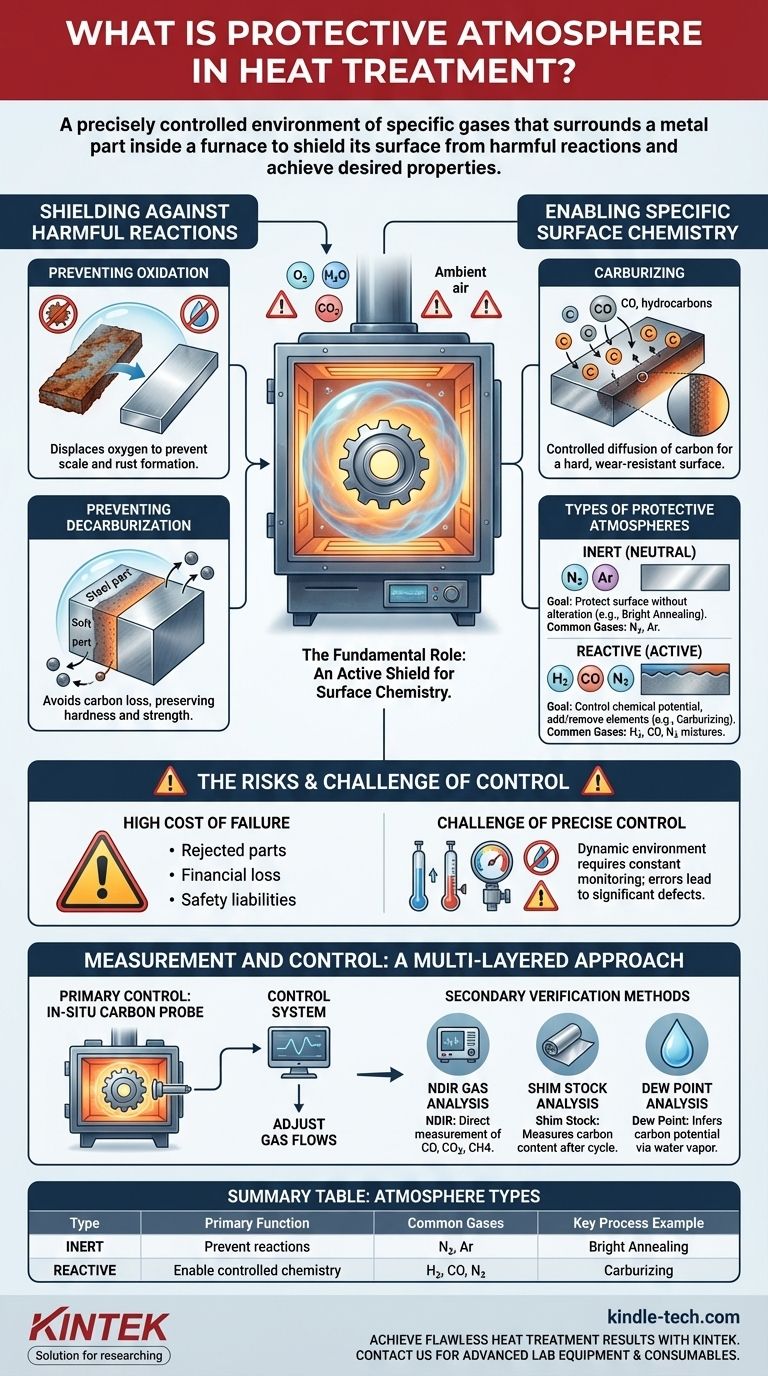
In heat treatment, a protective atmosphere is a precisely controlled environment of specific gases that surrounds a metal part inside a furnace. Its purpose is to shield the metal's surface from harmful chemical reactions, such as oxidation and decarburization, during the intense heating and cooling cycles. This controlled environment is fundamental to achieving the desired metallurgical properties and surface finish.
A protective atmosphere is not merely a passive shield; it is an active tool. Failing to control it properly can ruin a component's surface chemistry and mechanical properties, leading to rejected parts, financial loss, and potential safety liabilities.

The Fundamental Role of the Atmosphere
A protective atmosphere serves two primary functions: preventing unwanted reactions and, in some cases, causing desirable ones. Understanding this duality is key to successful heat treatment.
Shielding Against Harmful Reactions
During heating, a metal surface is highly reactive with oxygen and other elements in the air. A protective atmosphere displaces the ambient air to prevent these negative outcomes.
The two most common issues are oxidation (forming scale or rust) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel), which makes the part softer and weaker than intended.
Enabling Specific Surface Chemistry
Some heat treatment processes require an active atmosphere that intentionally reacts with the metal's surface in a controlled way.
For example, in carburizing, the atmosphere is rich in carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. These gases react with the steel to diffuse carbon into its surface, creating a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while maintaining a tougher core.
Types of Protective Atmospheres
Atmospheres are generally categorized as inert (preventing reaction) or reactive (causing a planned reaction). The choice depends entirely on the material and the goal of the heat treatment process.
Inert (Neutral) Atmospheres
These atmospheres are used when the sole goal is to protect the component's surface without altering its chemistry. They are essential for processes like bright annealing, where maintaining a clean, bright surface finish is critical.
Common inert gases include pure Nitrogen (N2) and Argon (Ar). Argon is more inert and used for highly reactive metals, but it is also more expensive than nitrogen.
Reactive (Active) Atmospheres
These are complex gas mixtures designed to control the chemical potential at the surface of the part. They can add or remove elements.
The most common reactive atmospheres are mixtures containing gases like Hydrogen (H2), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Nitrogen (N2). By carefully adjusting the ratios of these gases, a heat treater can precisely control carburizing or decarburizing potential.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While essential, managing a protective atmosphere is a demanding technical challenge where mistakes have significant consequences.
The High Cost of Failure
An improperly controlled atmosphere leads to chemical reactions that degrade the quality of the part. This can result in entire batches being rejected, wasting material, energy, and production time.
If these defects are not detected, a faulty component entering the supply chain for industries like automotive or aerospace can pose a serious safety risk to the end-user.
The Challenge of Precise Control
Furnace atmospheres are dynamic. Leaks, gas composition drift, and reactions with the parts themselves can alter the environment.
Maintaining the precise gas ratios and chemical potential required for consistent results demands constant monitoring and sophisticated control systems.
How the Atmosphere is Measured and Controlled
Because of the high stakes, heat treaters use a multi-layered approach to ensure the atmosphere is correct throughout the entire process.
Primary Control: The Carbon Probe
Most modern furnaces use an in-situ carbon probe (or oxygen probe) as the primary control method. This sensor sits inside the furnace and provides real-time data on the atmosphere's "carbon potential"—its tendency to add or remove carbon from steel.
This data is fed back to a control system that automatically adjusts the flow of gases to maintain the desired setpoint.
Essential Verification Methods
Relying on a single probe is risky. To ensure accuracy and catch potential sensor drift or failure, operators use several secondary verification methods:
- NDIR Gas Analysis: An external Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) analyzer samples the furnace gas to directly measure the concentrations of CO, CO2, and CH4.
- Shim Stock Analysis: A thin piece of metal foil (shim stock) is placed in the furnace with the parts. After the cycle, its carbon content is measured to confirm the atmosphere had the intended effect.
- Dew Point Analysis: Measuring the water vapor content (dew point) of the atmosphere is a traditional but effective way to infer its carbon potential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and controlling the atmosphere is determined by the desired outcome for the specific metal alloy being treated.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation and maintaining surface finish (e.g., bright annealing copper): Use a simple, inert atmosphere like nitrogen or a nitrogen-hydrogen blend.
- If your primary focus is increasing surface hardness and wear resistance (e.g., carburizing steel gears): You must use a reactive atmosphere with a precisely controlled carbon potential, typically an endothermic gas mixture.
- If your primary focus is process reliability and quality assurance: Implement a robust system of both primary control (carbon probe) and secondary verification (NDIR analysis or shim stock) to guarantee the atmosphere is correct.
Ultimately, mastering the protective atmosphere transforms heat treatment from a potential source of error into a precise and reliable manufacturing capability.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Function | Common Gases | Key Process Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert (Neutral) | Prevent surface reactions | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Bright Annealing |
| Reactive (Active) | Enable controlled surface chemistry | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Nitrogen (N₂) | Carburizing |
Achieve Flawless Heat Treatment Results with KINTEK
Precise control over the protective atmosphere is non-negotiable for achieving the desired hardness, durability, and surface finish of your metal components. Inconsistent atmospheres lead to rejected batches, wasted resources, and potential safety risks.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to master your heat treatment processes. We supply the reliable furnaces, gas control systems, and monitoring tools (like carbon probes and gas analyzers) essential for maintaining the exact atmosphere your application demands.
Let us help you transform your heat treatment from a variable process into a repeatable, high-quality capability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and ensure your next project is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What inert gas is used in a heat treat oven? Choosing Nitrogen vs. Argon for Your Process
- Why is it necessary to place a high-temperature furnace inside an argon-atmosphere glove box for FLiNaK preparation?
- What sintering temperatures may be required for tungsten in a pure hydrogen atmosphere? Reach 1600°C for Peak Performance
- Why use a precision atmospheric control furnace for annealing HEAs? Unlock Pure Material Stability Data
- What are the benefits of steam processing on sintered iron? Enhance Strength, Wear, and Corrosion Resistance Today
- How does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace work with KOH? Master Carbon Activation for Ultra-High Surface Area
- How does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace ensure the active structure of calcium-aluminum catalysts?
- What are atmosphere furnaces? Mastering Controlled Heat Treatment for Superior Materials



















