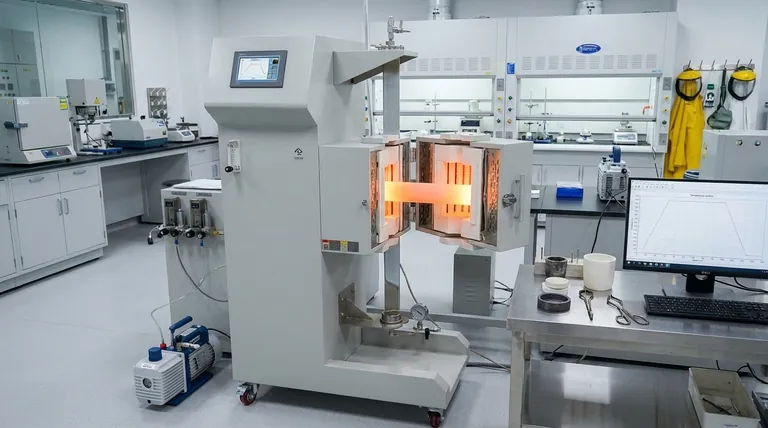
At its core, a heat treatment furnace is a specialized oven designed to modify a material's fundamental properties through a highly controlled cycle of heating and cooling. Its purpose is not merely to heat something up, but to precisely manipulate its internal crystalline structure to make it stronger, softer, more durable, or more resistant to wear. This is achieved by controlling not just the temperature, but also the chemical environment within the furnace chamber.
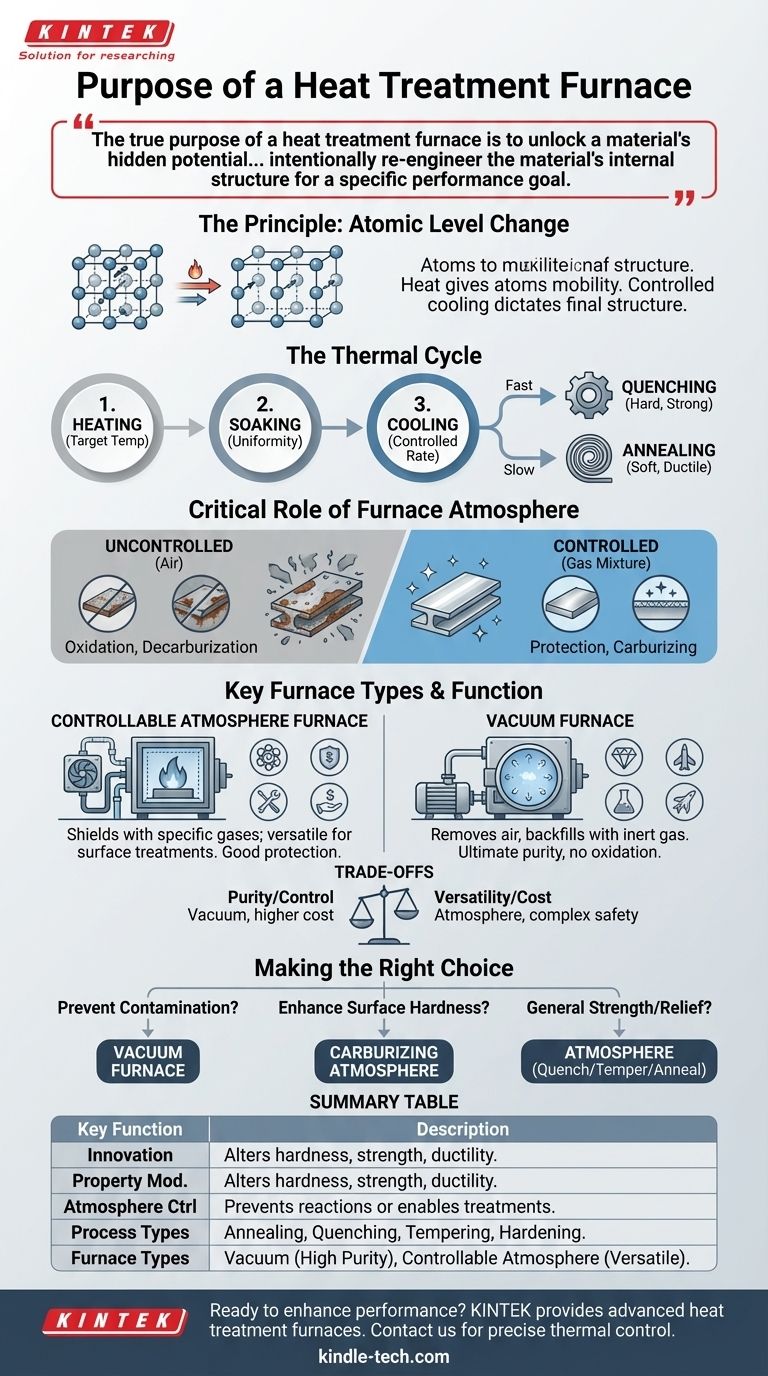
The true purpose of a heat treatment furnace is to unlock a material's hidden potential. It achieves this by using a precise thermal cycle within a carefully controlled atmosphere to intentionally re-engineer the material's internal structure for a specific performance goal.

The Principle: Changing Materials at the Atomic Level
The function of a heat treatment furnace is based on a simple principle: heat gives atoms mobility. By controlling this mobility and the subsequent cooling, you can dictate the final structure and, therefore, the properties of the material.
The Thermal Cycle
A heat treatment process consists of three main stages: heating, soaking, and cooling. The furnace manages each stage with extreme precision.
First, the material is heated to a specific target temperature. Then, it is held at that temperature—a stage called soaking—to ensure the entire part is heated uniformly and the desired internal changes can occur.
Finally, the material is cooled at a specific, controlled rate. Rapid cooling, or quenching, can lock in a hard, strong structure, while slow cooling, or annealing, can make a material softer and more ductile.
The Critical Role of the Furnace Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is just as important as the temperature. At high temperatures, materials can react with gases in the air, leading to undesirable effects like oxidation (rusting) or decarburization (loss of carbon, which weakens steel).
The furnace's atmosphere is designed to prevent these reactions. In some cases, the atmosphere is also used to intentionally introduce elements into the material's surface, such as in carburizing, where carbon is added to harden the surface of steel.
Key Furnace Types and Their Function
The primary difference between furnace types lies in how they control this internal atmosphere.
Controllable Atmosphere Furnaces
These furnaces use a specific mixture of gases to create a protective or reactive environment. Key components include a perfectly sealed furnace body and a fan system to circulate the gas mixture evenly.
This controlled atmosphere acts as a shield, protecting the part from exposure to air. It can also serve as a carrier for elements intended to chemically react with the material's surface to enhance its properties.
Vacuum Furnaces
A vacuum furnace represents the ultimate level of atmospheric control. The process begins by placing parts in the chamber and pumping out nearly all of the air and oxygen.
The chamber is then often backfilled with a neutral, non-reactive gas like argon. This creates an extremely pure environment, completely preventing oxidation and other unwanted surface reactions. This method is critical for high-performance, sensitive materials like titanium and nickel-based superalloys used in the aerospace industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process involves balancing precision, material needs, and cost. Each furnace type comes with its own set of considerations.
Process Purity vs. Cost
A vacuum furnace offers the highest level of purity and control, making it ideal for critical components that cannot tolerate any surface contamination. However, this precision comes with higher equipment and operational costs.
An atmosphere furnace provides excellent protection and is more versatile for processes that require adding elements to the surface. It is a cost-effective workhorse for a vast range of industrial applications.
Safety and Complexity
Both furnace types are complex industrial systems. Controllable atmosphere furnaces require careful management of potentially flammable or explosive gas mixtures, necessitating robust safety and explosion-proof devices.
Vacuum furnaces operate under extreme pressures and temperatures (up to 2400°F or 1315°C), requiring sophisticated, computer-controlled systems to ensure uniformity, repeatability, and safe operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct furnace and process depend entirely on the final properties you need to achieve in your component.
- If your primary focus is preventing all surface contamination: A vacuum furnace is the superior choice, as it removes the reactive elements that cause oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface hardness: A controllable atmosphere furnace configured for a process like carburizing is the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is general strength or stress relief: A controllable atmosphere furnace offers a reliable and cost-effective solution for processes like quenching, tempering, or annealing.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about using the furnace as a tool to precisely dictate a material's final form and function.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Property Modification | Alters material hardness, strength, and ductility through controlled thermal cycles. |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation/decarburization or enables surface treatments like carburizing. |
| Process Types | Includes annealing, quenching, tempering, and specialized surface hardening. |
| Furnace Types | Vacuum (for high purity) and Controllable Atmosphere (for versatility and cost-effectiveness). |
Ready to enhance your materials' performance? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced heat treatment furnaces tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Whether you require the ultimate purity of a vacuum furnace or the versatile capabilities of an atmosphere-controlled system, our equipment ensures precise thermal control, repeatable results, and enhanced material properties.
Let our experts help you select the perfect solution for applications ranging from aerospace components to industrial hardening processes.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can empower your research and production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















