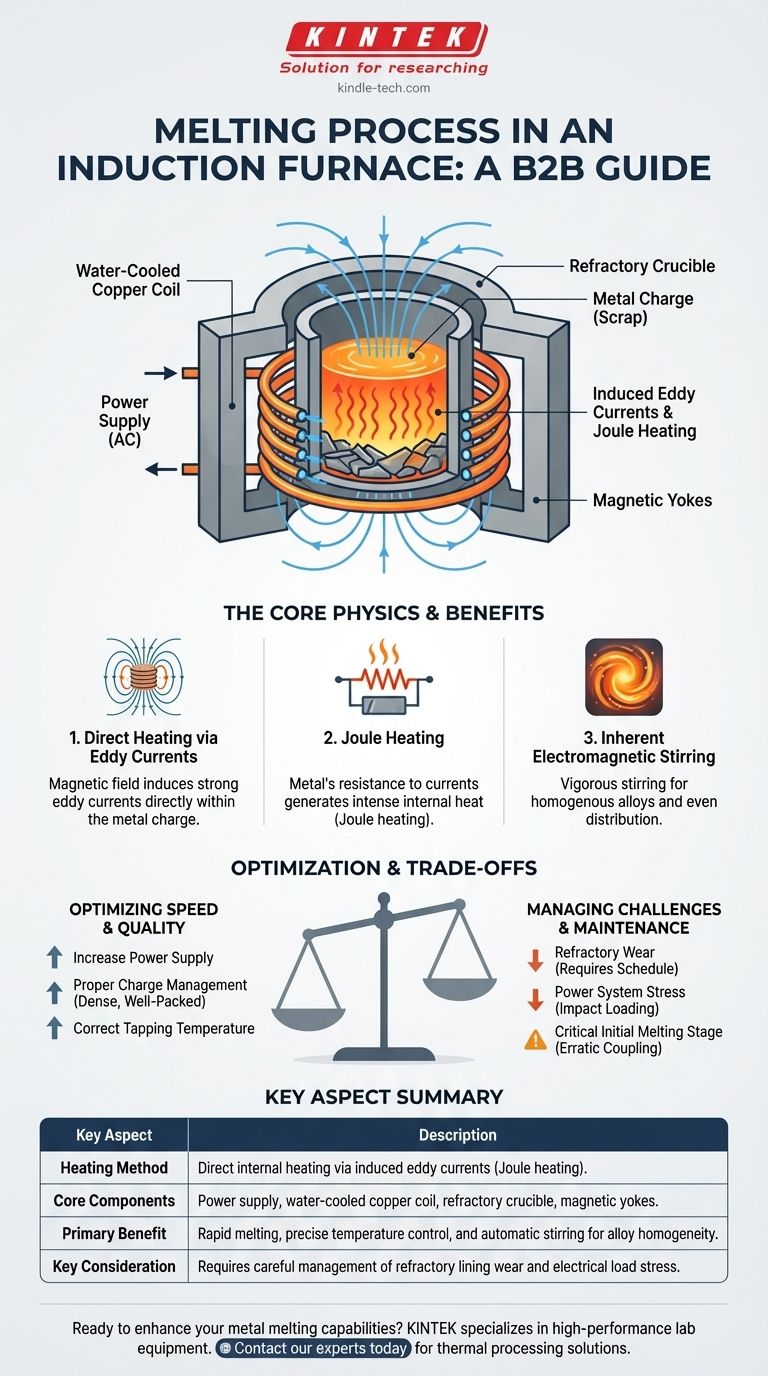
At its core, the melting process in an induction furnace is a method of direct heating. An alternating electrical current is passed through a water-cooled copper coil, which generates a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field inside the furnace's crucible. This magnetic field induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge, and the metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt rapidly.
The critical takeaway is that induction melting bypasses conventional heating methods. Instead of heating the furnace to heat the metal, it turns the metal itself into the heat source, offering exceptional speed and control but demanding careful management of the electrical load and furnace lining.

Deconstructing the Induction Process
To truly understand melting, we must first look at the key components and the physics that connect them. The process is elegant in its simplicity but powerful in its execution.
The Core Components
The furnace is an assembly of four essential parts working in concert.
- The power supply provides the high-frequency alternating current (AC) that powers the entire system.
- The water-cooled copper coil receives this current and generates the powerful magnetic field.
- The crucible, a refractory-lined container, sits inside the coil and holds the metal charge to be melted.
- Yokes are magnetic shields that surround the coil, concentrating the magnetic field on the charge and protecting the furnace structure.
The Physics of Induction Heating
The heating effect is a direct result of Faraday's Law of Induction and Joule heating. The AC current in the coil creates a constantly changing magnetic field.
This magnetic field penetrates the conductive metal placed inside the crucible, inducing powerful eddy currents to flow within the metal.
As these eddy currents swirl through the metal, they encounter the material's inherent electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy into heat at an incredible rate, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. The heat is generated inside the metal, not transferred from an external source.
The Inherent Stirring Effect
A secondary, highly beneficial effect of the electromagnetic field is a vigorous stirring action within the molten metal bath. This force ensures the liquid metal is constantly mixed.
This automatic stirring is crucial for creating homogenous alloys of exact composition, as it evenly distributes all elements throughout the melt without mechanical intervention.
Optimizing the Melting Operation
Simply understanding the process is not enough; efficient operation requires controlling key variables that directly impact speed, quality, and equipment longevity.
Factors Influencing Melting Speed
To increase melting speed, three primary levers can be adjusted:
- Increased Power: A higher-power supply will generate a stronger magnetic field, inducing larger eddy currents and thus more heat.
- Proper Charge Management: The size, shape, and density of the metal scrap (the charge) affect how well it couples with the magnetic field. A dense, well-packed charge melts more efficiently.
- Correct Tapping Temperature: Overheating the molten metal wastes energy and time and can increase refractory wear. Maintaining an appropriate outlet temperature is key to maximizing throughput.
The Critical Initial Melting Stage
The beginning of the melt cycle is the most demanding on the equipment. An irregularly distributed charge can cause erratic magnetic coupling.
This leads to strong impacts on the power supply, which can potentially damage sensitive electronic components like thyristors if the system is not designed to handle such loads.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Maintenance
While highly effective, induction melting is not without its operational challenges. Understanding its limitations is as important as knowing its benefits.
The Benefit: Precision and Control
Because the heat is generated within the metal and the process can be contained, induction furnaces offer unparalleled control. This allows for melting under a vacuum or inert atmosphere, which is essential for producing high-purity metals and alloys sensitive to oxygen.
The Challenge: Refractory Wear
The crucible's lining is constantly exposed to extreme temperatures and chemical reactions with the molten metal, causing it to erode. This requires a strict maintenance and repair schedule.
Minor erosion or cracks may only require a partial repair, where damaged areas are scraped out and refilled. However, uniform erosion requires a full reline, a more involved process of setting a form and compacting new refractory material.
The Risk: Power System Stress
The furnace's high power demand and the potential for load fluctuations, especially at the start of a cycle, place significant stress on the electrical system. A robust power supply designed for impact resistance is non-negotiable for reliable operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational priorities will dictate where you focus your attention when running an induction furnace.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: Prioritize a high-power supply and a disciplined charging practice that ensures a dense, consistent scrap feed.
- If your primary focus is alloy quality: Leverage the electromagnetic stirring and consider furnaces capable of atmosphere control to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: Implement a rigorous preventative maintenance schedule for the refractory lining and ensure your power supply is adequately specified for impact loading.
Mastering induction melting is a balance of harnessing its powerful physics while respecting its operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct internal heating via induced eddy currents (Joule heating). |
| Core Components | Power supply, water-cooled copper coil, refractory crucible, magnetic yokes. |
| Primary Benefit | Rapid melting, precise temperature control, and automatic stirring for alloy homogeneity. |
| Key Consideration | Requires careful management of refractory lining wear and electrical load stress. |
Ready to enhance your metal melting capabilities? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for all your laboratory needs. Our expertise in thermal processing solutions can help you achieve faster melt times, superior alloy quality, and greater operational reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction furnace solutions can power your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- How does temperature control in vacuum hot press furnaces affect aluminum matrix composites? Optimize Bonding & Strength
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve Nanoscale Hardness in Material Sintering



















