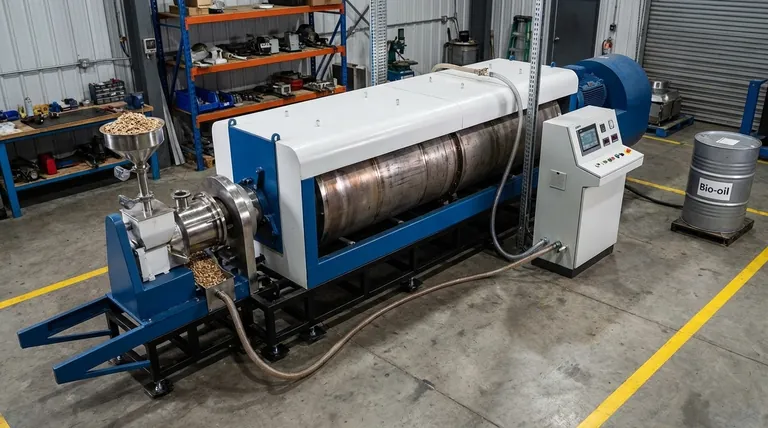
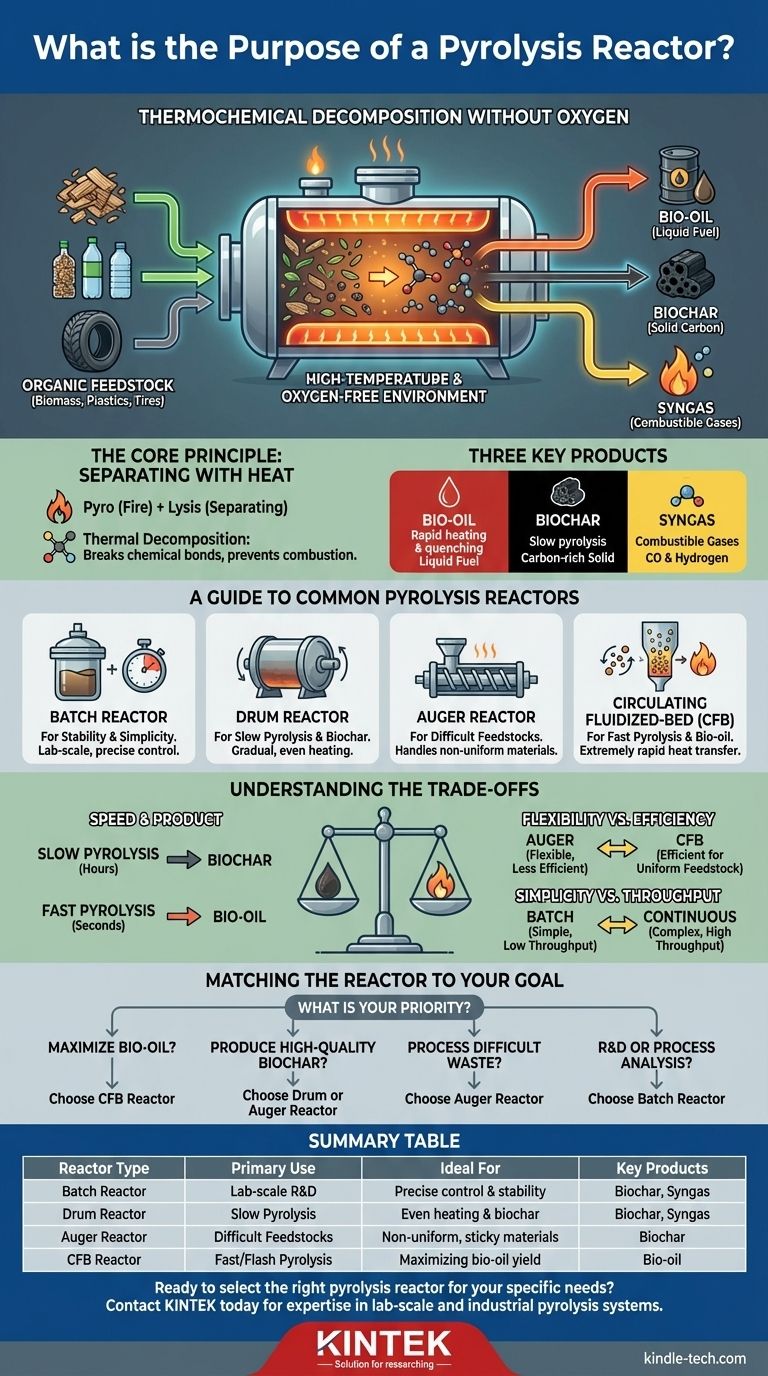
At its core, a pyrolysis reactor is a specialized, high-temperature vessel designed for thermochemical decomposition. Its purpose is to heat organic materials—such as biomass, plastics, or tires—in a nearly oxygen-free environment, breaking them down into valuable byproducts like bio-oil, biochar, and syngas instead of allowing them to combust.
The specific design of a pyrolysis reactor is not arbitrary; it is engineered to control heat transfer rates and processing time, which directly determines which end products are maximized. Choosing the right reactor is fundamentally about deciding whether you want to prioritize liquid fuels, solid carbon, or combustible gases.

The Core Principle: What Happens Inside a Reactor?
The term "pyrolysis" comes from the Greek-derived elements pyro ("fire") and lysis ("separating"). This is precisely what a reactor accomplishes: it uses heat to separate materials into their constituent chemical components without fire.
Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
The defining feature of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When you heat organic matter with oxygen present, you get combustion—fire, smoke, ash, and heat.
By removing oxygen, the reactor prevents burning. Instead, the intense heat breaks the complex chemical bonds within the feedstock, transforming it into simpler, often more valuable, substances.
The Three Key Products
The output of a pyrolysis reactor typically falls into three categories. The ratio of these products is heavily influenced by the reactor type and operating conditions.
- Bio-oil (or Pyrolysis Oil): A liquid fuel created by rapidly heating the material and then quickly cooling the resulting vapors.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off. It is the primary product of slow pyrolysis.
- Syngas (Synthesis Gas): A mixture of combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide and hydrogen, that do not condense into liquid with the bio-oil.
A Guide to Common Pyrolysis Reactors
Different reactor designs are optimized for specific feedstocks, heating rates, and desired outputs. Understanding these types is key to understanding their purpose.
Batch Reactors: For Stability and Simplicity
A batch reactor, also known as a fixed-bed reactor, is the simplest design. It is a sealed vessel loaded with a "batch" of material, heated for a set duration, and then emptied.
They are ideal for laboratory-scale investigations, especially for studying the energy stability of pyrolytic reactions, as conditions can be precisely controlled. Semi-batch reactors are a variation that allows more material to be added at intervals.
Drum Reactors: For Slow Pyrolysis and Biochar
Also called a rotating drum reactor, this design uses a large, rotating cylindrical vessel to tumble the feedstock. This continuous motion ensures gradual and even heat distribution.
This method is well-suited for slow pyrolysis, a process that maximizes the production of biochar and syngas from biomass.
Auger Reactors: For Difficult Feedstocks
An auger reactor uses a large screw mechanism (an auger) to transport material through a heated chamber. This design excels at handling non-uniform, sticky, or otherwise difficult-to-process materials.
Its primary output is typically biochar, as the slower, churning process favors solid production over the rapid vapor generation needed for bio-oils.
Circulating Fluidized-Bed (CFB) Reactors: For Fast Pyrolysis and Bio-oil
This advanced reactor design is engineered for extremely rapid heat transfer. A hot, fluid-like bed of material (like sand) circulates at high speed, instantly heating the biomass fed into it.
CFB reactors are ideal for fast pyrolysis and flash pyrolysis, where the goal is to maximize the yield of bio-oil. Their ability to distribute heat almost instantaneously is critical for this purpose.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single reactor is universally superior. The choice always involves balancing competing priorities.
Speed vs. Product: The Pyrolysis Spectrum
The rate of heating is the most critical variable. This creates a clear trade-off:
- Slow Pyrolysis (hours): Low temperatures and slow heating rates maximize contact time, favoring the creation of stable biochar. Drum and auger reactors excel here.
- Fast Pyrolysis (seconds): High temperatures and extremely rapid heating rates "crack" the material quickly, creating vapors that can be condensed into bio-oil. Circulating fluidized-bed reactors are built for this.
Feedstock Flexibility vs. Efficiency
An auger reactor can process a wide variety of inconsistent materials but may be less efficient in its energy use or product yield for a uniform feedstock.
Conversely, a circulating fluidized-bed reactor is highly efficient at converting uniform biomass into bio-oil but can be sensitive to variations in feedstock size and moisture content.
Simplicity vs. Throughput
A batch reactor is simple and cheap to build and operate but offers very low throughput, making it unsuitable for commercial-scale production.
Continuous reactors like drum, auger, and CFB types are far more complex and expensive but are designed for the high throughput required for industrial applications.
Matching the Reactor to Your Goal
The purpose of a reactor is defined by the goal of the project. To make the right choice, you must first define your priority.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil production: Choose a fast pyrolysis reactor like a circulating fluidized-bed (CFB) to ensure rapid heating and vapor quenching.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar: Choose a slow pyrolysis reactor, such as a rotating drum or an auger design, to control the heating process over a longer duration.
- If your primary focus is processing difficult or mixed waste materials: Choose an auger reactor for its robust mechanical handling of heterogeneous feedstocks.
- If your primary focus is research and development or process analysis: Choose a batch reactor for its simplicity and the precise control it offers over experimental variables.
Ultimately, a pyrolysis reactor is a tool engineered to transform a specific input into a desired output by expertly managing heat and time.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Primary Use | Ideal For | Key Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Reactor | Lab-scale R&D | Precise control & stability testing | Biochar, Syngas |
| Drum Reactor | Slow Pyrolysis | Even heating & biochar production | Biochar, Syngas |
| Auger Reactor | Difficult Feedstocks | Non-uniform, sticky materials | Biochar |
| Circulating Fluidized-Bed (CFB) | Fast/Flash Pyrolysis | Maximizing bio-oil yield | Bio-oil |
Ready to select the right pyrolysis reactor for your specific needs? Whether your goal is to maximize bio-oil, produce high-quality biochar, or process challenging waste streams, KINTEK's expertise in lab-scale and industrial pyrolysis systems can help you achieve optimal results. Our team will guide you in choosing the right reactor design—from batch to CFB—to match your feedstock and target products. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our specialized equipment can drive your pyrolysis process forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of pyrolysis machine? Turn Waste into Fuel, Chemicals, and Soil Amendment
- What is different between calcination? Unlocking Thermal Processing for Material Science
- What is the use of biochar from pyrolysis? Unlock its potential as fuel, material, and soil amendment
- What is the disadvantage of pyrolysis? Key Economic and Technical Challenges Explained
- What is the end product of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas
- What are the solid products of pyrolysis? Unlock the Value of Biochar and Coke
- What are the main products formed from the pyrolysis process? A Guide to Bio-char, Bio-oil, and Syngas
- What are waste to energy pyrolysis plants? Convert Non-Recyclable Waste into Valuable Energy



















