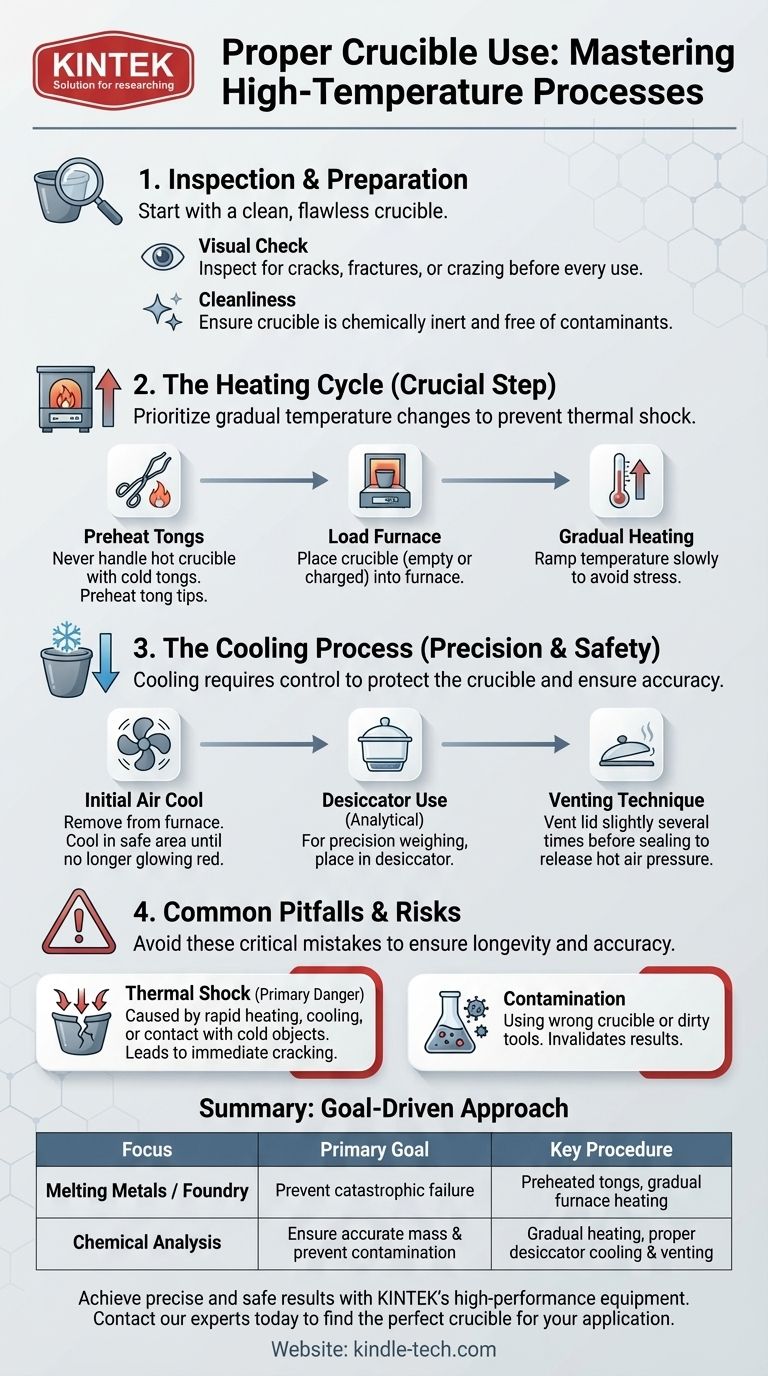
Properly using a crucible is a process defined by careful temperature management and precise handling to prevent damage and ensure the integrity of your work. It involves inspecting the crucible for flaws, using preheated tongs for handling, controlling heating and cooling rates to avoid thermal shock, and using specific procedures like a desiccator for analytical applications.
A crucible is not just a simple container; it is a piece of high-performance equipment. The core principle of its proper use is mitigating thermal shock and preventing contamination to ensure safety, accuracy, and the longevity of the crucible itself.

The Role and Nature of a Crucible
A crucible is engineered for extreme environments, and understanding its properties is the first step to using it correctly.
A High-Performance Container
A crucible is a ceramic or metal pot designed to hold materials, most often metals or chemical compounds, for melting or other high-temperature processing. Its primary function is to withstand temperatures far higher than standard lab or foundry equipment.
Essential Material Properties
To be effective, a crucible must possess exceptional stability. It needs a melting point significantly higher than the material it holds and must be chemically inert, meaning it won't react with its contents and cause contamination or deterioration.
The Core Procedure: Heating and Handling
The most critical phase of using a crucible is the heating cycle. Mistakes here can lead to equipment failure and compromised results.
Step 1: Pre-Use Inspection
Before every use, visually inspect the crucible for any cracks, fractures, or significant crazing. Heating a flawed crucible can cause it to fail catastrophically, spilling its molten contents.
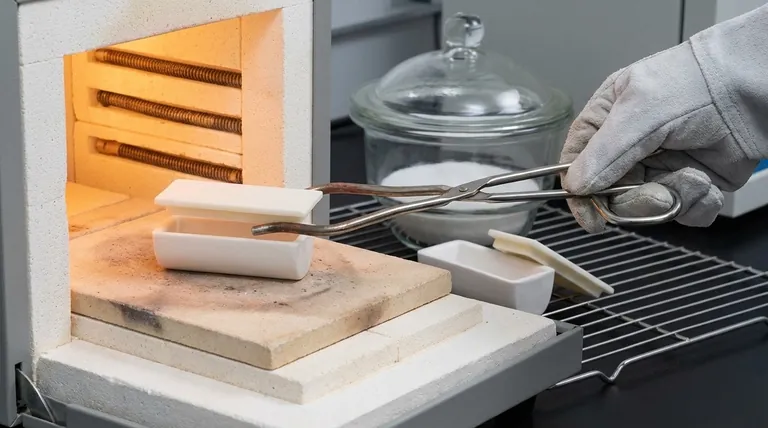
Step 2: Handling with Preheated Tongs
Never handle a hot crucible with cold tongs. The abrupt temperature difference can induce thermal shock and crack the crucible. Briefly preheat the tips of your crucible tongs in the furnace before making contact.
Step 3: Gradual Heating in the Furnace
Place the crucible, either empty or with its charge, into the furnace. Heat should be applied gradually. Ramping the temperature up too quickly is a primary cause of thermal shock and failure.
The Cooling Process: Preserving Your Crucible and Sample
Cooling is just as critical as heating. Improper cooling can destroy the crucible or, in analytical work, ruin the accuracy of your measurements.
Step 1: Initial Air Cooling
Once removed from the furnace, allow the crucible to cool partially in a safe, heat-resistant area. It should cool to a point where it is no longer glowing red before being moved to a desiccator.
Step 2: Using a Desiccator for Precision
For applications like gravimetric analysis, where preventing moisture absorption is critical for accurate weighing, a desiccator is essential. The hot crucible will heat the air inside this sealed container.
Step 3: The Critical Venting Technique
When placing the hot crucible into the desiccator, place the lid on top but do not seal it completely. Gently slide the lid open a tiny amount to release the expanding hot air. Repeat this venting process a few times before sealing the lid completely to cool to room temperature. This prevents pressure from building up and popping the lid off.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the risks is key to developing a safe and effective technique.
The Primary Danger: Thermal Shock
The single greatest risk to a crucible is thermal shock. This occurs from any rapid change in temperature, such as heating too fast, cooling too fast, or allowing a cold object (like tongs) to touch a hot crucible. The resulting stress can cause immediate cracking.
The Hidden Risk: Contamination
A crucible must be chemically compatible with its contents. Using the wrong type of crucible or introducing foreign material from dirty tools can contaminate your melt or sample, invalidating your results.
Physical Handling Hazards
Always remember you are working with extreme temperatures. Use appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including heat-resistant gloves, aprons, and full-face protection, especially when handling molten materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific procedure should be tailored to your objective.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or foundry work: Your priority is preventing catastrophic crucible failure. Always preheat your tongs and ensure a gradual furnace heating schedule.
- If your primary focus is precise chemical analysis: Your priority is preventing contamination and ensuring accurate mass. The desiccator venting and cooling procedure is absolutely critical for reliable results.
Mastering the proper use of a crucible transforms it from a simple pot into a reliable instrument that delivers safe and accurate outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Use Focus | Primary Goal | Key Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Metals / Foundry | Prevent catastrophic failure | Preheated tongs, gradual furnace heating |
| Chemical Analysis | Ensure accurate mass & prevent contamination | Gradual heating, proper desiccator cooling & venting |
Achieve precise and safe high-temperature results with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing crucibles designed for durability and chemical inertness to meet your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect crucible for your application and ensure the integrity of your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of porcelain crucibles? Ideal for High-Temp, Cost-Effective Lab Work
- Why are porcelain grinding bowls and crucibles preferred for pigment synthesis? Ensure Purity and Thermal Stability
- Do you need to preheat a crucible? The Critical Step to Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What crucible is best for melting gold? Choose the Right Tool for a Clean, Efficient Melt
- What are the risks of crucibles? Prevent Thermal Shock, Contamination, and Failure
- What is the primary function of an alumina crucible in Li2.07Ni0.62N synthesis? Ensure High Purity & Thermal Stability
- How long does a crucible last? Maximize Lifespan with Proper Material & Handling
- Why is a high-density MgO crucible required for lithium molten salt experiments? Ensure Purity & Chemical Stability



















